In this article, You will read Road Transport in India – for UPSC IAS (Transport, Communication and Trade).
Transport System in India
- The transport system in India includes Rail transport, Road transport, Air transport, water transport, and portal connectivity. India has one of the largest road networks in the world, the largest railway system in Asia, and the second-largest in the world.
- The use of transport and communication depends upon our need to move things from place of their availability to the place of their use. Human-beings use various methods to move goods, commodities, ideas from one place to another.
- The following diagram shows the major means of transportation.
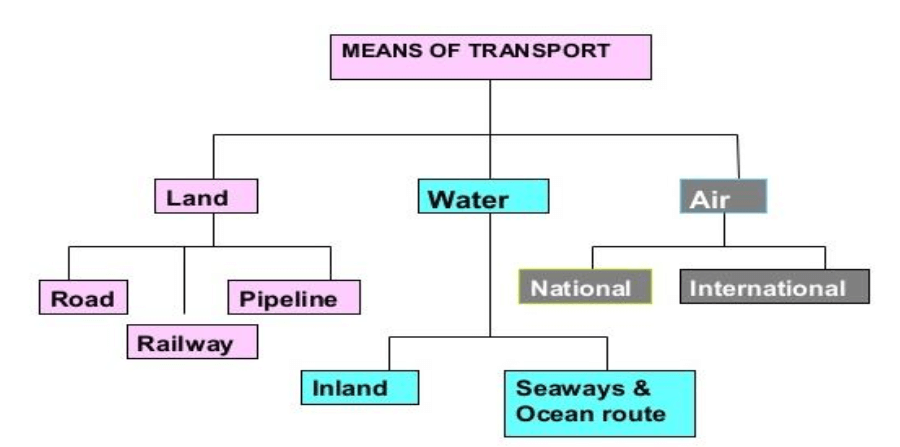
Data and figures will vary because of development in each year.
Road Transport in India
- The pathways and unmetalled roads have been used for transportation in India since ancient times. With the economic and technological development, metalled roads and railways were developed to move large volumes of goods and people from one place to another. Roads happen to be the most popular mode of transportation.
