Plateau is an area of raised land that is flat on top. Plateaus are often by themselves with no surrounding plateau. National Geographic describes plateaus as flat and elevated landform that rises sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side.
Features of the Peninsular Plateau
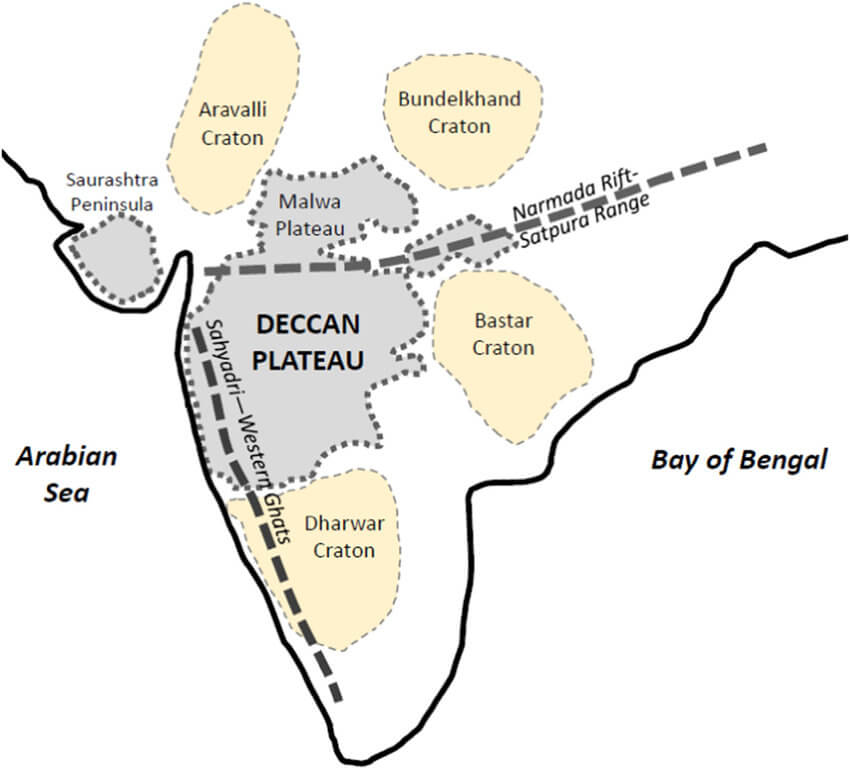
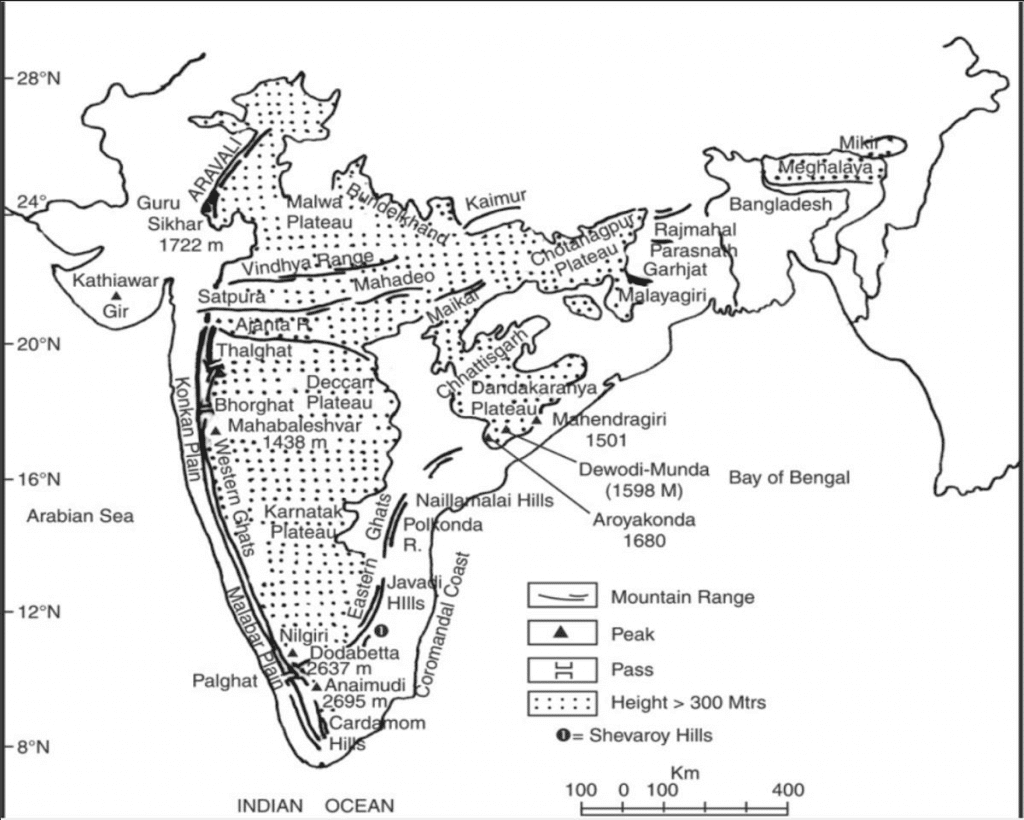
- Roughly triangular in shape with its base coinciding with the southern edge of the great plain of North India. The apex of the triangular plateau is at Kanniyakumari.
- It covers a total area of about 16 lakh sq km (India as a whole is 32 lakh sq km).
- The average height of the plateau is 600-900 m above sea level (varies from region to region).
- Most of the peninsular rivers flow west to east indicating it’s the general slope.
