In this article, You will read the Important list of Multi Purpose Projects in India – for UPSC.
Multi Purpose Projects
Multipurpose project is the scientific management of water resources in the country. A multipurpose project is a massive project which serves a variety of purposes like- flood control, fish breeding, irrigation, generation of electricity, soil conservation, etc. whereas, the hydropower projects are those related to providing only electricity mainly.
Main objectives or Advantages of Multipurpose Project:
- Generation of Power : They produce neat, pollution free and cheapest energy which is the back bone of industry and agriculture. According to the economic survey 2005-06 these produce more than 30, 000 M.W. power.
- Flood Control : These projects control the flood because water can be stored in them. These projects have converted many ‘rivers of sorrow’ into river of boon. Example River Kosi.
- Soil Conservation : These conserve the soil because they slow down the speed of water.
- Irrigation : They irrigate the fields during the dry seasons. Many canals have been dug and they irrigate dry areas.
- Afforestation : Trees are systematically planted in and around reservoirs. This helps in preserving “Wild life” and natural ecosystm.
- Water Navigation : They provide for Inland water navigation through main river or canal. It is the cheapest means of transport for heavy goods.
- Fisheries : These provide ideal condition for the breeding of fish. Choosen varieties of fish are allowed to grow.
- Tourist Centres : These projects are well cared and are scientifically developed. So these become the centre of tourist attraction.
Disadvantages of Multi-purpose Projects:
- Fertile agricultural land submerged under the river water.
- Forest land are either cleared or submerged under water. It is great loss for environment.
- Large no. of people are displaced. They have to leave their own houses and properties.
- Siltation in the dam reduces the lifespan of the project.
- Big Multipurpose projects can result into minor earthquakes.
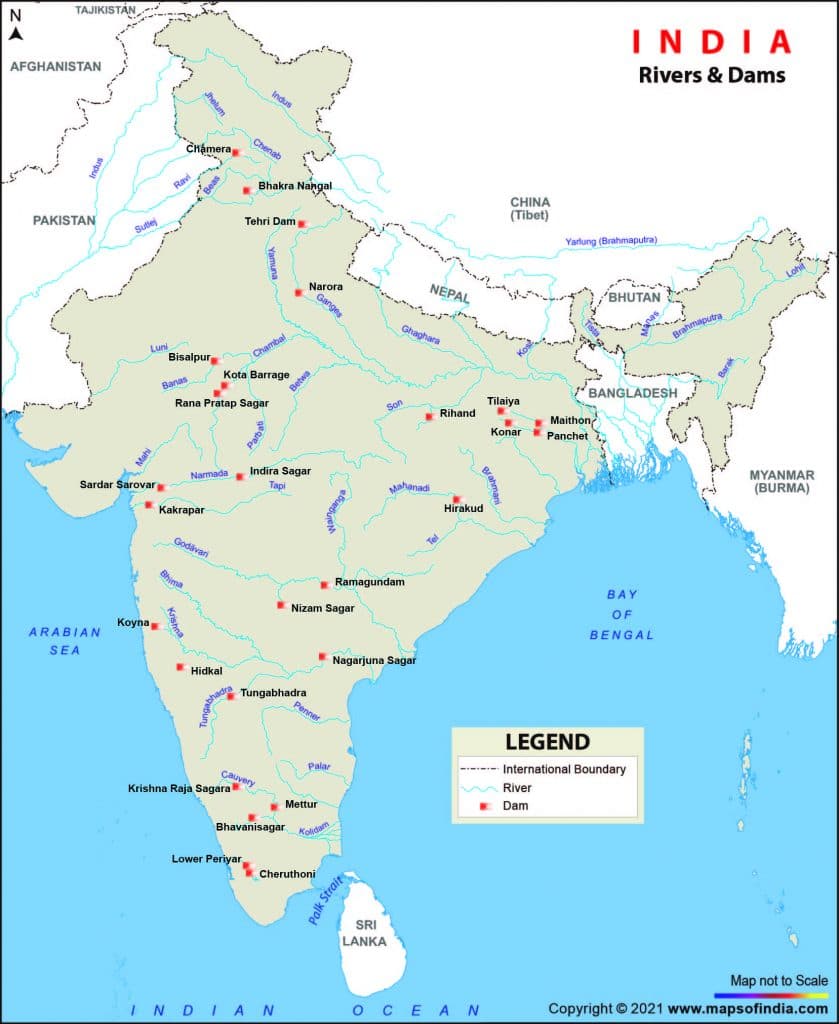
Multi Purpose Projects in India
| Multipurpose Project | River | State |
| Bansagar Project | Son | Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh |
| Bargi Project | Bargi | Madhya Pradesh |
| Beas Project | Beas | HaryanaPunjabRajasthan |
| Bhadra Project | Bhadra | Karnataka |
| Bhakhra Nangal Project | Sutlej | Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Rajsthan |
| Bheema Project | Pawana | Maharashtra |
| Chambal Project | Chambal | Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh |
| Damodar Ghati Project | Damodar | Jharkhand, West Bengal |
| Dulhasti Project | Chenab | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Durga Barrage Project | Damodar | West Bengal, Jharkhand |
| Farakka Project | Ganga, Bhagirathi | West Bengal |
| Gandak Project | Gandaki | Bihar, Uttar Pradesh |
| Ganga Sagar Project | Chambal | Madhya Pradesh |
