Important Rivers in India
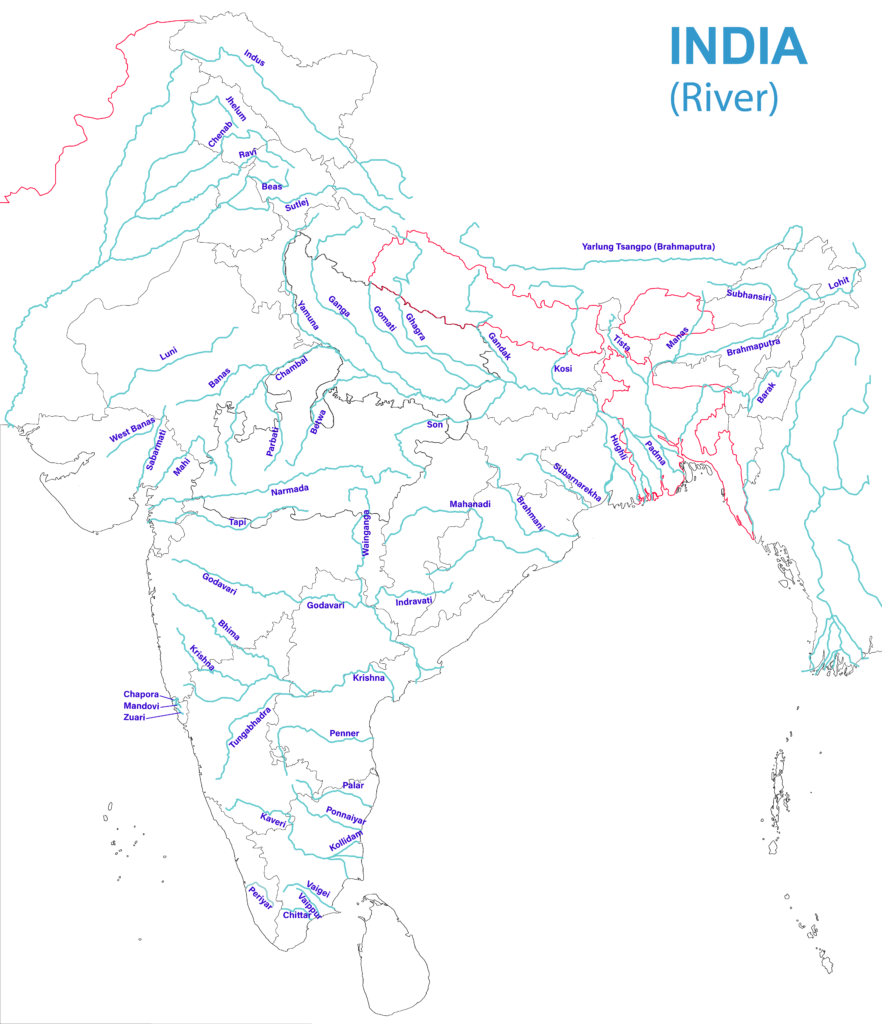
Indus :
- 2880 km long river originates in Tibet near the Mansarovar Lake and empties into the Arabian Sea
- Its five great tributaries meet it at Mithankot in Pakistan.
- Flows between Ladakh and Zaskar ranges in India, forming a gorge.
- Leh is located on its bank
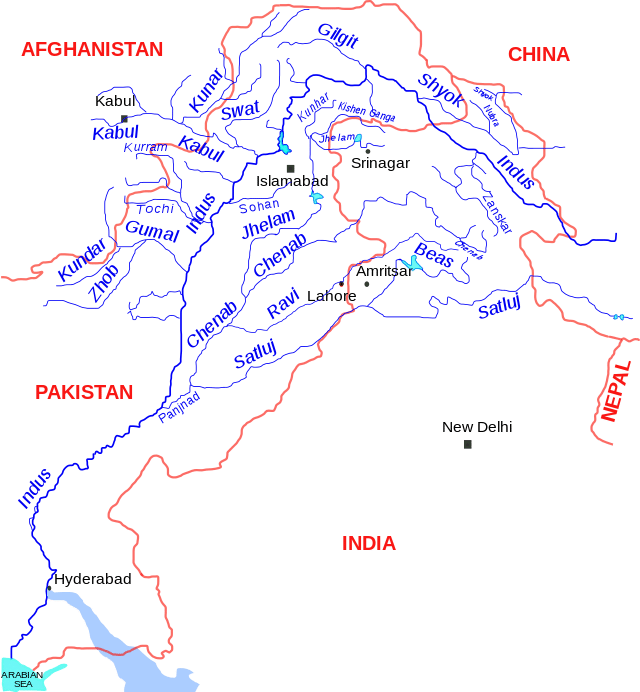
Shyok :
- Right bank tributary of the Indus, originates in Depsang Plains and flows along the Karakoram Range
- Forms the eastern limit of the Karakoram
- Fed by various glaciers like Siachen Glacier
- Found completely inside Jammu and Kashmir
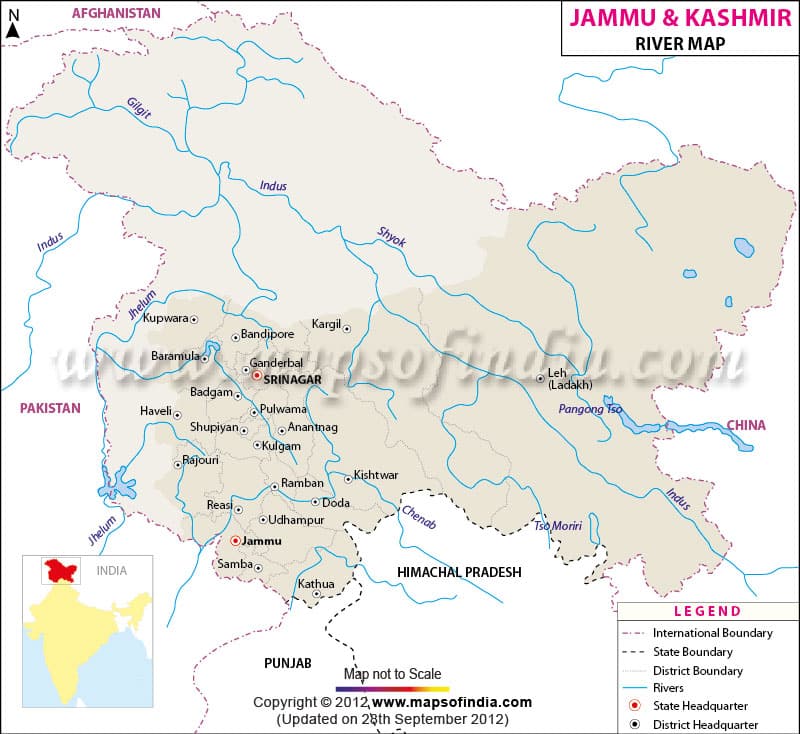
Zaskar :
- Left bank tributary of the Indus, flows between the Zaskar Range (S) and the Ladakh Range (N)
- It meets the Indus just west of Leh
- Found completely inside Jammu and Kashmir
Gilgit :
- Right bank tributary of the Indus River, at present in the PoK.
- Rises in the northwest corner of India proper and meet the Indus very near, where the latter bends towards the southwest
- Gilgit city is located on its bank
Jhelum :
- Rises from Verinag, located at the foothill of the Pir Panjal in the southeast Kashmir
- It is the main river of the Kashmir Valley flow through the Wular Lake
- Srinagar is located on its bank
- Tributaries– Kishanganga, Lidar, Sind, Pohru
- Forms 170 km.boundary between India and Pakistan
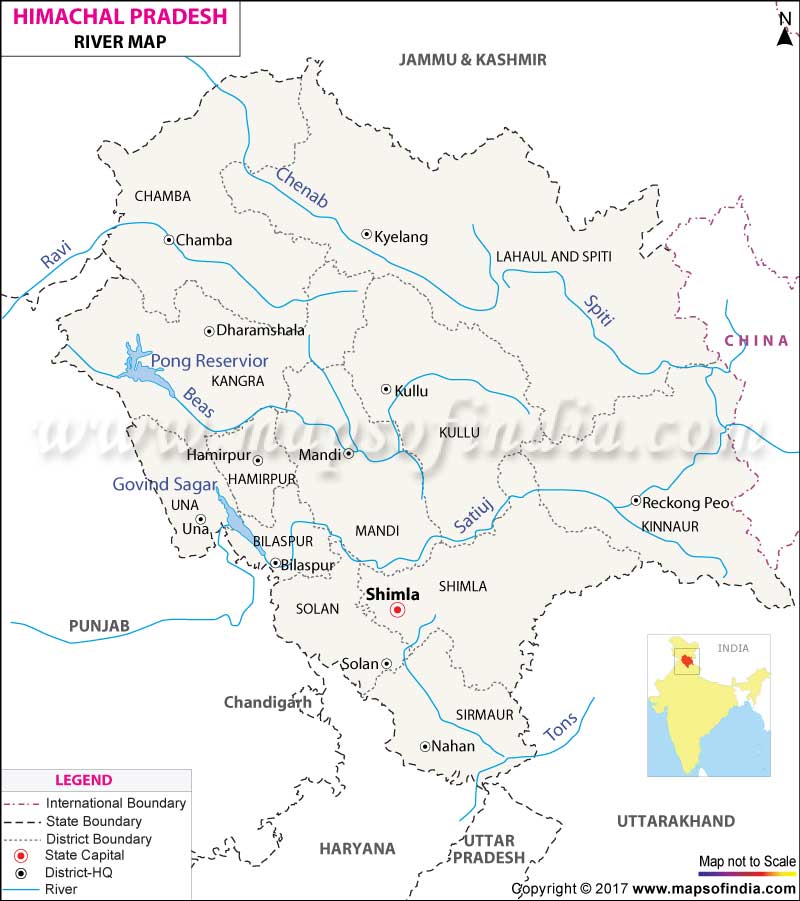
Chenab :
- It originates near the Bara Lacha Pass as two headstreams Chandra and Bhanga on the both sides of the pass.