- Narmada-Tapti is the exception that flows from east to west in a rift (rift is caused by a divergent boundary (Go back to Interaction of plates).
- The Peninsular Plateau is one of the oldest landforms of earth.
- It is a highly stable block composed mostly of the Archaean gneisses and schists.
- It has been a stable shield that has gone through little structural changes since its formation.
- Since a few hundred million years, the Peninsular block has been a land area and has never been submerged beneath the sea except in a few places.
- Peninsular Plateau is an aggregation of several smaller plateaus, hill ranges interspersed with river basins and valleys.
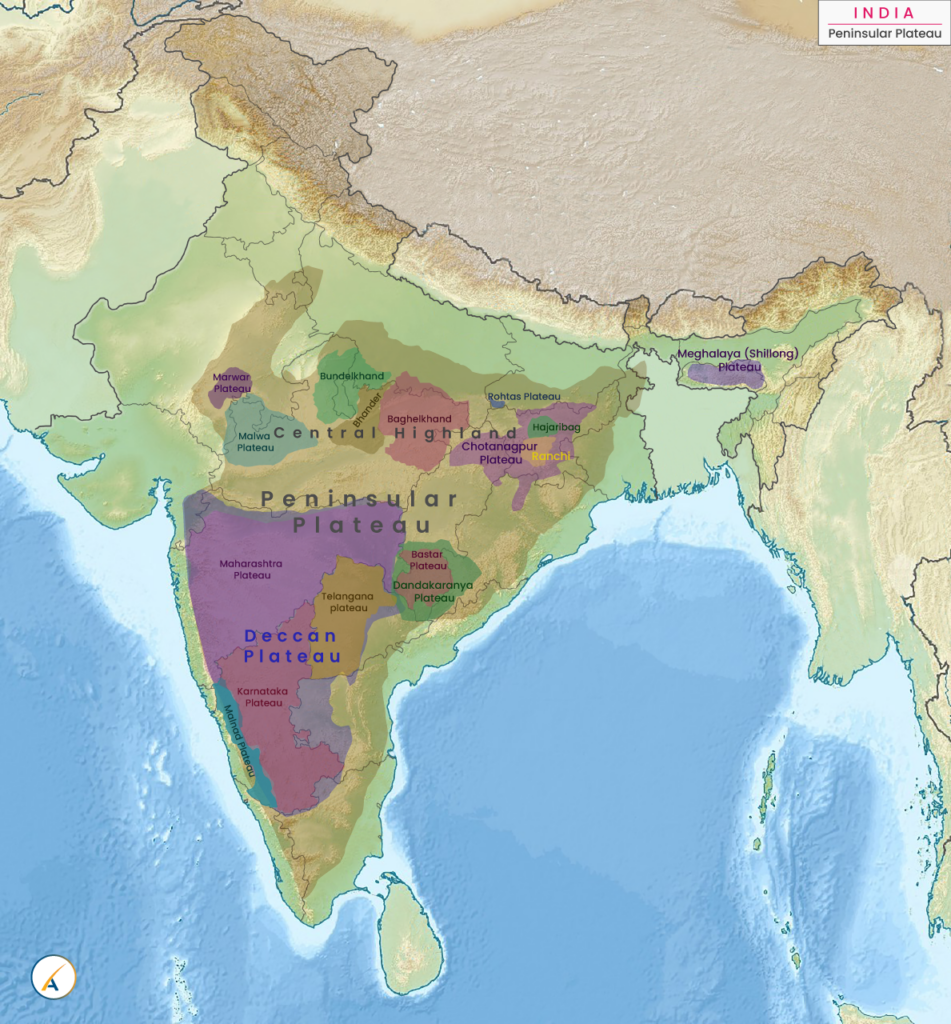
Minor Plateaus in the Peninsular Plateau
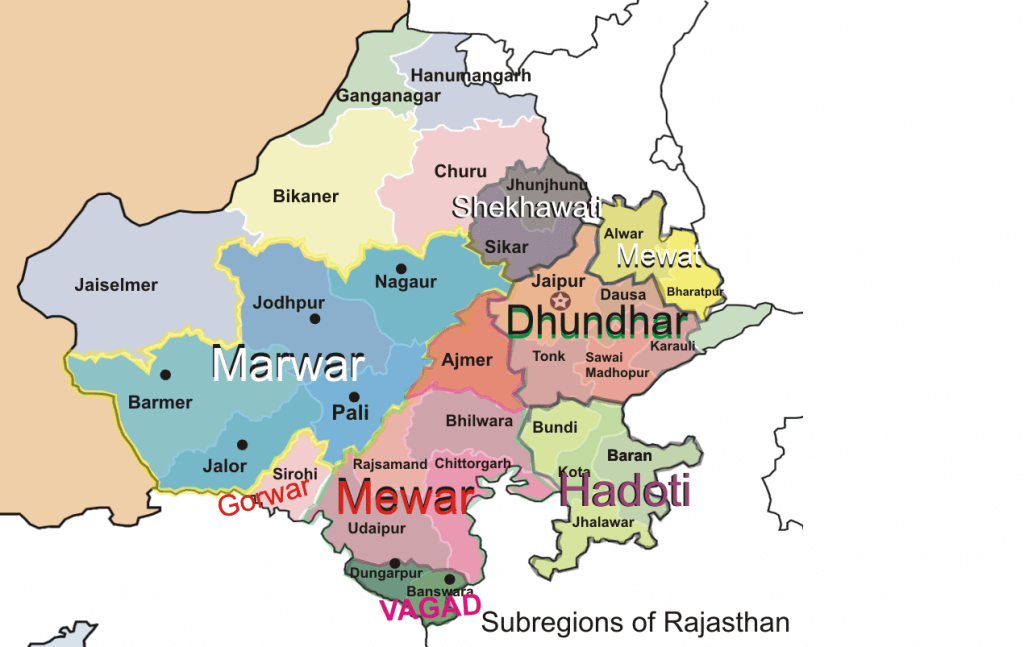
Marwar Plateau or Mewar Plateau
- It is the plateau of eastern Rajasthan. [Marwar plain is to the west of Aravalis whereas Marwar plateau is to the east].
- The average elevation is 250-500 m above sea level and it slopes down eastwards.
- It is made up of sandstone, shales, and limestones of the Vindhayan period.
- The Banas River, along with its tributaries [Berach river, Khari rivers] originate in the Aravali Range and flow towards northwest into the Chambal river. The erosional activity of these rives makes the plateau top appear like a rolling plain.
- Rolling Plain: ‘Rolling plains’ are not completely flat: there are slight rises and falls in the landform. Ex: Prairies of USA
Central Highland
- Also called the Madhya Bharat Pathar or Madhya Bharat Plateau.