- India has one of the largest road networks in the world with a total length of 5,897,671 kilometers (3,664,643 mi) as of 31 March 2017. About 85 percent of passengers and 70 percent of freight traffic are carried by roads every year. Road transport is relatively suitable for shorter distance travel.
- For the purpose of construction and maintenance, roads are classified as
- National Highways (NH),
- State Highways (SH),
- Major District Roads, and
- Rural Roads.
National highways
- The main roads which are constructed and maintained by the Central Government are known as the National Highways.
- These roads are meant for inter-state transport and movement of defence men and material in strategic areas.
- These also connect the state capitals, major cities, important ports, railway junctions, etc.
- India has 142,126 km (88,313 mi) of National Highways as of April 2019. The National Highways constitute only 2 percent of the total road length but carry 40 percent of the road traffic.
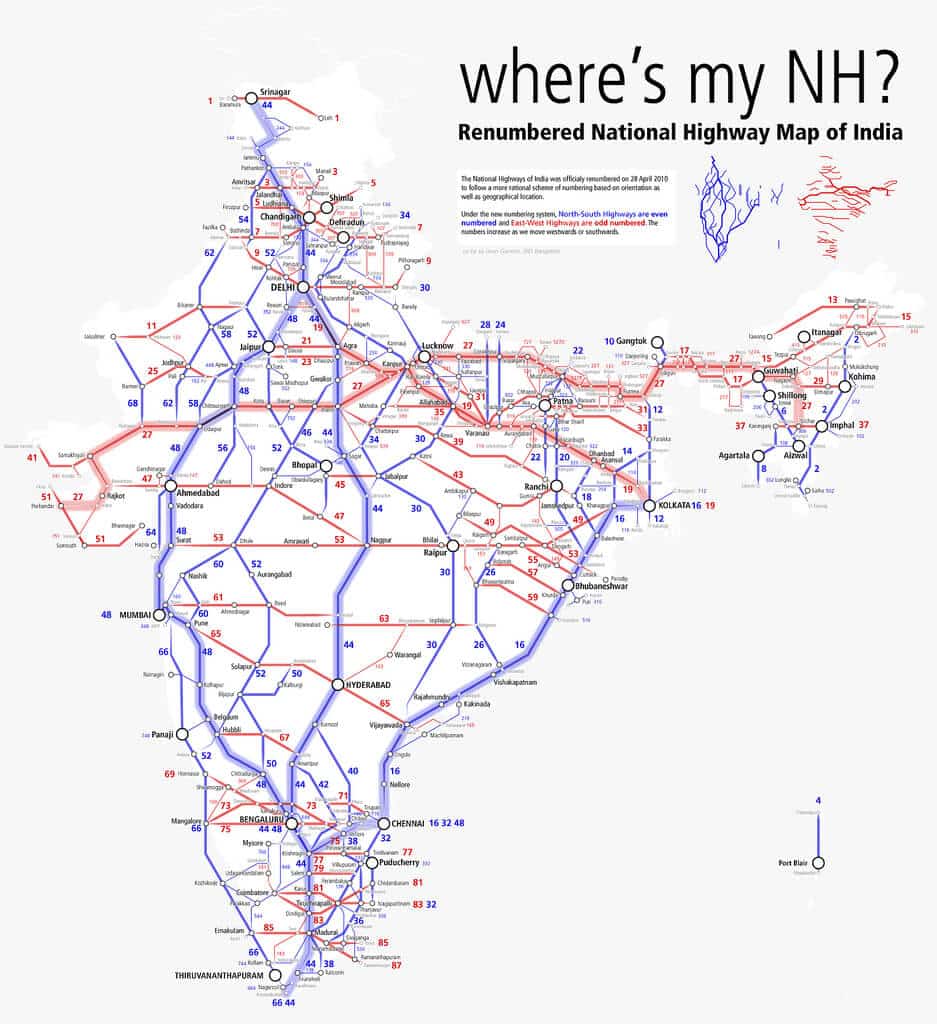
- Golden quadrilateral: Golden Quadrilateral comprises construction of 5,846 km long 4/6 lane, high-density traffic corridor, to connect India’s four big metro cities of Delhi-Mumbai-Chennai-Kolkata. With the construction of the Golden Quadrilateral, the time-distance and cost of movement among the megacities of India will be considerably minimized.