- The united stream flows through the Pangi Valley parallel to the Pir Panjal Range.
- Meets the Indus at Panchnad in Pakistan.
- Cities – Doda, Kishtwar, Ramban.
- Projects– Salal, Baglihar, Dul Hasti.
Ravi :
- Rises in the Kullu hills near the Rohtang Pass in Himachal Pradesh.
- Flows between the Pir Panjal and the Dhauladhar
- Forms deep gorge in the Dhaula Dhar Range
- Cities-Chamba, Kathua
- Forms boundary between Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir and then between India and Pakistan.
Beas :
- Rises near the Rohtang Pass in HP and meets the Satluj at Harike near Kapurthala
- Completely in India
- Pong Reservoir (HP)
- Forms a deep gorge in the Dhaula Dhar Range
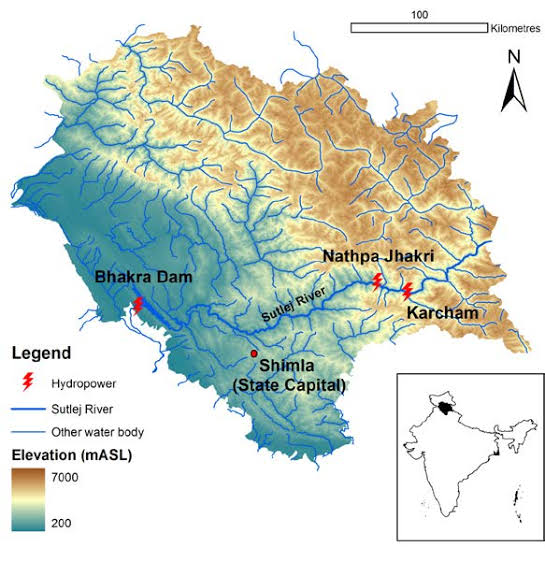
Satluj :
- Southernmost major tributary of the Indus, it originates from the Rakas Lake in Tibet and enters India through the Shipki La
- Projects : Nathpa Jhakri, Bhakra – Nangal
- Tributaries: Beas, Spiti, Parechhu.
Spiti :
- Right bank tributary of the Satluj rises near the Rohtang Pass
- Completely found inside Himachal Pradesh in its northeastern corner
- Tributaries: Parechhu, Rohtang, Surahi, Hanze etc.
- In Kinnaur it merges with the Satluj
- In the summer its flow is increased and becomes dangerous
Parechhu :
- Right bank tributary of the Satluj rises near the Tso Moriri Lake, then flows through Tibet and meets the Satluj after the Shipki La
- Its flow is increased in the summer and becomes dangerous, while in the winter it is somewhat frozen.
Tons :
- The tributary of the Yamuna, rises in the Yamunotri Glacier and flows through the western part of Uttrakhand
- The NH-94 runs along it.
Bhagirathi :
- The headstream of the Ganga, rises from the Gangotri Glacier and meets the Alaknanda River at Devprayag
- Cities – Uttarkashi, Tehri
- Projects: Tehri, Koteshwar.
Alaknanda :
- First major tributary of the Ganga found completely inside Uttarakhand
- Rises near the Niti Pass , at the border with Tibet
- Meets Bhagirathi River at Devprayag
- Tributaries: Pindar, Mandakini
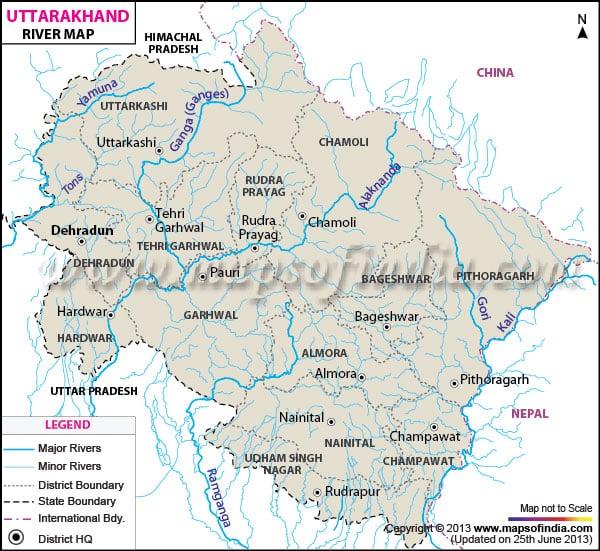
Pindar :
- Most important tributary of the Alaknanda River, found completely inside Uttarakhand
- Rises from the Pindar Glacier near the Nanda Devi Peak
- Joins the Alaknanda at Karan Prayag
Kali-sarda :
- Important tributary of the Ghaghra, that rises in Tibet near the Rakas Lake
- Flow between India and Nepal forming a natural boundary and known as Kali in the Nepal section and Sarda in the Indian part
- Passes through the Doodhwa National Park
Karnali/ghaghra :
- Originates near Gurla Mandhata peak, south of Mansarovar in Tibet
- Known as Karnali in western Nepal
- Tributaries: Sarda, Sarju, Rapti.
- Meets Ganga a few kilometers downstream of Chapra in Bihar.
- Forms boundary between UP and Bihar.
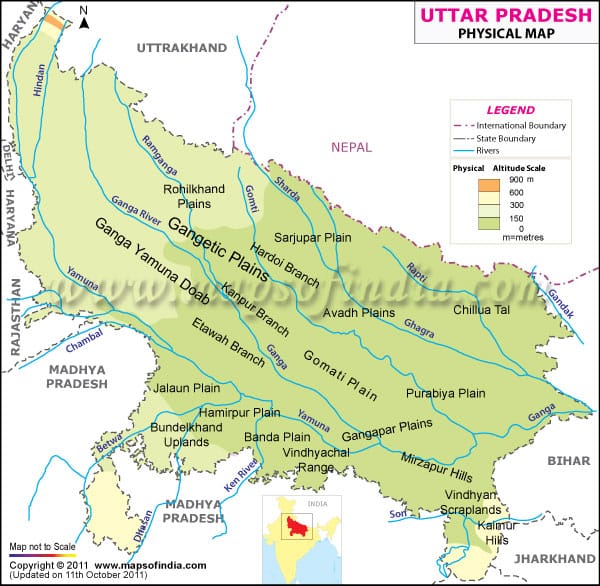
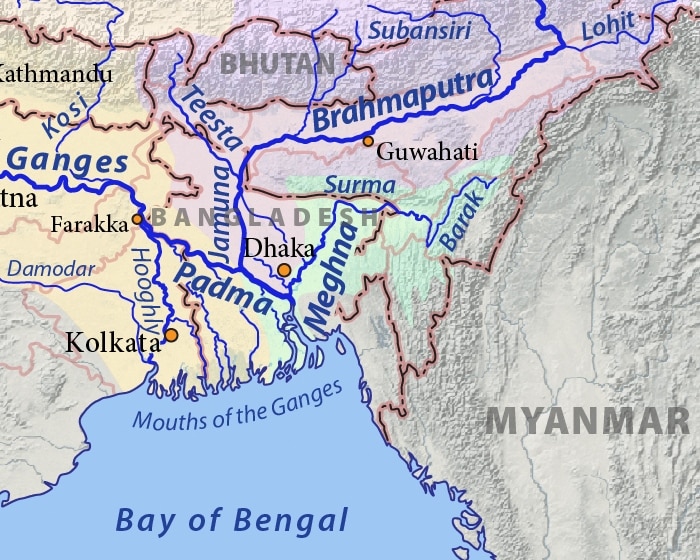
Ganga :
- Largest and longest river inside India.
- Originates from the Gangotri Glacier as the Bhagirathi and drains into the Bay of Bengal.
- Named Ganga after Devprayag and enters the plain after Haridwar.
- Known as Padma in Bangladesh.
- Holiest river of India.
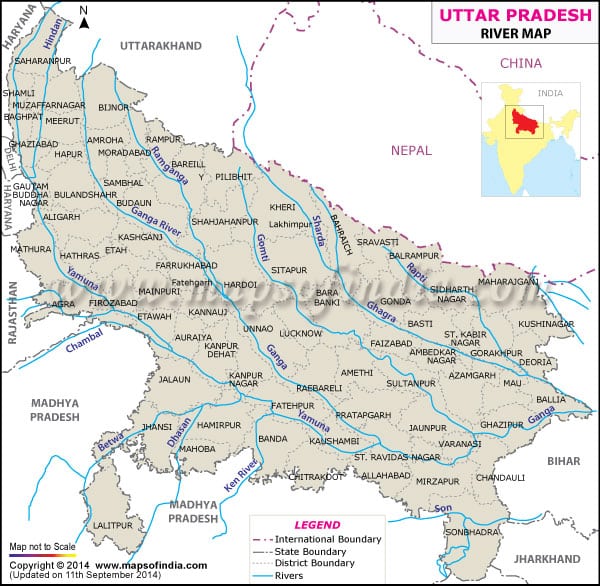
Ramganga :
- Important tributary of the Ganga between the Gomati (E) and the Ganga (W)
- Rises in Garhwal district of Uttarakhand and joins the Ganga near Kannauj
- City: Moradabad
Gomati :
- Important tributary of the Ganga, rises from the Pilibhit district of UP and joins the Ganga downstream of Sarnath.