- It is to the east of the Marwar or Mewar Upland.
- Most of the plateau comprises the basin of the Chambal river which flows in a rift valley.
- The Kali Sindh, flowing from Rana Pratap Sagar, The Banas flowing through Mewar plateau, and The Parwan and the Parbati flowing from Madhya Pradesh are its main tributaries.
- It is a rolling plateau with rounded hills composed of sandstone. Thick forests grow here.
- To the north are the ravines or badlands of the Chambal river [They are typical to Chambal river basin].

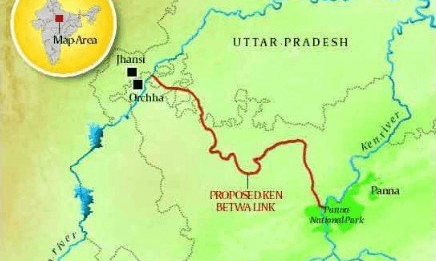
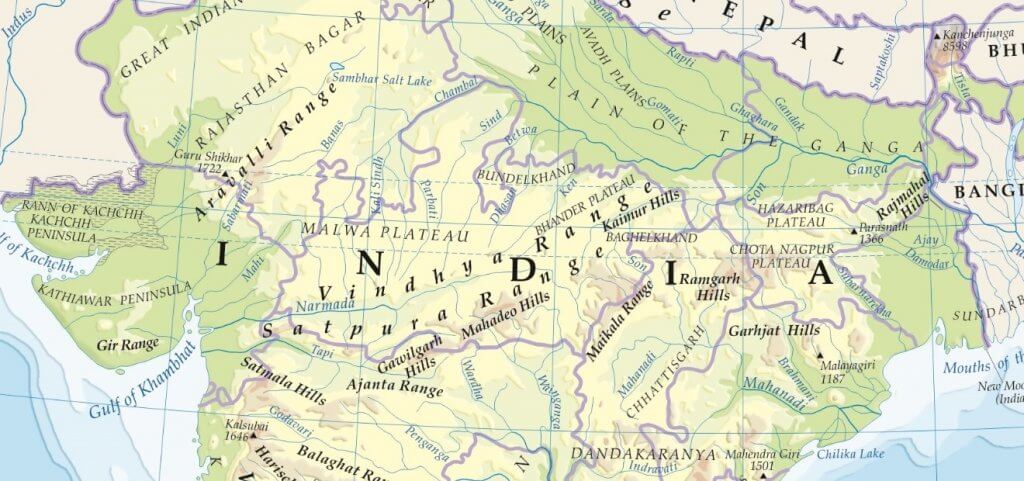
Bundelkhand Upland
- Yamuna river to the north, Madhya Bharat Pathar to the west, Vindhyan Scarplands to the east and south-east, and Malwa Plateau to the south.
- It is the old dissected (divided by a number of deep valleys) upland of the ‘Bundelkhand gneiss’ comprising of granite and gneiss.
- Spreads over five districts of Uttar Pradesh and four districts of Madhya Pradesh.
- An average elevation of 300-600 m above sea level, this area slopes down from the Vindhyan Scarp toward the Yamuna River.
- The area is marked by a chain of hillocks (small hill) made of granite and sandstone.
- The erosional work of the rivers flowing here have converted it into an undulating (wave-like surface) area and rendered it unfit for cultivation.
- The region is characterized by senile (characteristic of or caused by old age) topography.
- Streams like Betwa, Dhasan, and Ken flow through the plateau.
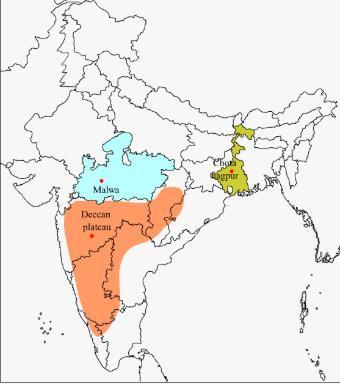
Malwa Plateau
- The Malwa Plateau roughly forms a triangle based on the Vindhyan Hills, bounded by the Aravali Range in the west and Madhya Bharat Pathar to the north, and Bundelkhand to the east.