- North-South and East-West Corridor: North-South corridor aims at connecting Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir with Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu (including Kochchi-Salem Spur) with a 4,076 km long road. The East-West Corridor has been planned to connect Silchar in Assam with the port town of Porbandar in Gujarat with 3,640 km of road length.
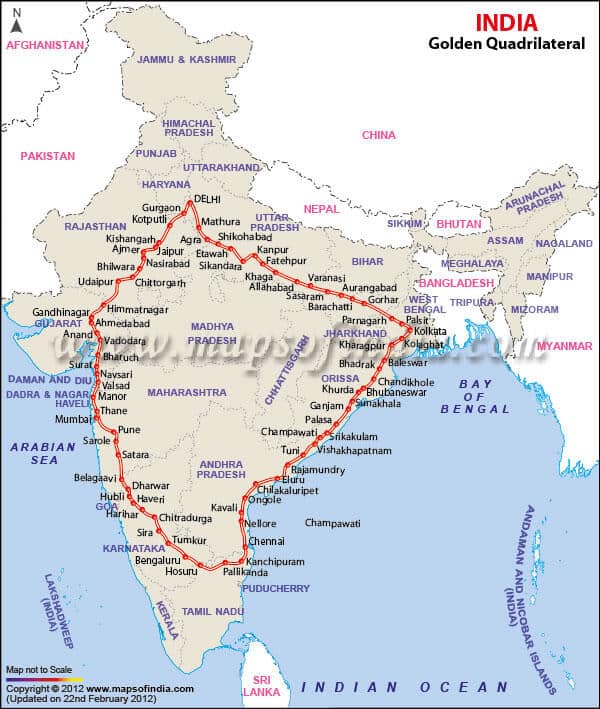
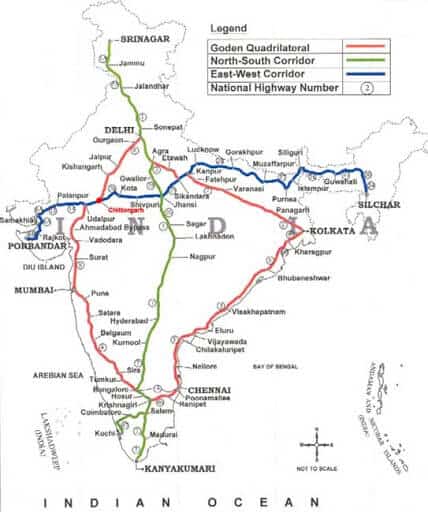
Some important National Highways
| National Highway | Extension |
| NH-1 | Delhi-Amritsar |
| NH-2 | Delhi-Kolkata |
| NH-3 | Agra-Mumbai |
| NH-4 | Chennai-Thane |
| NH-5 | Chennai-Cuttack |
| NH-6 | Surat-Kolkata |
| NH-7 | Varanasi-kanyakumari |
| NH-8 | Delhi-Mumbai |
| NH-9 | Pune-Machlipatnam |
| NH-15 | Samakhali(kutch)-Pathankot |
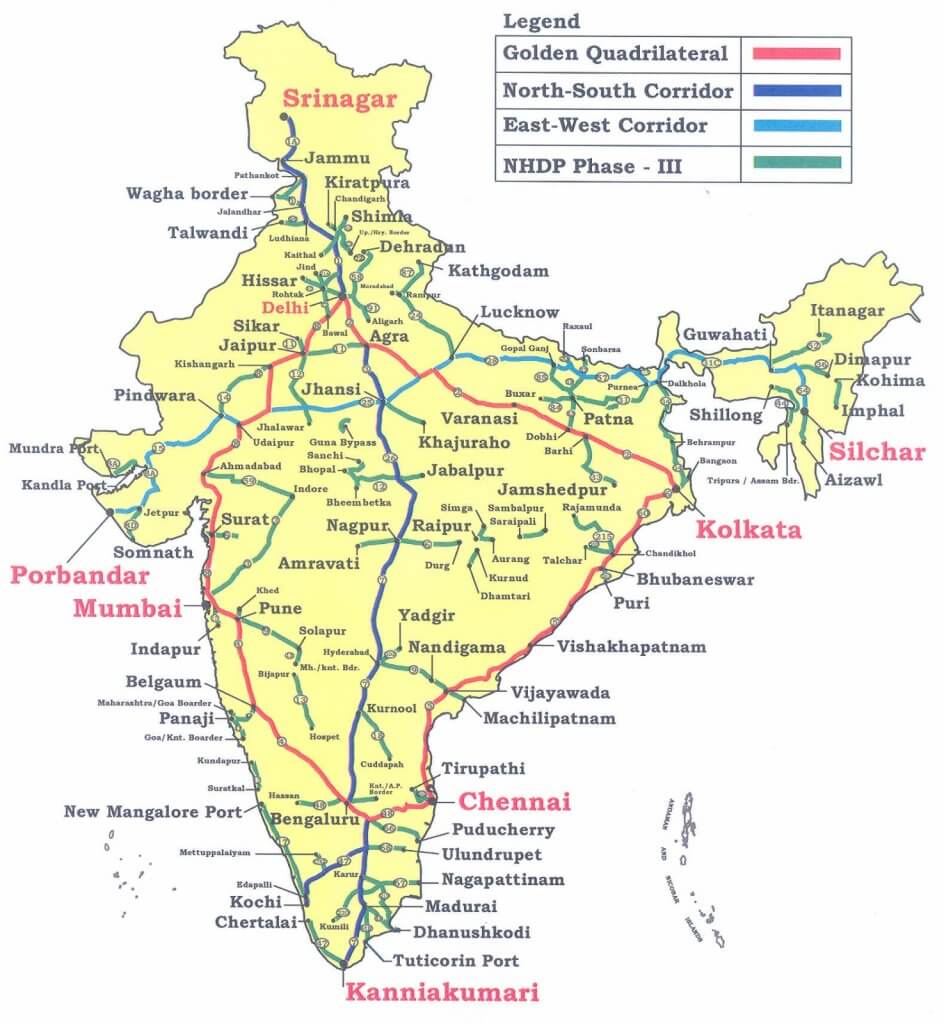
State highways
- These are constructed and maintained by state governments (PWDs). They join the state capitals with district headquarters and other important towns.
- These roads are connected to the National Highways.