- Irrigates the Avadh Plain
- Cities: Lucknow
Sarju :
- A small river in UP on the bank of which Ayodhya is located
- Some times synonymous with the river Ghaghra or some time as its tributary
Rapti :
- Important tributary of the Ghaghra
- Rises in Nepal and joins the Ghaghra downstream Gorakhpur
- Tributary : Burhi –Rapti
- Cities : Shrasvati , Gorakhpur
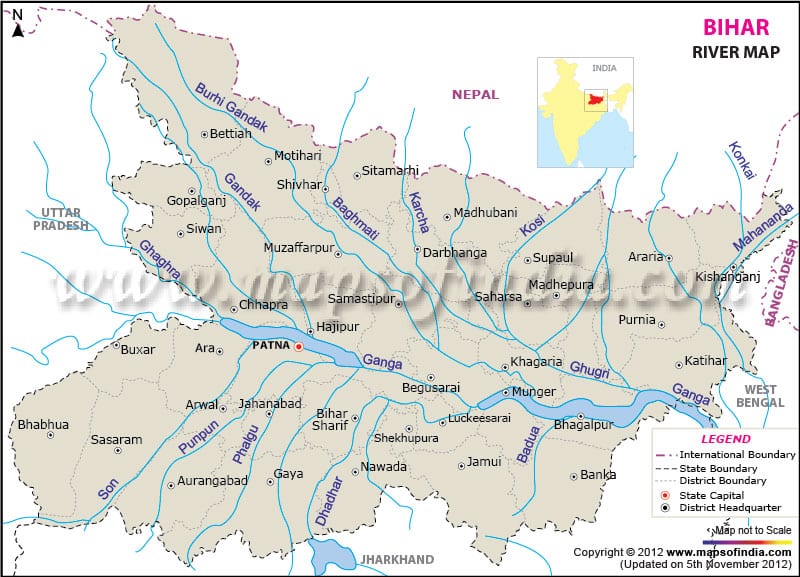
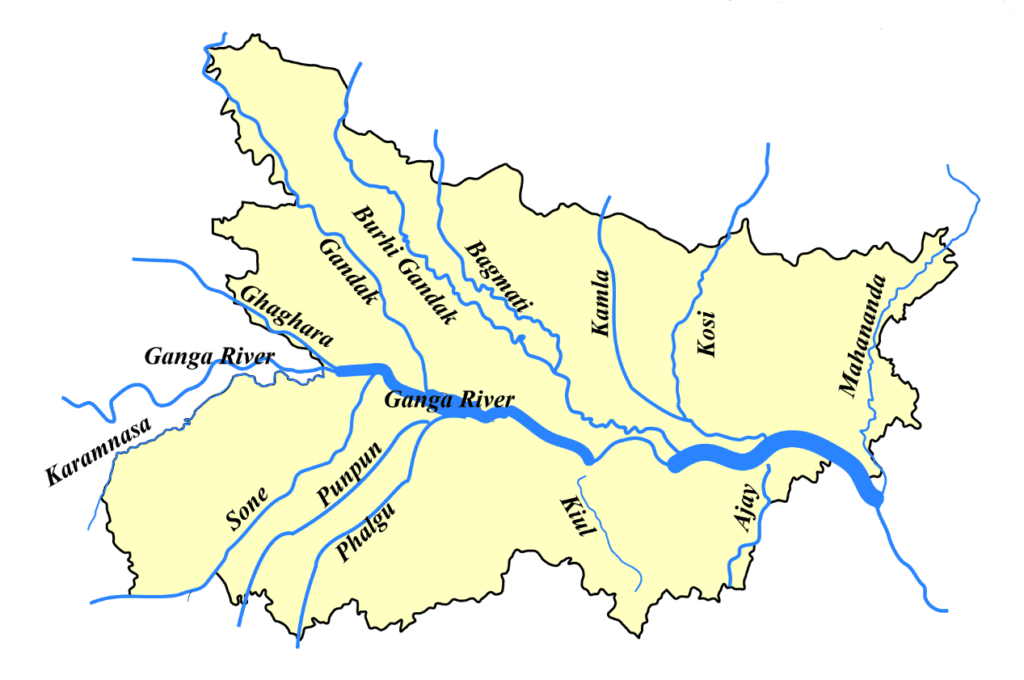
Gandak :
- Important tributary of Ganga, originates near the Tibet-Nepal border
- Tributaries: Kali-Gandak, Mayagadi, Bari, Trishula
- Join the Ganga at Hajipur, just east of Patna.
- Flows between UP and Bihar
Burhi gandak :
- Originates from the western slopes of Sumesar Hills near the India- Nepal border, joins the Ganga opposite Monghyr town.
- Cities : Motihari, Muzaffarpur, Samastipur
- Flows through the Valmiki National Park
Bagmati :
- River of Nepal and India which flows through the Kathmandu Valley and joins Kosi in India
- Forms Chokar Gorge in the Mahabharat Range
- Kathmandu is located on its bank
- Considered holy by both Budhists and Hindus
Kosi :
- Consists of seven streams namely Sut Kosi, Tamba Kosi, Talkha, Doodh Kosi, Botia Kosi, Arun and Tamber
- Arun is the main stream which rises to the north of Gosainthan
- The three important streams (Tumar, Arun and Sun Kosi ) unite at Triveni
- North of the Mahabharat Range to form Kosi
- It is ill-famous for floods and changing its directions as it enters India and known as the ‘Sorrow of Bihar’
- A barrage has been built at Hanuman Nagar in Nepal
Rangit :
- The largest river of Sikkim
- A tributary of Teesta
- Famous among the rafters owing to its turbulent waters
- Forms boundary between Sikkim and West Bengal
- Has 60 MW electricity plant
Mahananda :
- Trans-boundary river that flows through West Bengal, Bihar and Bangladesh.
- Last important left bank tributary of the Ganga before the Brahmaputra.
- Rises in the Darjeeling district and flows through the Mahananda Wildlife Sanctuary.
- 360 km long (324 km in India ).
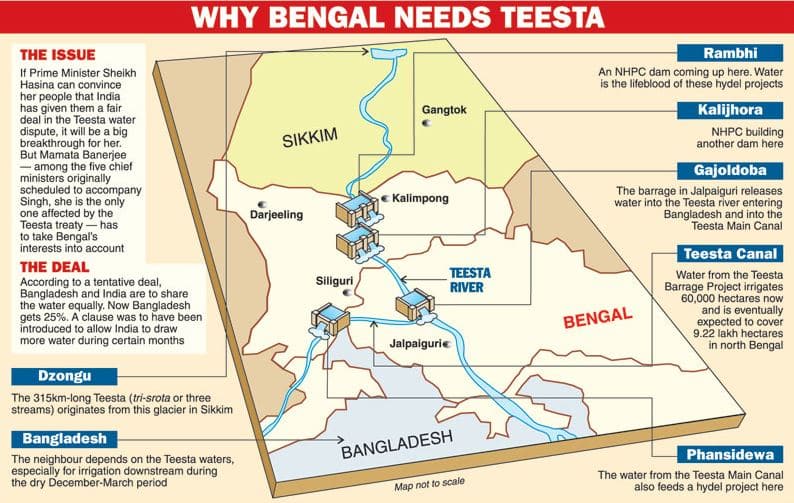
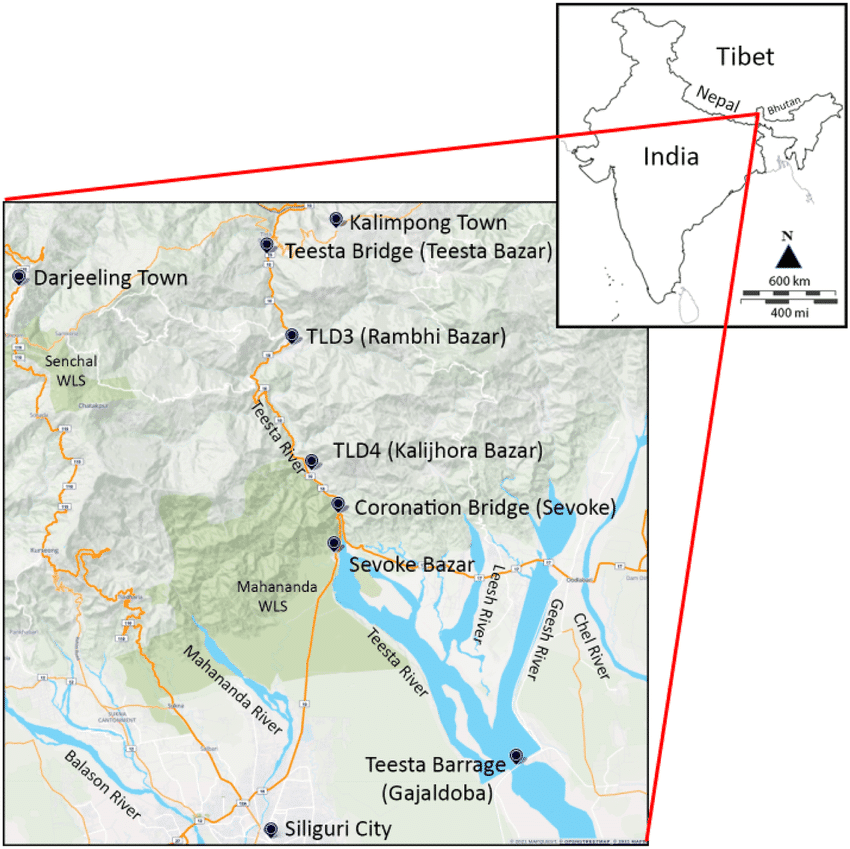
Tista :
- A major tributary of the Brahmaputra
- Rises in Tibet and flows through Sikkim and West Bengal and joins the Brahmaputra in Bangladesh
- Upto 1787 it was a tributary of the Ganga, when a devastating flood diverted it eastward
- An antecedent river, does large scale cutting during the rainy season
Sankosh :
- An important tributary of the Brahmaputra, rises in Bhutan and joins the Brahmaputra near the Indo-Bangladesh border
- Forms boundary between West Bengal and Assam
Manas :
- Important right bank tributary of the Brahmaputra , rises in Bhutan and joins the Brahmaputra opposite to Goalpara
- Flows through the Manas Biosphere Reserve
- NH-31 passes over it, linking Bongaigaon with Nalbari.