- This plateau has two systems of drainage; one towards the Arabian sea (The Narmada, the Tapi, and the Mahi), and the other towards the Bay of Bengal (Chambal and Betwa, joining the Yamuna).
- In the north, it is drained by the Chambal and many of its right bank tributaries like the Kali, the Sindh, and the Parbati. It also includes the upper courses of the Sindh, the Ken, and the Betwa.
- It is composed of the extensive lava flow and is covered with black soils.
- The general slope is towards the north [decreases from 600 m in the south to less than 500 m in the north]
- This is a rolling plateau dissected by rivers. In the north, the plateau is marked by the Chambal ravines.
Baghelkhand
- North of the Maikal Range is the Baghelkhand.
- Made of limestones and sandstones on the west and granite in the east.
- It is bounded by the Son river on the north.
- The central part of the plateau acts as a water divide between the Son drainage system in the north and the Mahanadi river system in the south.
- The region is uneven with general elevation varying from 150 m to 1,200 m.
- The Bharner and Kaimur are located close to the trough-axis.
- The general horizontality of the strata shows that this area has not undergone any major disturbance.
Rohtas Plateau
- The Rohtas Plateau (also referred to as Kaimur Plateau) is a plateau that lies in the south-western part of Bihar.
- The Rohtas Plateau or Kaimur Plateau comprises about 800 square miles (2,100 km2). It is an undulating table land. At Rohtasgarh it attains a height of 1,490 feet (450 m) above sea level.
- Surrounding geography: A series of fluvial plateaux that run along the Kaimur Range consist of a series of descending plateaux, starting with the Panna Plateau in the west, followed by Bhander Plateau and Rewa Plateau and ending with Rohtas plateau in the east.
Bhander Plateau
- The Bhander Plateau is a plateau in the state of Madhya Pradesh in India. It has an area of 10,000 square kilometres.
- It links the Deccan Plateau to the south with the Indo-Gangetic Plains and the Chota Nagpur Plateau to the north and east respectively.
- The plateau is part of the Vindhya Range in central India.
- A series of plateaux runs along the Kaimur Range. These fluvial plateaux consist of a series of descending plateaux, starting with the Panna Plateau in the west, followed by Bhander Plateau and Rewa Plateau, and ending with Rohtas Plateau in the east.
Chotanagpur Plateau
- Chotanagpur plateau represents the north-eastern projection of the Indian Peninsula.
- Mostly in Jharkhand, the northern part of Chhatisgarh and Purulia district of West Bengal.
- The Son River flows in the north-west of the plateau and joins the Ganga.
- The average elevation of the plateau is 700 m above sea level.
- This plateau is composed mainly of Gondwana rocks.
- The plateau is drained by numerous rivers and streams in different directions and presents a radial drainage pattern. {Drainage Pattern}
- Rivers like the Damodar, the Subarnrekaha, the North Koel, the South Koel, and the Barkar have developed extensive drainage basins.
- The Damodar River flows through the middle of this region in a rift valley from west to east. Here are found the Gondwana coal fields which provide the bulk of coal in India.
- North of the Damodar river is the Hazaribagh plateau with an average elevation of 600 m above mean sea level. This plateau has isolated hills. It looks like a peneplain due to large scale erosion.
- The Ranchi Plateau to the south of the Damodar Valley rises to about 600 m above mean sea level. Most of the surface is rolling where the city of Ranchi (661 m) is located.
- At places, it is interrupted by monadnocks (an isolated hill or ridge of erosion-resistant rock rising above a peneplain. Ex: Ayers Rock in Australia) and conical hills.
- The Rajmahal Hills forming the northeastern edge of the Chotanagpur Plateau are mostly made of basalt and are covered by lava flows {Basaltic Lava}.
- They run in the north-south direction and rise to an average elevation of 400 m (the highest mount is 567 m). These hills have been dissected into separate plateaus.