| Ghatprabha Project | Ghatprabha | Karnataka |
| Girna Project | Girna | Maharashtra |
| Hansdev Bango Project | Hansdev | Madhya Pradesh |
| Hidkal Project | Ghatprabha | Karnataka |
| Hirakud Project | Mahanadi | Orissa |
| Idduki Project | Periyar | Kerala |
| Indira Gandhi Canal Project | Satlaj | Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana |
| Jawahar Sagar Project | Chambal | Rajasthan |
| Jayakwadi Project | Godawari | Maharashtra |
| Kakrapara Project | Tapti | Gujrat |
| Kangsawati Project | Kangsawati | West Bengal |
| Kol Dam Project | Sutlej | Himachal Pradesh |
| Kosi Project | Kosi | Bihar & Nepal |
| Koyana Project | Koyana | Maharashtra |
| Krishna Project | Krishna | Karnataka |
| Kunda Project | Kunda | Tamilnadu |
| Let Bank Ghaghra Canal | Ganga | Uttar Pradesh |
| Madhya Ganga Canal | Ganga | Uttar Pradesh |
| Mahanadi Delta Project | Mahanadi | Odisha |
| Malprabha Project | Malprabha | Karnataka |
| Mandi Project | Vyas | Himachal Pradesh |
| Matatilla Project | Betwa | Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh |
| Mayurakshi Project | Mayurakshi | West Bengal |
| Minimato Bango Hasdeo Project | Hasdeo Bango river | Madhya Pradesh |
| Muchkund Project | Muchkund | Odisha, Andhra Pradesh |
| Nagarjunsagar Project | Krishna | Andhra Pradesh |
| Nagpur Power Project | Koradi | Maharashtra |
| Narmada Sagar Project | Narmada | Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat |
| Nathpa Jhakri Project | Sutlej | Himachal Pradesh |
| Panam Project | Panam | Gujarat |
| Panama Project | Panama | Gujarat |
| Panchet Project | Damodar | Jharkhand, West Bengal |
| Pong Project | Beas | Punjab |
| Poochampad Project | Godawari | Andhra Pradesh |
| Purna Project | Purna | Maharashtra |
| Rajasthan Canal Project | Sutlej, Vyas, Ravi | Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana |
| Ramganga Project | Ramganga | Uttar Pradesh |
| Rana Pratap Sagar Project | Chambal | Rajasthan |
| Ranjeet Sagar Project | Ravi | Punjab |
| Rihand Project | Rihand | Uttar Pradesh |
| Salal Project | Chenab | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Sardar Sarovar Project | Narmada | Madhya PradeshMaharashtraRajasthan |
| Sarhind Project | Sutlej | Haryana |
| Sharawati Project | Sharawati | Karnataka |
| Sharda Project | Sharda, Gomti | Uttar Pradesh |
| Shivsamundram Project | Kaveri | Karnataka |
| Sutlej Project | Chenab | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Tawa Project | Tawa | Madhya Pradesh |
| Tehri Dam Project | Bhagirathi | Uttarakhand |
| Tilaiya Project | Barakar | Jharkhand |
| Tulbul Project | Chenab | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Tungabhadra Project | Tungabhadra | Andhra Pradesh.Karnataka |
| Ukai Project | Tapti | Gujarat |
| Upper Penganga Project | Penganga | Maharashtra |
| Uri Power Project | Jhelum | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Umiam Project | Umiam | Shillong (Meghalaya) |
| Vyas Project | Vyas | RajasthanPunjabHaryanaHimachal Pradesh |