Kameng :
- Important right bank tributary of the Brahmaputra, rises near the Indo- Tibet border in Arunachal Pradesh and joins the Brahmaputra, a few kilometres downstream of Tezpur
Subansiri :
- Important right bank tributary of the Brahmaputra, rises near the Indo – Tibet border, and joins the Brahmaputra near the Majuli Island
- Separates the Abor Hills (East) from the Miri and Dafla Hills
- Tributary – Kamla
- Rises in the Chemayungdung Glacier in the Kailas Range and joins the Padma in Bangladesh.
- Known as Tsangpo in Tibet.
- Forms the largest riverine island Majuli.
- Largest volume of water of any river in India.
- Famous for floods.
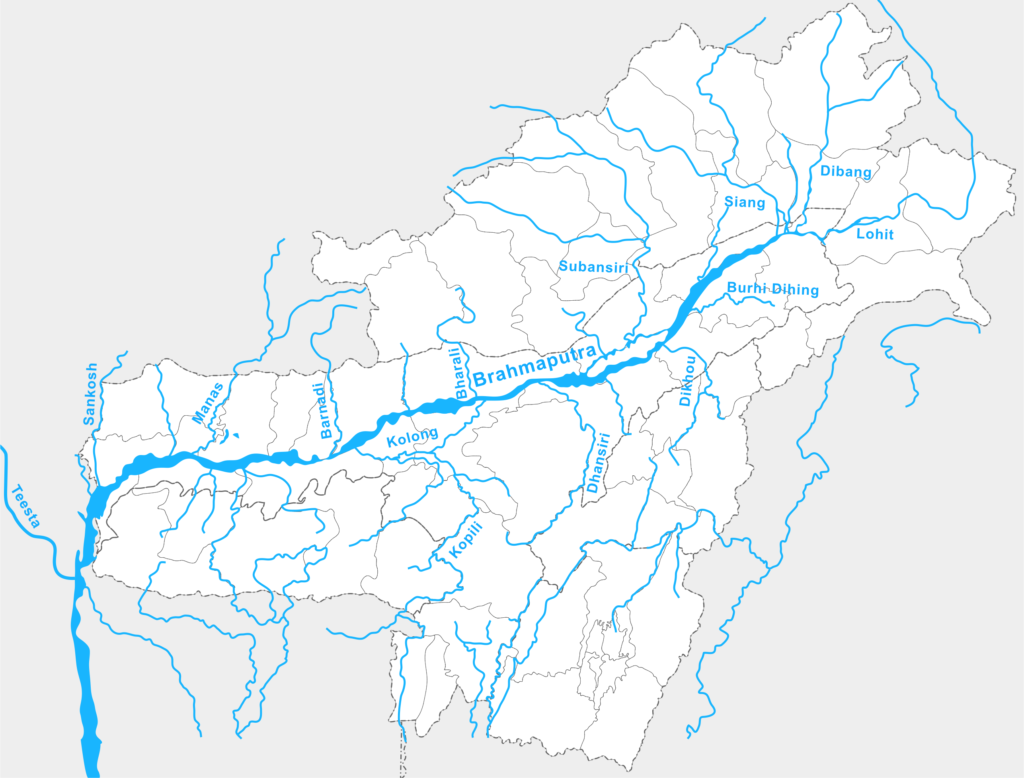
Dibang :
- Important left bank tributary of the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam
- Flows through the Mishmi Hills
- Forms a Trijunction in the northeast Assam along with the Dihang and the Lohit
- Cities – Tezu, Parasuram Kund
Lohit :
- Important left bank tributary of the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam
- Forms a Trijunction in the northeast corner of Assam along with the Dihang and the Dibang
Burhi Dibang :
- Left bank tributary of the Brahmaputra, rises from the Patkai Bum in Arunachal Pradesh and joins the Brahmaputra downdream of Dibrugarh before the Majuli Island
- Cities: Naharkatia , Digboi
Dikhu :
- Left bank tributary of the Brahmaputra, rises from the Naga Hills and joins the Brahmaputra at the south of the Majuli Island
- City: Sibsagar
Dhansiri :
- Left bank tributary of the Brahmaputra rises from the Barail Range and joins the Brahmaputra just downstream of the Majuli Island
- Flows east of the Rengma Hills and the Mikir Hills where the Kaziranga National Park is situated
- Boundary between Assam and Nagaland
- Cities – Dimapur, Golaghat
Barak :
- Important river of the northeast India rises from the Barail Range , near the trijunction of Assam, Manipur and Nagaland
- Forms boundary between Assam and Manipur
- Tipaimukh Dam in Manipur
- It becomes Surma and then Meghna
- City – Silchar.
- NH-53 crosses it.
Manipur :
- It originates in the Manipur Hills and flows southward, just east of the Loktak Lake and enters Myanmar to join the Myitha River, a tributary of the Chindwin.
- Flows between the Laimatol Range and the east Manipur Hills.
Dhaleshwari :
- Originates in the Mizo Hills and flows northward to join the Barak River
- Passes through the Tropic of Cancer
Ajay :
- Important northernmost tributary of the Hoogly
- Flows through Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal
- Shantiniketan is situated north of it
Damodar :
- Most important tributary of the Hoogly originates from the Palamau district of Jharkhand.
- Known as ‘Sorrow of Bengal’.
- DVC-First multipurpose project of India.
- Tributaries: Barakar, Konar, Jamunia, Ghari etc.
Rupnarayan :
- Tributary of Hoogly south of the Damodar
- Rises in the western part of West Bengal and meets Silai River before joining the Hoogly
- City – Bankura
- NH-6 passes over it.
Haldi :
- Important southernmost tributary of the Hoogly River, rises from the Purulia district of West Bengal and joins the Hoogly at Haldia
- Cities –Medinipur , Haldia
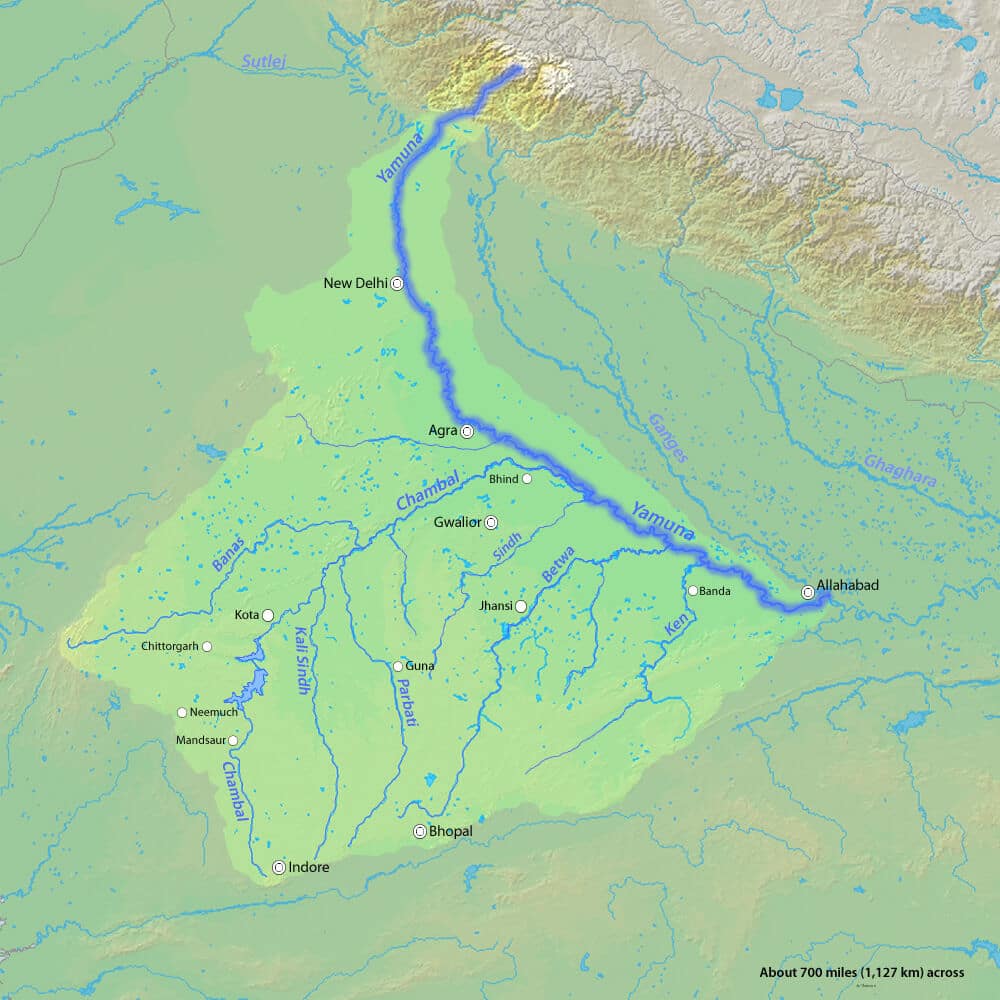
Yamuna :
- Most important tributary of the Ganga, rises from the Yamunotri Glacier and joins the Ganga at Allahabad
- Tributaries : Chambal, Sind, Betwa , Ken
- Cities – Delhi, Mathura, Agra, Allahabad
- Excessively used and highly polluted
Barakar :
- Main tributary of the Damodar River
- 225 km long, originates in the Hazaribagh district and joins the Damodar in the Bardhman district of West Bengal
- Tributaries – Barsoti, Usri.
- Dams and HEPs – Tilaiya , Maithon
Gambhir :
- Important tributary of the Yamuna, between the Yamuna and the Chambal.
- Rises from the northeastern part of the Aravallis, north of Jaipur.
- Before meeting the Yamuna , it forms boundary between Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh
- Keoladeo Ghana Bird Sanctuary is located just north of it
Chambal :
- Most important tributary of the Yamuna
- Rises from the Janapao Hills of the Vindhyas and meets the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh near Etawah
- Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Parbati
- Reservoirs: Gandhi Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Jawahar Sagar.