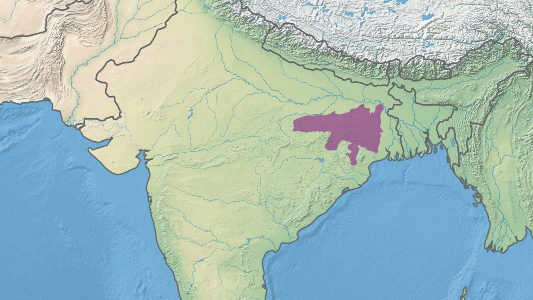
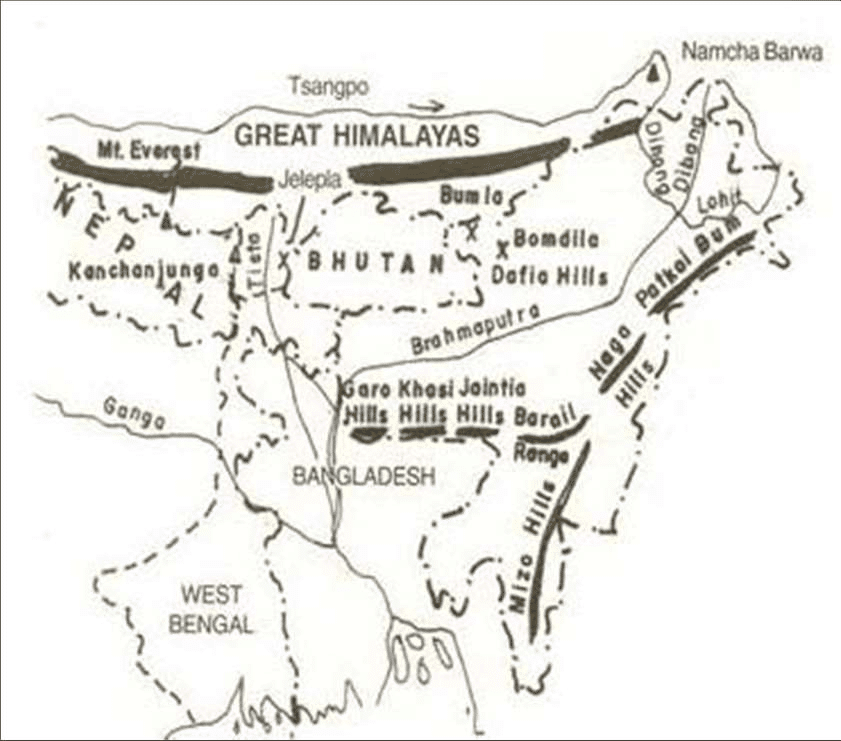
Meghalaya Plateau
- The peninsular plateau extends further east beyond the Rajmahal hills to from Meghalaya or the Shillong plateau.
- Garo-Rajmahal Gap separates this plateau from the main block.
- This gap was formed by down-faulting (normal fault: a block of earth slides downwards). It was later filled by sediments deposited by the Ganga and Brahmaputra.
- Down warping along Rajmahal–Garo hills = ‘Malda gap’
- Ganga-Brahmaputra flow through the Malda gap.
- The plateau is formed by Archaean quartzites, shales, and schists.
- The plateau slopes down to Brahmaputra valley in the north and the Surma and Meghna valleys in the south.
- Its western boundary more or less coincides with the Bangladesh border.
- The western, central, and eastern parts of the plateau are known as the Garo Hills (900 m), the Khasi-Jaintia Hills (1,500 m), and the Mikir Hills (700 m).
- Shillong (1,961 m) is the highest point of the plateau.
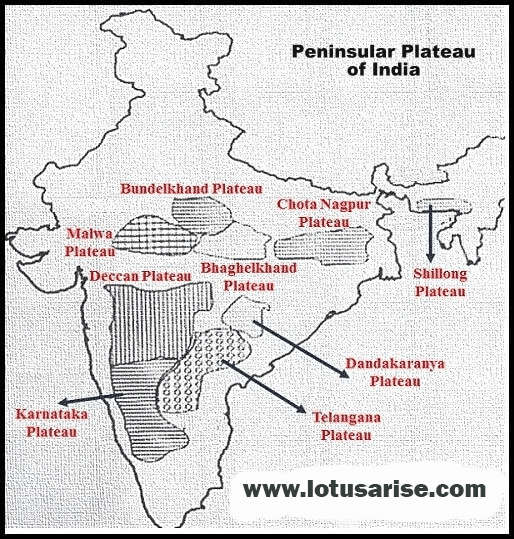
Deccan Plateau
- It covers an area of about five lakh sq km.