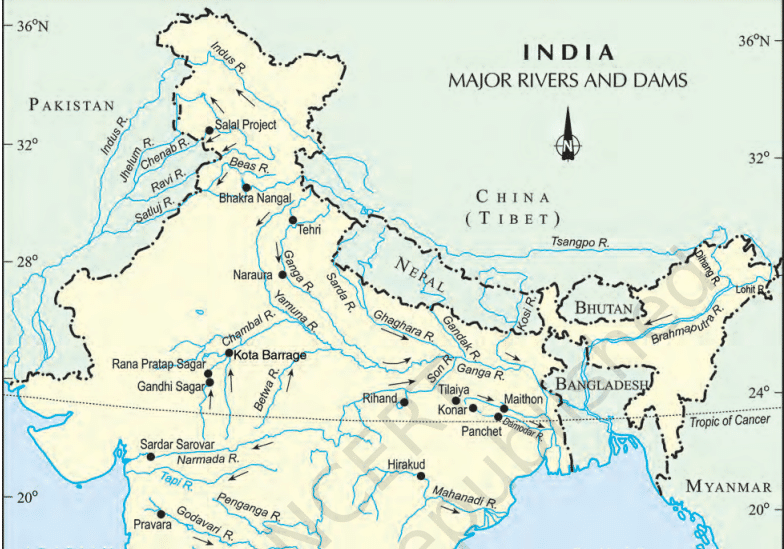
Ranjit Sagar :
- Also known as Thein Dam, is located in the Gurudaspur district of Punjab near Pathankot
- Constructed on the Ravi River
- Project is used for both irrigation and HEP
- It is the biggest HEP project of Punjab (4X150 MW)
- One of the highest Earth Fill Dams of India
Pong Dam :
- A 116m high dam at Pong in the Dhaoladhar Range near Pong village (Himachal Pradesh) on the Beas River
- Mainly an irrigation scheme to irrigate about 21 lakh hectares in Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan
- Total istalled capacity of HEP at the Beas complex – 1020MW
Pandoh Dam :
- The Beas –Satluj link involves the construction of 61m high diversion dam at Pandoh on the Beas in Himachal Pradesh
- Power Plant at Dehar -660 MW
- Irrigates about 5.25 lakh hectares in Punjab and Haryana
Govind Sagar :
- 88 km long and 8 km wide reservoir formed behind the Bhakra Dam
- Storage capacity – 969.8 crore cubic metres
- Named after the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh.
Bhakra :
- One of the highest gravity dams in the world on the Satluj at the Bhakra gorge near Rupnagar (Ropar)
- 222 metre high and 518m long
- Formed reservoir called Govind Sagar
- Joint venture of Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan
- HEP-450MW +600MW
Nangal :
- About 13km downstream of the Bhakra on the Satluj
- 29m high and 305m long
- Serves as balancing reservoir for taking up daily fluctuations from the Bhakra Dam
- HEPs at Ganguwal and Kotla
- Joint venture of Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan
Maithon :
- Part of the DVC in Jharkhand
- On the Barakar River near the confluence of the Damodar and Barakar
- 49m high and 994m long
- HEP- 60MW
Konar :
- On the Konar River in the Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand
- 3549m long and 49m high
- An earthen dam with a concrete spill-way part of the DVC
- HEP-10MW- Bokaro Steel Plant and BokaroThermal Plant receive HEP and water from it
- Irrigation-45000 hectares
Tilaiya :
- Part of the DVC on the Barakar River in Jharkhand
- 30m high and 366m long
- Only concrete dam in the area
- Two power stations of 2000 KW each
- Irrigation -40,000 hectares
Farakka Barrage :
- On the Ganga River in the Murshidabad district of WB,10 km away from the Indo-Bangladeshi border
- Built to divert water into the Hoogly, so that during the dry season silt can be flushed out to keep the Kolkata Port navigable
- Longest Barrage in the world
- Disputed between India and Bangladesh
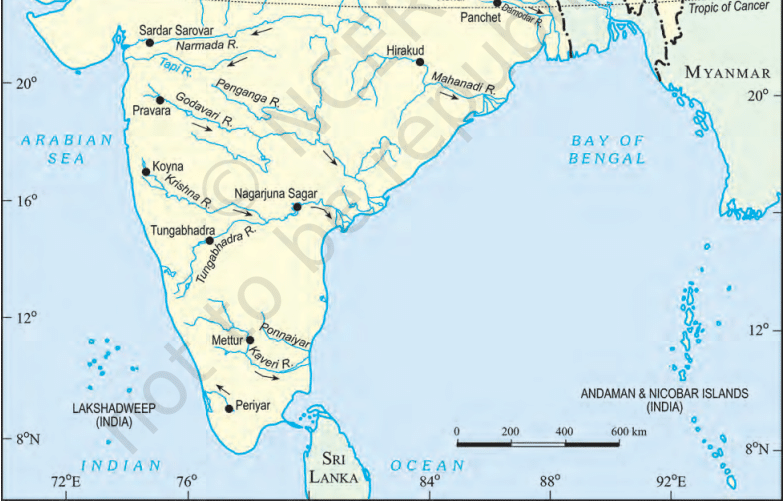
Hirakud :
- On the Mahanadi in Orissa at Hirakud about 14km upstream off the city of Sambalpur
- 61m high and 4801m long (one of the longest dams in the world )
- Two other dams at Tikrapara and Naraj near Cuttack
- HEP- 3.5 lakh KW
- Irrigation -1 million hectares
Balimela :
- Constructed across the Sileru River at Balimela in Malkangiri district of Orissa
- Both irrigation and HEP(510 Mw)
- It is a joint project of odisha and andhra pradesh.