- Famous for ‘ravines’ (bandland topography )
- Forms border between Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh
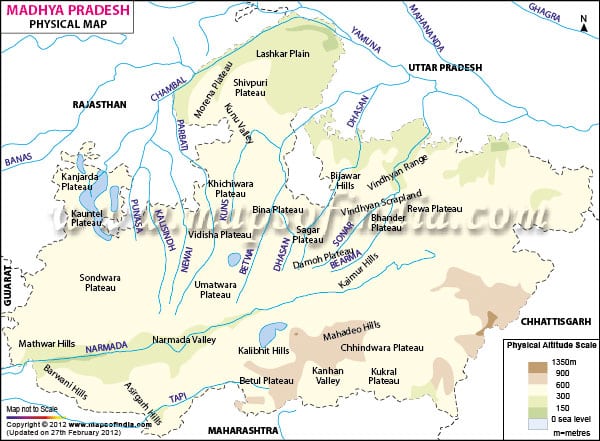
Sind :
- A right bank tributary of the Yamuna, flows between Chambal and Betwa rivers through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh
- Originates in the Vidisha district of Madhya Pradesh and joins the Yamuna in the Etawah district of Uttar Padesh
- Manikheda Dam in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh
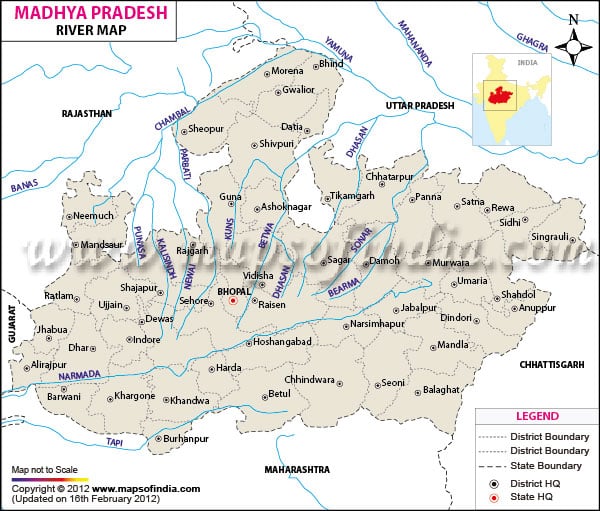
Banas :
- Most important left bank tributary of the Chambal
- ∙Rises from the southeastern part of the Aravallis and meets the Chambal at the Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh border
- Ranthambore National Park is situated at the confluence of the Banas and the Chambal
- Tributaries: Berach, Khairi, Bandi, Dhand
Kali sindh :
- First important right bank tributary of the Chambal flows through the Malwa Plateau in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
- Crosses the Tropic of Cancer from the south to north
- Tributaries: Parwan, Ahu
- Forms ravines in its lower course
Parbati :
- Important right bank tributary of the Chambal
- Flows through the Malwa Plateau in Madhya Padesh and Rajasthan
- Crosses the Tropic of Cancer from the south to north
- Forms the boundary between Madhya Padesh and Rajasthan for a short length twice
Betwa :
- Tributary of the Yamuna rises from the Vindhyan Range near Kumara Village of the Raisen district of Madhya Padesh
- Flows through the Bundelkhand Plateau
- Dams: Matatila, Rajghat
- Cities – Sanchi , Orchha
Ken :
- Rises from the Kaimur Hills in the Satna district of MP and joins the Yamuna in the Banda district of Uttar Padesh
- Flows through the Bundelkhand Plateau
- Almost dried up during the summer
- There is a plan to link it with the Betwa
Tons :
- Tributary of the Ganga between the Yamuna and the Son
- Rises from the Vindhyan Range and joins the Ganga few kilometers downstream of Allahabad
Son :
- Important right bank tributary of the Ganga, rises near Amarkantak and joins the Ganga near Ramnagar in Bihar
- Flows between the Kaimur Hills and the Sonpar Hills
- Forms various waterfalls
- Forms short border between Jharkhand and Bihar
- Tributaries: Johilla, Gopad, Rihand , Kanhar, North Koel.
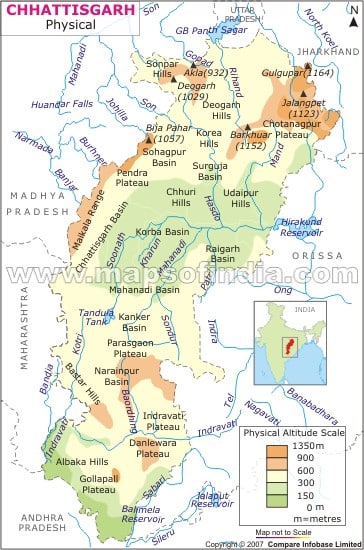
Rihand :
- Most important tributary of the Son
- Rises from the Ramgarh Hills of Chhattisgarh and joins the Son in the Mirzapur district of Uttar Pradesh
- Gobind Ballabh Pant Sagar is formed behind the Rihand Dam
- Passes through the Tropic of Cancer
North koel :
- Last important tributary of the Son, rises from the Chotanagpur Plateau and joins the Son at the Jharkhand-Bihar border.
- Passes through the Tropic of Cancer as well as the Palamau Tiger Reserve.
- City: Daltenganj
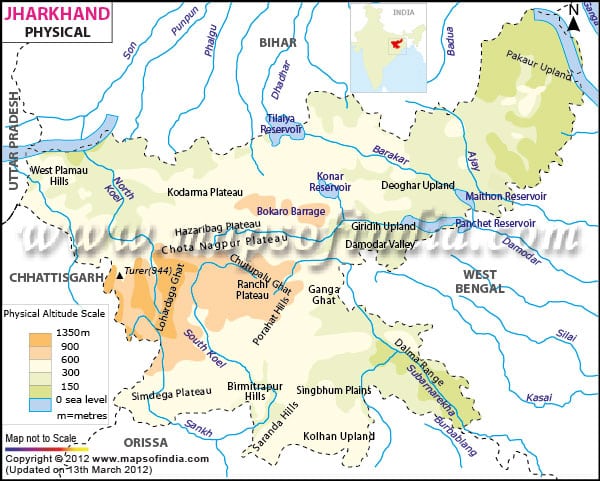
Subarnarekha :
- Rises from the Ranchi Plateau and flows through Jharkhand , West Bengal and Orissa before emptying into the Bay of Bengal
- Cities – Ranchi, Jamshedpur
- Its valley is famous for the alluvial g
Baitarni :
- Important river of Orissa rises from the Garhjat Hills and before emptying into the Bay of Bengal joins the Mahanadi delta along with the Brahmani River
- Dhamra Port is located at its mouth
Brahmani :
- Important river of the northern Orissa, forms when the Sankh and the South Koel join together.
- It joins the Mahanadi Delta before emptying into the Bay of Bengal
- Flows through the Garhjat Hills.
- Cities: Rourkela, Talcher.
- Its valley has rich coal deposits.
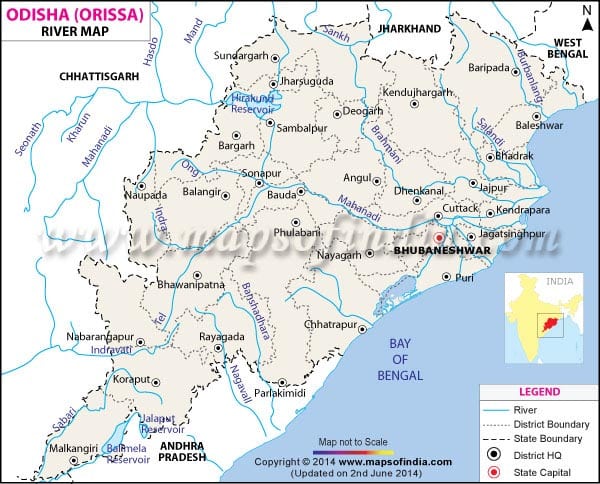
Mahanadi :
- Rises from the Sihava Parbat of the Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and forms large delta in the Bay of Bengal
- Hirakud Dam near Sambalpur in Orissa.
- Tributaries: Sheonath, Hasdo, Ib, Mand, Jonk, Tel etc.
- Cities – Sambalpur, Cuttack
- Forms the Chhattisgarh Plain, ‘Rice Bowl of India’.
Banshadhara :
- Important river of the southwest Orissa and the northeast Andhra Padesh.
- Rises from the Eastern Ghats and empties into the Bay of Bengal
Sileru :
- Last important left bank tributary of the Godavari rises from the Eastern Ghats and joins the Godavari in Andhra Padesh after forming boundary between Orissa and Andhra Padesh
- Tributary – Sabari
- Reservoirs – Jalaput, Machhkund, Balimela
- Dudma Falls after the Machhkund Reservoir
Indravati :
- Important left bank tributary of the Godavari rises from the Eastern Ghats near the Nimgiri (1515m.)in Orissa.
- Flows through the centre of the Bastar Plateau and forms boundary between Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh before joining the Godavari at the trijunction of Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh and Andhra Padesh
- City – Jagdalpur–main city of Bastar region
Wainganga :
- Important left bank tributary of the Godavari rises from the eastern part of the Mahadeo Hills in Madhya Padesh and after joining the Penganga it becomes Pranhita which forms boundary between Maharashtra and Andhra Padesh
- Short boundary between MP and Maharashtra
- Tribturies: Pench , Kanhan , Mul
- Cities: Balaghat , Bhandara , Garchiroli
Wardha :
- Important tributary of Penganga , rises from the southern Mahadeo Hills and meets the Penganga near Chandrapur
- Tributaries : Bemla , Wunna
Penganga :
- Important left bank tributary of the Godavari , rises from the Ajanta Range and joins Wainganga near the Andhra Padesh – Maharashtra border to form Pranhita which forms boundary between the above two states
- Upstream it forms the boundary between the two states.