- It is triangular in shape and is bounded by the Satpura and the Vindhya in the north-west, the Mahadev and the Maikal in the north, the Western Ghats in the west, and the Eastern Ghats in the east.
- Its average elevation is 600 m.
- It rises to 1000 m in the south but dips to 500 m in the north.
- Its general slope is from west to east which is indicated by the flow of its major rivers.
- Rivers have further subdivided this plateau into a number of smaller plateaus.
Maharashtra Plateau
- The Maharashtra Plateau lies in Maharashtra.
- It forms the northern part of the Deccan Plateau.
- Much of the region is underlain by basaltic rocks of lava origin [Most of the Deccan Traps lies in this region].
- The area looks like a rolling plain due to weathering.
- The horizontal lava sheets have led to the formation of typical Deccan Trap topography [step like].
- The broad and shallow valleys of the Godavari, the Bhima, and the Krishna are flanked [bordered on the opposite sides] by flat-topped steep-sided hills and ridges.
- The entire area is covered by black cotton soil known as regur.
Karnataka Plateau
- The Karnataka Plateau is also known as the Mysore plateau.
- Lies to the south of the Maharashtra plateau.
- The area looks like a rolling plateau with an average elevation of 600-900 m.
- It is highly dissected by numerous rivers rising from the Western Ghats.
- The general trend of the hills is either parallel to the Western Ghats or across it.
- The highest peak (1913 m) is at Mulangiri in Baba Budan Hills in the Chikmaglur district.
- The plateau is divided into two parts called Malnad and Maidan.
- The Malnad in Kannada means the hill country. It is dissected into deep valleys covered with dense forests.
- The Maidan on the other hand is formed of a rolling plain with low granite hills.
- The plateau tapers between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats in the south and merges with the Niligiri hills there.
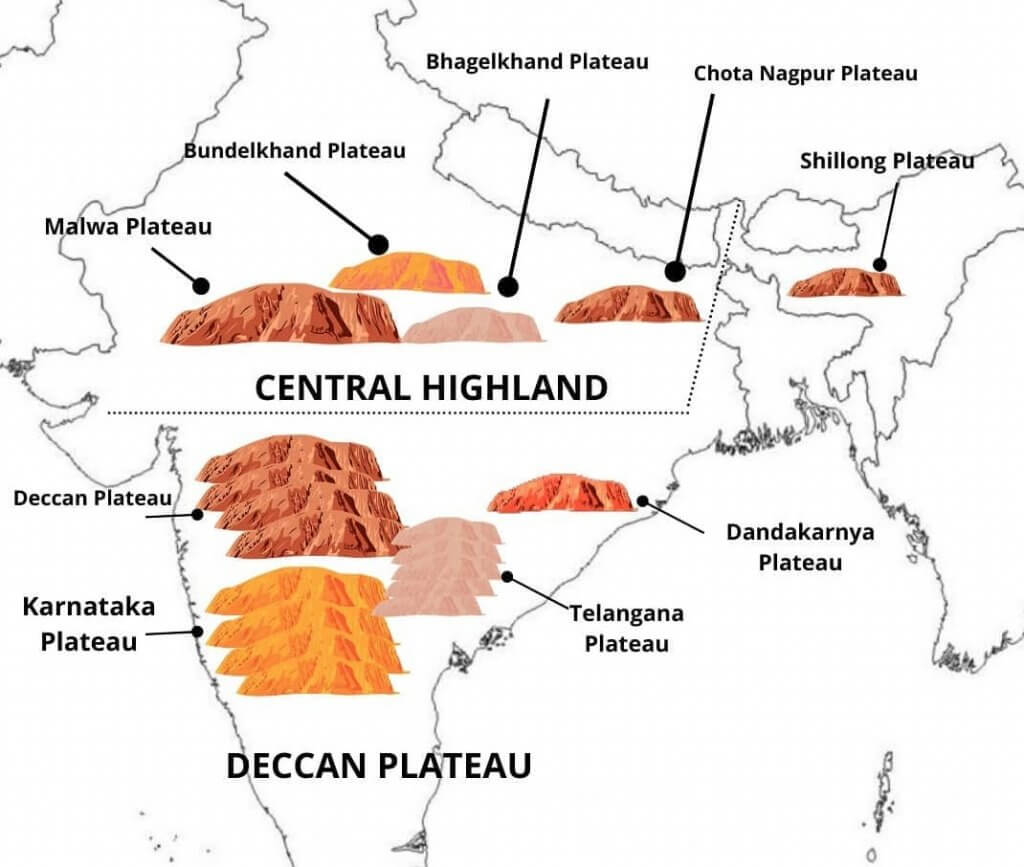
Telangana plateau
- The Telangana plateau consists of Archaean gneisses.