- These constitute 4 percent of the total road length in the country.
| Name | Responsibility of | Connects |
| National Highways | Central Government | State capitals |
| State Highways | State Government | State Capital to District HQ |
| District roads | Zila Parishad | District HQ to tehsil and Blocks |
| Village roads | Gram Panchayat | Villages to neighbouring towns |
District roads
- These roads are the connecting link between District Headquarters and the other important nodes in the district.
- They account for 14 percent of the total road length of the country.
Rural roads
- These roads are vital for providing links in the rural areas.
- About 80 percent of the total road length in India are categorized as rural roads.
- There is regional variation in the density of rural roads because these are influenced by the nature of the terrain.
Other Roads – Border roads and international highways
- Other roads include Border Roads and International Highways.
- The Border Road Organisation (BRO) was established in May 1960 for accelerating economic development and strengthening defence preparedness through rapid and coordinated improvement of strategically important roads along the northern and north-eastern boundary of the country.
- It is a premier multifaceted construction agency. It has constructed roads in high altitude mountainous terrain joining Chandigarh with Manali (Himachal Pradesh) and Leh (Ladakh). This road runs at an average altitude of 4,270 metres above the mean sea level.
- Apart from the construction and maintenance of roads in strategically sensitive areas, the BRO also undertakes snow clearance in high altitude areas. The international highways are meant to promote a harmonious relationship with the neighbouring countries by providing effective links with India.
- The distribution of roads is not uniform in the country. The density of roads (length of roads per 100 square km of area) varies from only 12.14 km in Jammu and Kashmir to 517.77 km in Kerala with a national average of 142.68 km in 2011.
- The density of roads is high in most of the northern states and major southern states. It is low in the Himalayan region, north-eastern region, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
Areas factors influence in roadways
- Terrain: Nature of terrain and the level of economic development are the main determinants of the density of roads. Construction of roads is easy and cheaper in the plain areas while it is difficult and costly in hilly and plateau areas
- Climate: Quality of roads is relatively better in plains as compared to roads in high altitude areas, rainy and forested regions.
- Economic development: Areas with a high level of economic development will have more road density as compared to areas with a low level of economic development. E.g. Maharashtra has more road density than Himanchal Pradesh
- Industries: Areas with more industrial concentration will have more road density as compared to areas with low industrial concentration. E.g. Jamshedpur is having more road density than Patratu in Jharkhand.
- Cities and towns: Cities and towns will have more road density than rural areas.
Importance of Roads
- Port connectivity
- Roadways serve for the special links for feeder roads to important railway routes and ports. This is essential for the development of domestic and international trade.
- Road connectivity for about 50 minor ports and road connectivity for 24 Airports serves the purpose of connecting basic infrastructure.
- Rural areas
- All villages will be connected with all-weather roads by the end of the 12th five-year plan. They serve an important purpose in the growth of the rural economy.
- Tribal areas
- Roads in Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) affected districts will be continued and works taken up earlier in the Eleventh Plan will be completed during the 12th five-year plan.
- Special Package for development of roads of around 1000 km length in the Scheduled Areas (under Fifth Schedule) has been taken up under Tribal Sub- Plan.
- JK and North East
- Road Development in the North-East has been boosted by the initiation of the Trans-Arunachal Pradesh Highway Project. The capacities of NHAI and BRO would be further development for this purpose.
- State road projects in the state of J&K are being developed from strategic considerations.
- Reforms in Motor Vehicles Act have been taken up to simplify inter-state movement with simplified procedures. There has been the creation of truck terminals to ease traffic congestion.
Some current initiatives in Roadways
Electronic Toll Collection (ETC)
- A committee was set up under the chairmanship of Shri Nandan Nilekani for reforms in road infrastructure in India.
- Recommendations of the Committee have been accepted and notified by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways for the use of National Highways.
- A Pilot project on ETC was inaugurated in 2012 on a section of NH-5 between Delhi and Parwanoo. The second pilot project will be on the Mumbai and Ahmadabad routes.
NATRIP
- The National Automotive Testing and R&D Infrastructure Project (NATRIP) will be under the Department of Heavy Industry (with representatives from the automobile sector)
- It aims to set up testing, validation, and R&D infrastructure across seven locations in India.