- Tributaries: Wardha , Aran , Pus
Purna :
- Small left bank tributary of the Godavari, rises from the southern part of the Ajanta Range
Godavari :
- Second largest river inside India and the longest river of southern India
- Rises from the Trimbak Plateau in the Nasik district and forms a large delta along with Krishna in the Bay of Bengal
- Known as the ‘Vriddha Ganga’
- Projects – Jayakwadi
- Tributaries : Pranhita, Indravati, Sileru, Manjra
Manjra :
- Most important right bank tributary of the Godavari, rises from the Balaghat Range in Maharashtra and flows through Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh
- Nizam Sagar is built on it in Andhra Pradesh near Nizamabad.
- Tributaries – Tirna ,Manar
Muneru :
- Last important left bank tributary of the Krishna
- Found completely inside Andhra Pradesh
- City: Khammam
Musi :
- Important left bank tributary of the Krishna , rises in the Balaghat Range in the Telangana Plateau (Andhra Pradesh)
- Hyderabad is located on its bank
- Hussain Sagar Reservoir is built on it
Bhima :
- Most important left bank tributary of the Krishna rises near Pune in the Matheron Hills of the Western Ghats , and flows through Maharashtra and Karnataka
- Joins the Krishna 26 km away from Raichur
- Tributaries –Mula , Mutha God, Nira , Sina , Bari , Kagna
Krishna :
- Second longest river of the Indian Peninsula rises from the Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar and empties into the Bay of Bengal , forming joint delta with the Godavari
- Tributaries – Koyna, Tungabhadra, Bhima, Musi etc.
- Dams – Srisailam , Nagarjunasagar
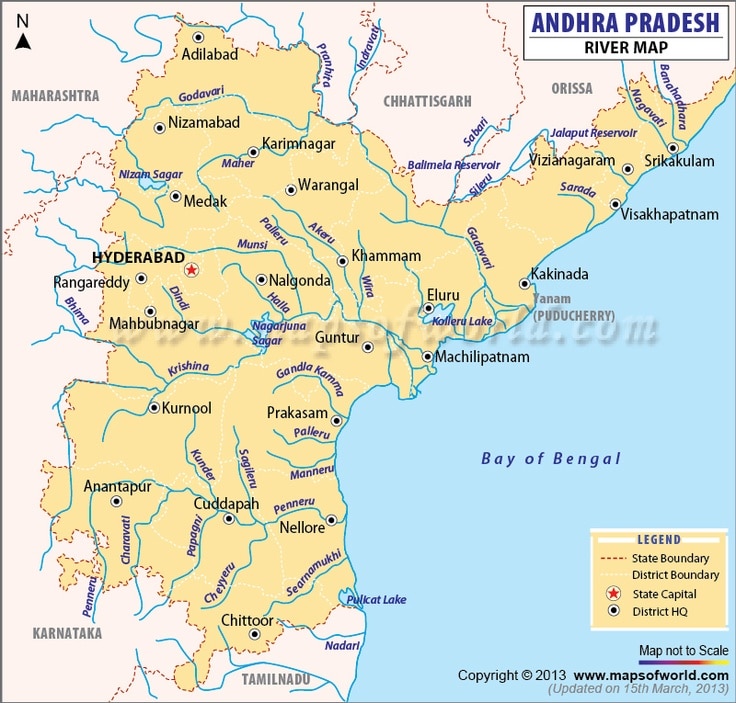
Ghatprabha :
- A right bank tributary of the Krishna flows in Karnataka
- 283- km long river that originates in the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats and joins the Krishna at Almatti
- Tributaries – Hiranyakeshi , Markandeya
- Ghatprabha Project (at Hidkal ) – A dam and HEP
- Gokak Falls is located in the Belgaum district of Karnataka
Malprabha :
- A right bank tributary of the Krishna in Karnataka rises from the Western Ghats in Belgaum district and joins the Krishna at Kudalasangam in the Balaghat district
- 304 km long
- Tributaries – Bennihalla , Hirehalla , Tuparihalla
- Reservoirs- Navilatirtha Dam
- Aihole, Pattadakal and Badami are located on its bank
Tungadhadra :
- A major right bank tributary of the Krishna, rises from the Western Ghats near the Baba Budan Hills, joins the Krishna in Andhra Pradesh, few kms downstream of Kurnool
- Formed after the confluence of the Tunga and Bhadra.
- Tungabhadra Reservoir near Hospet
- Tributaries: Varada , Hagari , Chikka Hagari
- Forms a short boundary between Karnataka and Andhra Padesh
- Cities: Hospet , Hampi , Kurnool
Penneru :
- Important river of southern AP, rises near Tumkur in Karnataka and empties into the Bay of Bengal near Nellore
- Bifurcates the Rayalseema into two almost equal parts.
- Separates Palkonda from the Nallamalla and passes through the Velikonda Range
- Cities – Cuddapah , Nellore
- Tributaries – Charavati , Papagni , Cheyyaru
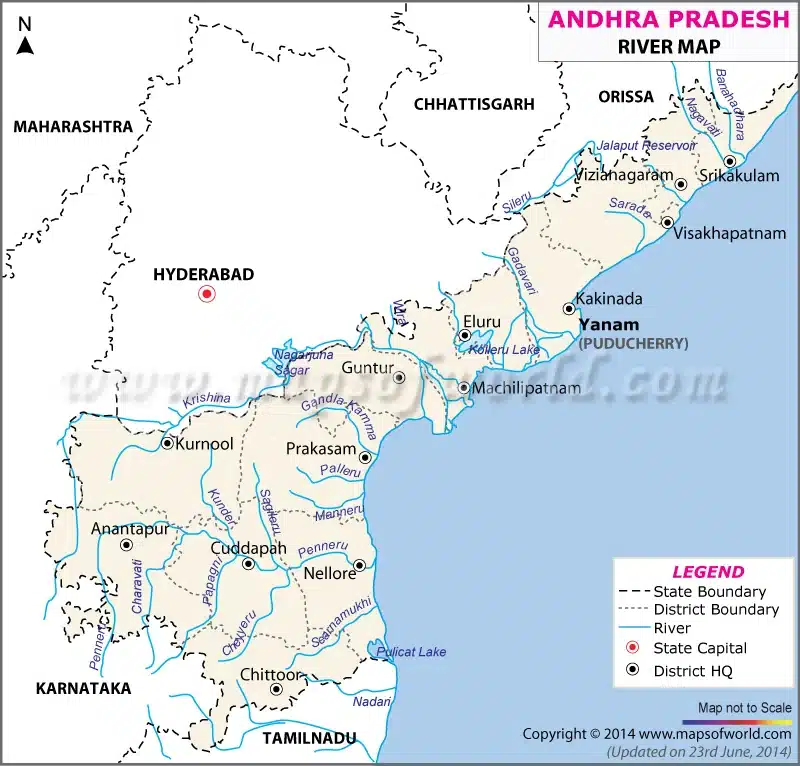
Palar :
- Important river of the northern Tamil Nadu
- Rises from Karnataka near the Kolar gold field region and empties into the Bay of Bengal midway between Chennai and Puducherry
- Tributaries – Ponri , Cheyyar
- Cities – Vellore , Kancheepuram
Ponnaiyar :
- Important river of northern Tamil Nadu.
- Rises from the Melagiri Range region and flows between the Javadi Hills and the Shevroy Hills.
- Krishnagiri Reservoir in Tamil Nadu.
- Tributaries – Chovrai.
- Cities:– Krishnagiri , Cuddalore (at the mouth )
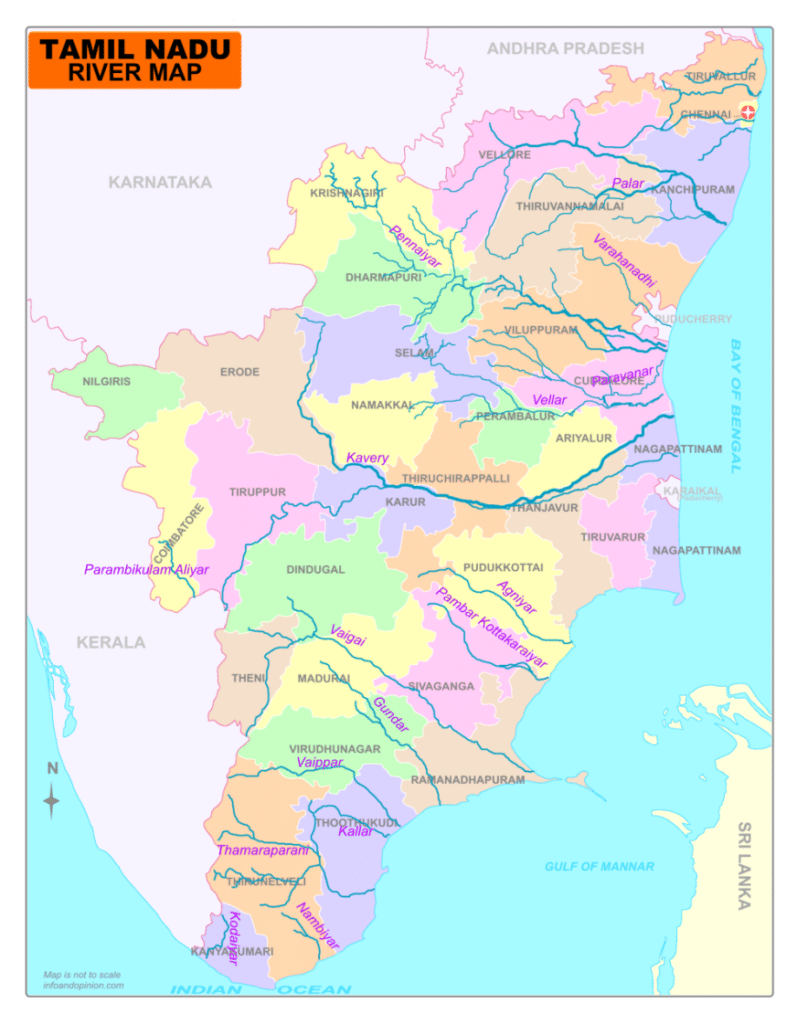
Cauvery :
- Rises from Taal Cauvery in the Brahmagiri Range of the Western Ghats in Karnataka
- Forms quadrilateral delta
- Falls–Sivasamudram and Hogenekkal
- Reservoirs – Krishnaraj Sagar , Stanley Reservoir
- Tributaries- Hemavati, Shimsa, Arkaveti, Lakshmantirtha, Kabani, Suvarnavati, Noyil and Amaravati
- Disputed among the riperian states.