- It is made up of Dharwar rocks. Gondwana rocks are also found in the Godavari valley, famous for its coal fields.
- Because of the Dharwar rock strata, the plateau is rich in mineral resources.
- Its average elevation is 500-600 m.
- The southern part is higher than its northern counterpart.
- The region is drained by three river systems, the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Penner.
- The entire plateau is divided into Ghats and the Peneplains (a vast featureless, undulating plain which the last stage of the deposition process).
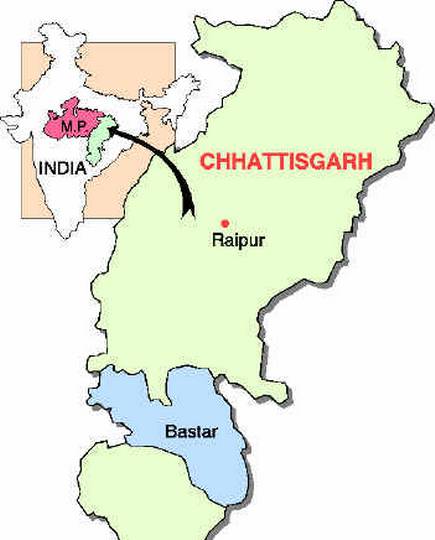
Bastar Plateau
- Bastar is a district in the southernmost region in the state of Chhattisgarh.
- It is a forested mineral rich region.
- Southern part of Chhattisgarh between the Mahanadi and Godavari rivers.
- Bisected into two parts by the Indravati River.
- Tribal dominated region.
- Under the strong grip of Naxalism.
Chhattisgarh Plain
- The Chhattisgarh plain is the only plain worth the name in the Peninsular plateau.
- It is a saucer-shaped depression drained by the upper Mahanadi.
- The whole basin lies between the Maikala Range and the Odisha hills.
- The region was once ruled by Haithaivanshi Rajputs from whose thirty-six forts (Chhattisgarh) it derives its name.
- The basin is laid with nearly horizontal beds of limestone and shales.
- The general elevation of the plain ranges from 250 m in the east to 330 m in the west.
Dandakaranya Plateau
- Dandakaranya is a historical region in India, mentioned in Ramayana. It is located in the Bastar region of the present-day state of Chhattisgarh in the central part of India.
- Dandakaranya is a physiographic region in the central part of India. Extending over a neighborhood of about 35600 square miles, it includes the Abujhmad Hills within the west and borders the Eastern Ghats within the east.
- Abujmarh is a hilly forest area in Chhattisgarh, covering Narayanpur district, Bijapur district, and Dantewada district. It is home to indigenous tribes of India, including Gond, Muria, Abuj Maria, and Halbaas.
- The Dandakaranya includes parts of the Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh states. It’s a dimension of about 200 miles from north to south and about 300 miles from east to west.

Nicely explained…. Well Illustrated content….. Liked too much
Thanka a lot
dhanyavad
Very very beneficial site thanks a lot 👍
Sir can u suggest any reference for rayaleseema plateau
Southern part of telengana plateau