SARDP-NE
- The special accelerated road Development program for North Eastern Region has been rolled out for improving road connectivity between State Capitals and District HQs in North Eastern Region.
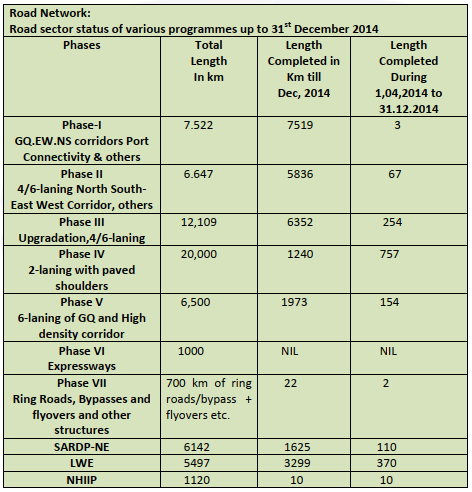
Road Network
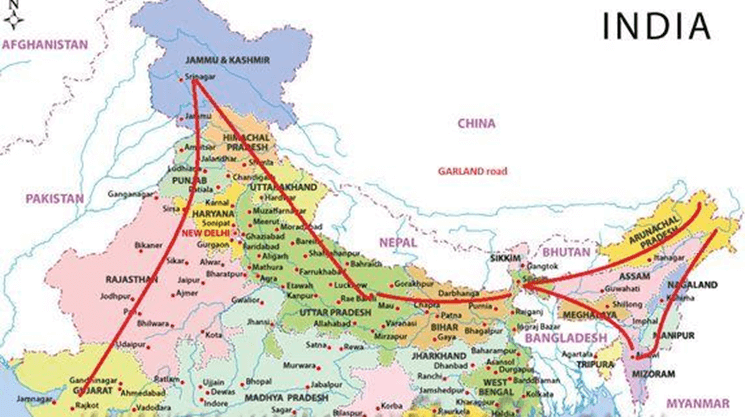
The “Bharat Mala” Project
- The “Bharat Mala” project envisaged across 13 states on a 5300 km stretch – starting from Gujarat & passing through Rajasthan, Punjab, J&K, Uttarakhand, UP, Bihar, Sikkim, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh & ending across the Indo-Myanmar border of Manipur & Mizoram.
- It involves an expenditure of Rs 12000 – 14000 crores during a three-year timeframe.
- The road adorns the country like a Garland & hence the name “Bharat Mala”
- This has a strategic component that includes countering the impressive Chinese network build-up across the border & to provide accessibility to the border hugging regions & improve border trade.
- Costs could increase if Nitin Gadkari’s suggestion of using cement instead of bitumen is accepted.
- Private participation to fund the difference may not fructify – considering their stretched balance sheets & therefore the onus shall be on the govt. to fund the project after accelerating the environmental clearances & land acquisition to complete the stretch within the stated timelines.
- This project in fact, is a late realization & a delayed response to the Chinese seamless road infrastructure on the other side & a dire necessity to prevent a repeat of the ignominy of the Indian defeat to the Chinese in 1962.