Hemavati :
- Left bank tributary of the Cauvery rises near the Baba Budan Hills and meets the Cauvery at Krishnarajsagar Reservoir
- Completely found in Karnataka
- Tributary – Yagachi
Shimsa :
- Left bank tributary of the Cauvery, completely lies in Karnataka
- Originates in Tumkur district
- Has Shimsha Reservoir
- Meets the Cauvery near the Sivanasamudram Falls
Arkaveti :
- Left bank tributary of the Cauvary, lies completely inside Karnataka
- Flows west of Bengaluru
- Chamraja Sagar has been built on it
Noyil :
- Right bank tributary of the Cauvery rises from the southern part of the Nilgiri Hills, near the Pal Ghat
- Coimbatore is located on its bank
Lakshmantirtha :
- Right bank tributary of the Cauvery, rises in the Western Ghats and joins the Cauvery at the Krishnaraja Sagar.
- Passes through Nagarhole national park
Kabani :
- Right bank tributary of the Cauvery rises from the Western Ghats near the Wayanad Sanctuary in Kerala, joins the Cauvery near Mysore
- Huge Kabani Dam (696m) near Mysore
- One of the most popular wild-life destinations of Karnataka.
Moyar :
- Right bank tributary of the Cauvery
- Rises from the Nilgiri Hills near Ooty and joins the Cauvery near Erode
- Bhavani Sagar Reservoir is located on it
- Forms a short boundary between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Amaravati :
- Right bank tributary of the Cauvery
- Rises near Anaimudi and meets the Cauvery a few kms downstream of Karur
- Tributaries – Sanmukta , Nanganji
- City –Karur
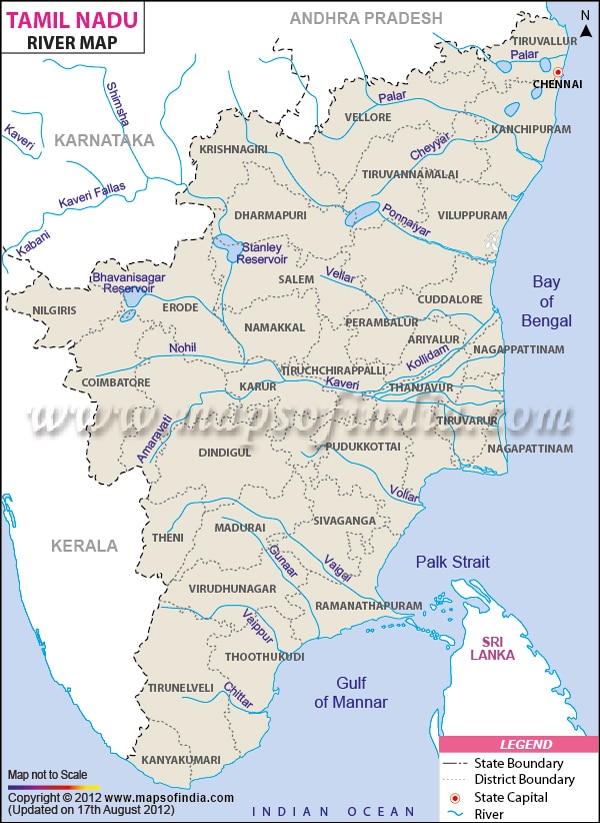
Vaigai :
- Most important river of southern Tamil Nadu , rises from the Cardamom Hills and flows between the Varushnad Hills and the Sirumalai Hills.
- Drains near the Pamban Channel.
- Cities: Madurai, Ramnathpuram, Theni.
Pambiyar :
- Third longest river of Kerala.
- Sabarimala Temple is located on its bank. Originates in Pulachimalai Hills of the Western Ghats and empties into the Vembanand Lake.
- It irrigates the rice cultivating region of Kuttanad.
- It is venerated as Dakshin Ganga.
Periyar :
- Longest river of Kerala (244 Km), known as ‘the life line of Kerala’
- Perennial river, source of drinking water
- Idukki Dam – HEP in large quantity.
- Source – Shivagiri Hills , flows through the Periyar National Park into Periyar Reservoir.
- Its water is diverted from the reservoir into the Vaigai River.
Kumardhar :
- Small river of S-W Karnataka , rises east of the Kudremukh and empties into the Arabian Sea
- Mangalore is located at its mouth
- Southernmost river of the western coast of Karnataka
Sharavati :
- West flowing river of Karnataka , rises in the Shimoga district and forms the Jog Falls
- Has Linganamakki Reservoir
- HEPs – Sharavati , Mahatma Gandhi
Kalinadi :
- Northernmost river of the western coast of Karnataka.
- Rises in the Western Ghats near Dharwad.
- Has an HEP Project.
- Karwar is located just south of its mouth.
- Konkan Railway and NH- 17 pass through it.
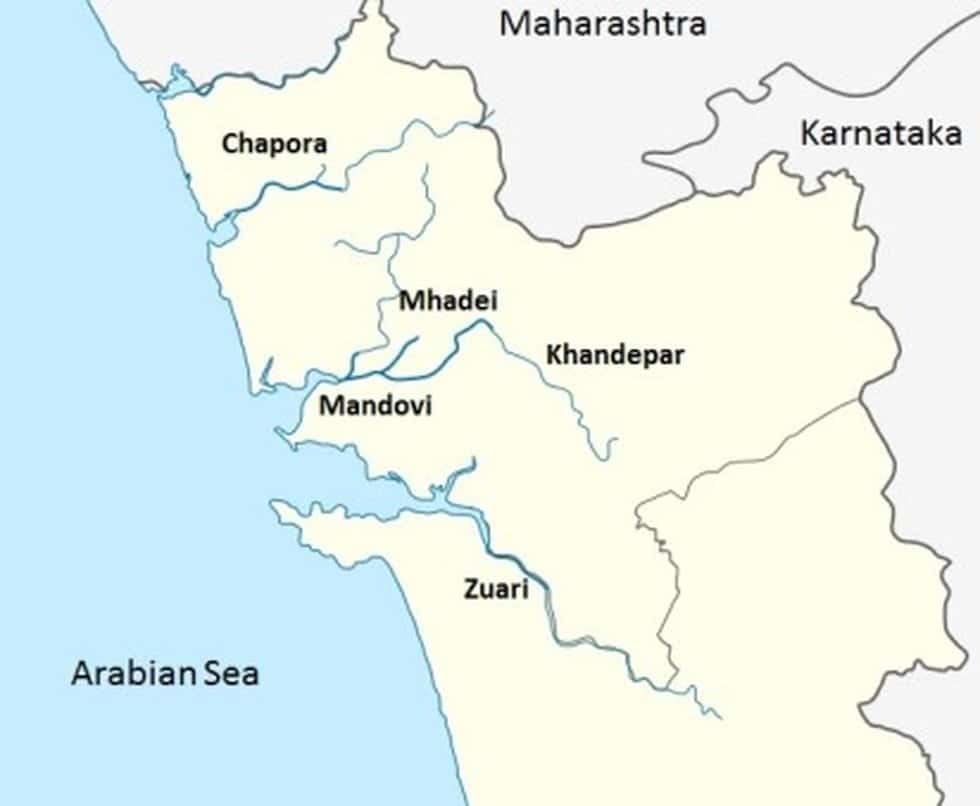
Zuari :
- Largest river of Goa (34 km long )
- Originates at Hemad – Barshem in the Western Ghats
- Zuari and Mandovi rivers form the backbone of Goa’s agriculture
- Cumbahuem Canal links the two rivers
- Vasco da Gama city is located at its mouth
Mandovi :
- Also known as Mahadeyi or Mahadei
- Lifeline of Goa
- 77 km. long (29 km.in Karnataka and 52km. in Goa )
- It originates at Bhimgad in the Belgaum district of Karnataka
- Falls – Dudhasagar Falls , Varapoha Falls
- Cumbahuem Canal links it with the Zuari River
- Cities: Panaji, Old Goa
Ulhas :
- West flowing river near Mumbai.
- Rises from the Western Ghats and empties into the Thane Creek.
- At Thane it branches off into two streams and the main branch empties into the Vasai Creek.
Tapi :
- Second longest west flowing river of the Indian Peninsula , rises in the Betul district of Madhya Pradesh in the Mahadeo Hills and empties into the Gulf of Khambhat near Surat.
- Flows parallel to the Satpura Range
- Tributaries – Purna, Girna, Bori, Panjhra
- Ukai Dam is located on it.
- Cities –Kakrapara, Surat, Jalgaon, Bhusaval, Burhanpur.
Purna :
- Most important tributary of the Tapi , rises from the Gawilgarh Hills and joins the Tapi near Bhusaval
- Completely inside Maharashtra
- Tributary : Mun
Narmada :
- Longest west flowing river of the Indian Peninsula, rises from the Amarkantak Plateau and empties into the Gulf of Khambhat
- Flow between the Vindhyas and Satpura, through a rift valley.
- Falls – Dhuandhar, Kapildhara
- Dams – Sardar Sarovar, Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, Indira Sagar
- Tributaries – Chota Tawa, Hiran, Shakkar, Burhner.