Govind Vallabh Pant Sagar :
- On the Rihand River behind the Rihand Dam near Pipri in the Mirzapur of Uttar Padesh
- Largest man made reservoir in India (446 sq km )
- Another dam at Obra, 25km north
- HEP and irrigation to Madhya Pradsh, Uttar Padesh and Bihar
Jawahar Sagar :
- On the Chambal River in Rajasthan about 29km upstream of Kota city
- 45m high and 548m long gravity dam
- Also known as Kota Dam
- Three HEP units of 33000 MW each
Kota Barrage :
- On the the Chambal in Rajasthan at a distance less than 1km from Kota
- 36m high and 600m long earthen barrage
- Canals taken from both sides of the barrage irrigates 4.4 lakh hectares in Rajasthan and MP
Harike Barrage :
- Located at the confluence of the Satluj and Beas rivers in the Firozpur district of Punjab
- The Indira Gandhi Canal has been taken out of this barrage
Indira Sagar :
- The most important project of the Narmada Valley Development Project.
- Omkareshwar , Maheshwar and Sardar Sarovar receive water from it
- Largest water storage capacity in the country
- Located in the Khandwa district of Madhya Pradesh
- HEP-8X125= 1000MW
- Irrigation 1.23 lakh hectares
Omkareshwar :
- On the Narmada at Mandhata village in East Nimar (Khandwa) district of Madhya Pradesh
- HEP -8X65=520 MW
- Irrigation -1,46,800 hectares
- Its power generation capacity is directly related with the amount of water released from the Indira Sagar
Maheshwar :
- On the Narmada in Madhya Pradesh downstream off the Omkareshwar
- HEP- 10X40=400MW
- A project which does not affect the forest land
- First privately financed hydroelectric dam in India
Chota Tawa :
- On the Chota Tawa, left bank tributary of the Narmada, at Ranipur village of the Hoshangabad district of Madhya Pradesh
- HEP-13.50 MW
- Irrigation – 24,700 hectares
- Located at the confluence of the Tawa and the Denwa rivers
- Third largest dam of the Narmada Valley Project
Sardar Sarovar :
- Project of MP, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Rajasthan
- On the Narmada at Kevadia village of the Vadodara district of Gujarat
- 121.92 m high can be raised upto 163 m as per the proposal
- HEP-1450MW
- Irrigation – Around 20 lakh hectares.
Ukai :
- Built on the Tapi River when it enters Gujarat
- Mainly for HEP
- Capacity -300 MW
- Electricity is supplied to Surat and other neighbouring cities
Koyna :
- Constructed across the Koyna River in the Satara district of Maharashtra
- Has formed the Shivaji Sagar
- Constructed mainly to generate HEP
- HEP capacity -860 MW
- Experienced earthquake in 1967, which proved that the Deccan Plateau is made of several minor plates
Nizam Sagar :
- An irrigation and HEP project on the Manjra River in AP near Nizamabad
- Water is supplied to Nizamabad and Hyderabad
- Constructed in 1923 by Nizam-Ul-Mulk, the then ruler of the erstwhile Nizam state
- A masonry dam over which fourteen feet wide motorable road is present
- Frequented by tourists
Hussain Sagar :
- An artificial lake in Hyderabad built by Hazrat Husain Shah Wali in 1562 during the rule of Ibrahim Quli Qutub Shah
- Built on a tributary of the Musi River to meet the water and irrigation needs of Hyderabad
- A large monolith statue of the Lord Buddha in the middle of the lake
Nagarjunasagar :
- On the Krishna River in Nalgonda district of Andhra Pradesh
- 125m high and 1450m long concrete dam
- 2 Canals – Jawahar Canal (349km) and Lal Bahadur Canal (357km)
- Irrigation -7 lakh hectares
- HEP- 100 MW
Tungabhadra :
- Joint venture of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh on the Tungabhadra River at Mallapur in Bellary district
- 50 m and 2441 m long straight gravity masonasy dam
- Two irrigation canals -41.32 lakh hectares
- Three power houses -126MW
Almatty Dam :
- Located on the Krishna River in the Bijapur district of Karnataka
- Main reservoir of the Upper Krishna Project
- HEP – 290 MW
- 52.25 m high and 1565.15 m long.
Linganamakki :
- Located on the Sharavati River about 6km upstream from the Jog Falls
- 2.4 km long and 193 feet high
- HEP capacity – 55MW
Shivanasamudra Dam:
- Shivanasamudra Dam (1902) is located on the Kaveri River.
- It was built in Karnataka during the British era and was designed by Diwan Sheshadri Iyer.
Bhadra :
- Located on the Bhadra River, a tributary of the Krishna River, in Karnataka
- The project consists a dam and 2 canals
- Located 50km upstream of the point where the Bhadra River joins the Tungabhadra
- The Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the vicinity
Krishnaraj Sagar :
- Irrigation and HEP project on the Cauvery River near Mysore in Karnataka
- The Vrindavan Park is located near the dam
- Located in the Mandya district
- Named after the then ruler of the Mysore Kingdom, Krishnaraja Wodeyar
- Mokshagundam Visvesvarayaya served as the chief engineer
Chamraj Sagar :
- Built across the Arkavati River, about 35km from Bengaluru
- Attractive picnic spot for relaxation and fishing
- Supplies water to Bengaluru
Periyar Lake :
- Formed behind the Mulla Periyar Dam in Kerala inside the Periyar National Park
- Operated by Tamil Nadu Govt according to a 999- year lease agreement made during the erstwhile British Rule
- Area – 26 sq km
- The dam is 1200 feet long and 155 feet high
- Disputed between Tamil Nadu and Kerala
- Located after the coufluence of Mullaiyar and Periyar
Stanley Reservoir :
- Formed by the Mettur Dam in northwestern Tamin Nadu
- One of the largest fishing reservoirs of India
- Length of the dam – 1700m
- Installed capacity -240 MW
Bhavani Sagar :
- Located on the Bhavani River in the Erode district of Tamin Nadu
- Among the biggest earthen dams of India
- The dam is used to divert water to the Lower Bhavani Project Canal
- 32m high
- Reservoir Capacity -32.80tmc
Bansagar Project :
- Joint venture of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar on the Son on the Rewa- Shahdol way in Madhya Pradesh
- HEP – 405 MW
- Irrigation in Sidhi, Satna, Rewa and Shahdol districts of Madhya Pradesh
Matatila :
- On the Betwa River in Madhya Pradesh
- Joint project of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh
- Irrigation 1.09 lakh hectares in Uttar Pradesh and 1.16 lakh hectares on Madhya Pradesh
- Famous as Rani Lakshmibai Project
Rajghat Project :
- Joint venture of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh on the Betwa in Lalitpur of Uttar Pradesh
- Irrigation – cum – HEP project
- HEP capacity – 45 MW (3X15)
Gandhi Sagar :
- On the Chambal at the border of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
- 64m high and 514 m long
- Irrigation – 4.44 lakh hectares
- HEP-5 units of 23000 KW each
Rana Pratap Sagar :
- On the Chambal at Rawatbhata
- 54m high and 1143 hectares
- HEP-4units of 43,000 KW each
Ravishankar Sagar Project :
- It is built across the Mahanadi river in the Dhamtari district, Chhattisgarh.
- It is the longest dam of Chhattisgarh.
- Alongwithtion it produces 10 MW of HEP
- It supplies water to the Bhiai steel plant.
Hasdo-Bango Project :
- It is built across the Hasdeo river in the Korba district, Chhattisgarh.
- It is the longest and highest dam of Chhattisgarh.
- Irrigation capacity : 2 ,55000 hectares
- It has three units of hydroelectric plant with the capacity of 40 MW each.

Super
thanks
superb