Chota Tawa :
- Important left bank tributary of the Narmada , rises from the Satpura Range near the Madhya Pradesh – Maharashtra border
- Khandwa and Nepanagar are located near to it
- Chota Tawa Project has been built on it
Mahi :
- It rises from the northwestern part of the Vindhyan Range in Madhya Pradesh
- Flows through Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Gujarat before emptying in the Gulf of Khambhat
- Tributary – Son , Anas, Panam
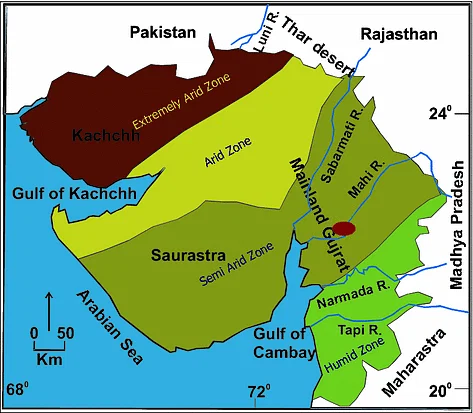
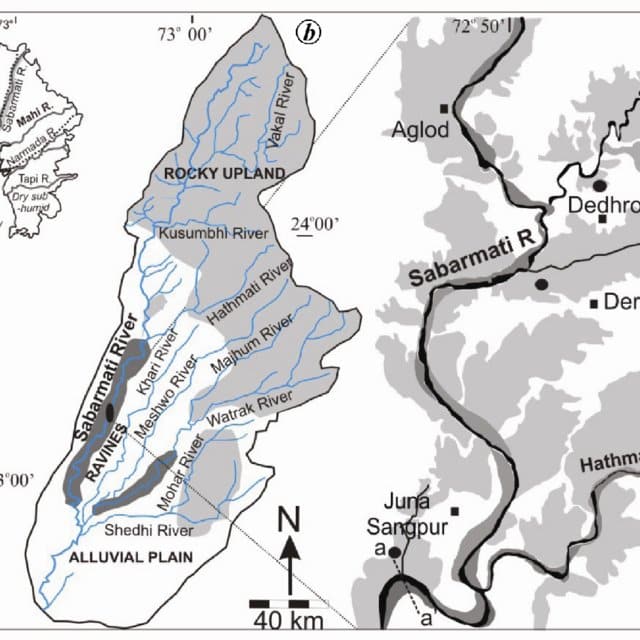
Sabarmati :
- The name given to the combined stream of the Sabar and Hathmati
- Rises from the hills of Mewar in the southern Aravalli Range
- Flows through a gorge at Dharoi and falls into the Gulf of Khambhat
- Tributaries – Hathmati, Sedhi, Wakrul, Harnav, Meshwa, Vatrak.
- Cities: Gandhinagar, Ahmedabad
Banas :
- Rises from the west of the Abu Hills in the southern Aravalli Range and disappears in the Little Rann
- Forms an inland drainage
- Flows through Rajasthan and Gujarat
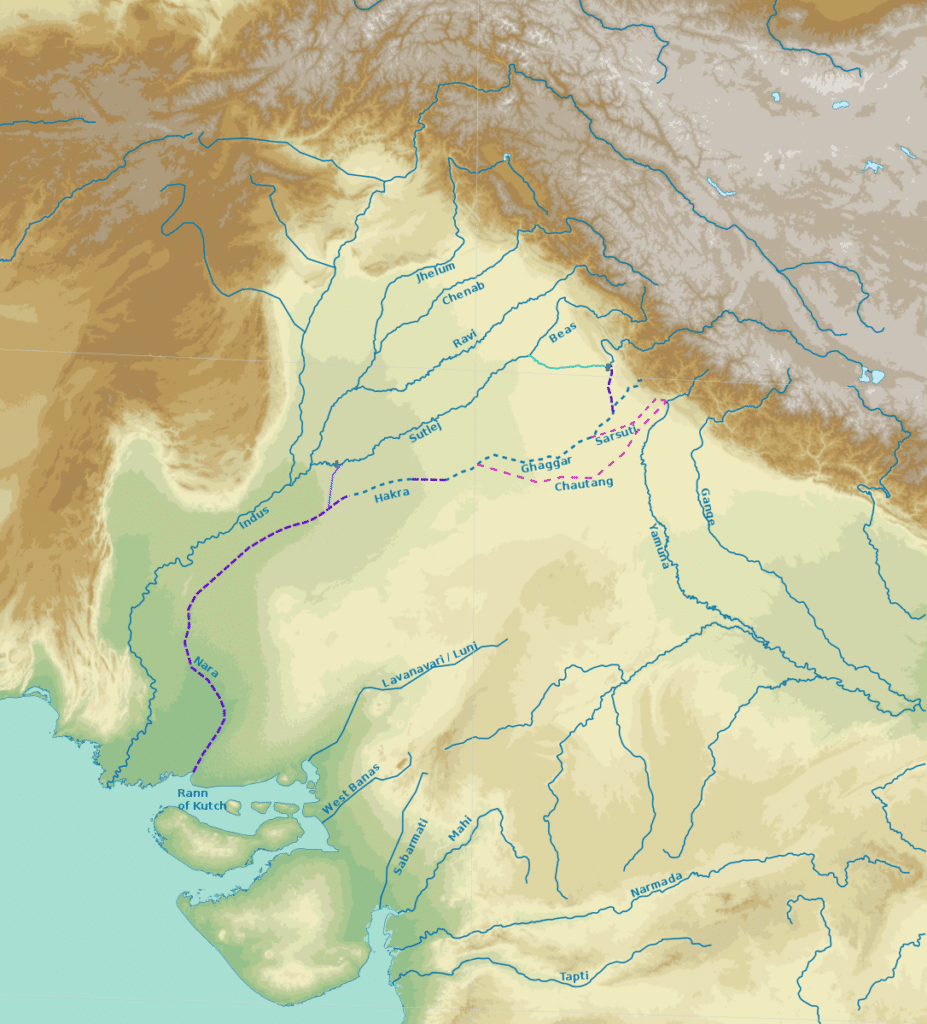
Luni :
- Named so because its water is brackish below Balotara.
- Rises west of Ajmer in the Aravalli Range at an elevation of 550 m.
- Flows south-west through the Thar Desert
- Disappears in the Rann of Kachchh ,so forms the most important inland drainage of India
- Tributaries: Sukai, Sukri, Jawai
Ghagghar :
- Believed to be the remnant of mythical Saraswati River, flows between Punjab and Haryana and disappears in the Thar Desert
- Seasonal and inland river, does not reach sea
Falgu :
- It is formed due to the confluence of the Lilajan and Mohana river near Bodh gaya.
- Gaya is located on its bank.
- People do ‘Pindadaan’ in it near Gaya.
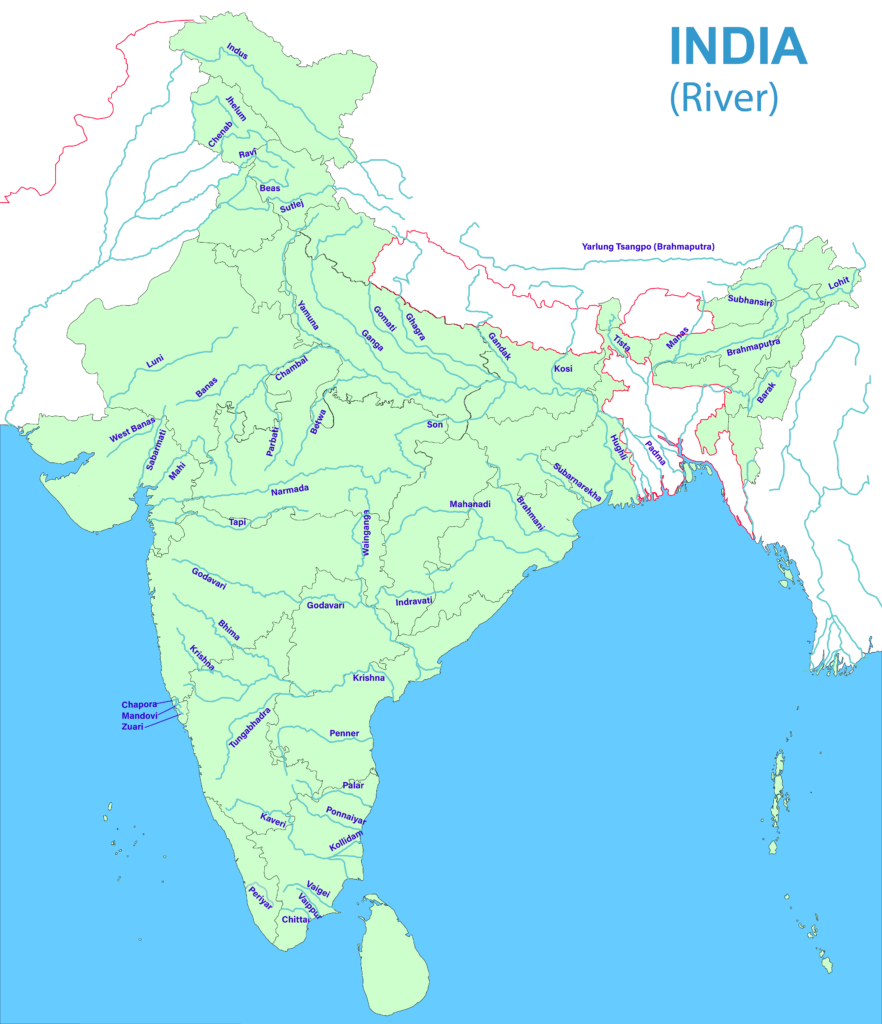

I honestly didnot know that there were these many rivers in India 🇮🇳
This is just a Trailer! 😊
u r the best
super…………….amazing
You are the best only one on google chrome 🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯📯
this very good composition of all the rivers