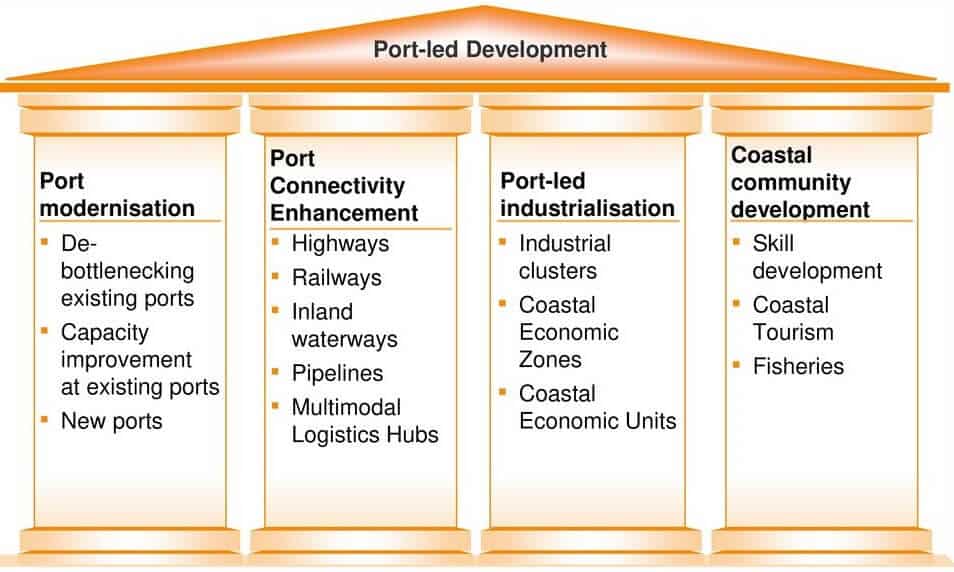
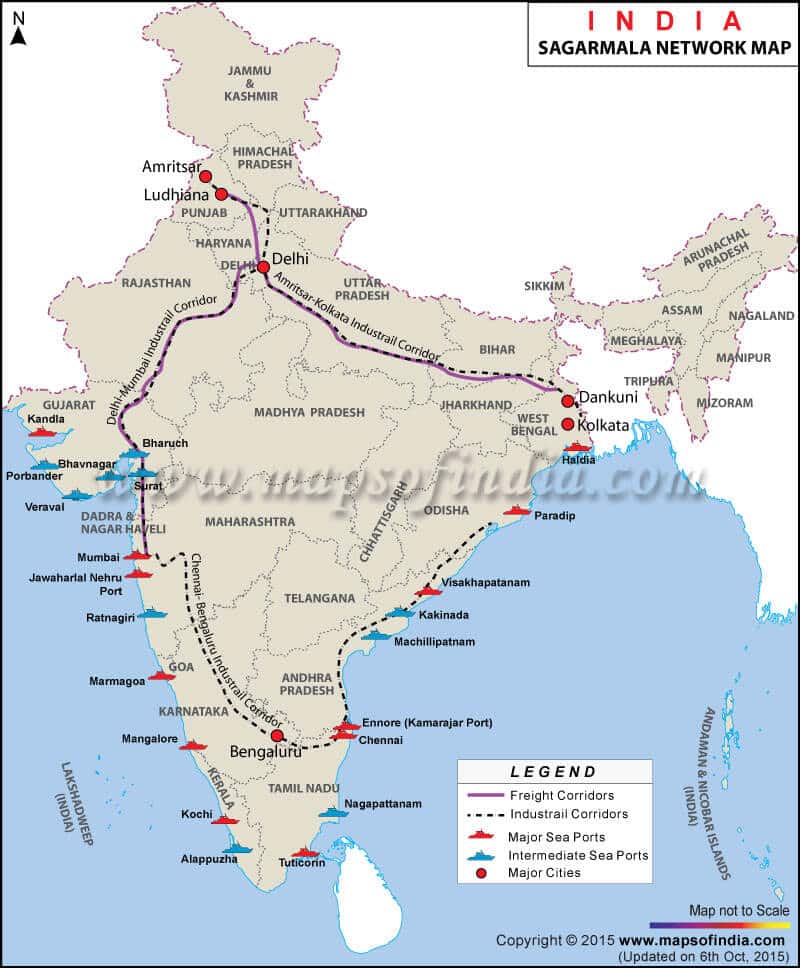
The “Sagar Mala” Project
- The Sagar Mala project, announced with much fanfare, on Aug 15th, 2003, by PM Vajpayee, remained in limbo during the UPA tenure till it was revived again under Modi’s tutelage.
- The new policy envisages a uniform policy framework for major parts – owned by the center & non-major ports owned by the states to develop a holistic policy encompassing the needs of industrialization trade, tourism & transportation,
- It involves the development of 10 CER (Coastal Economic Region) along with India’s vast 7000 Km coastline freight options – rail, land & inland waterways – for the smooth evacuation of cargo to & from ports.
- This plan includes the development of port-based industrial parks, captive industries, and ancillary facilities such as ship repair, shipbuilding, ship-recycling, logistics parks, warehousing, maritime zones/ services, offshore storage, drilling platforms, bunkering, container freight stations, industries requiring significant import of raw materials and industries with large export potential to create more jobs.
- It will also reduce the congestion at ports.

Thank you so much
Please upload rest of the topic as soon as possible
Yeah, Sure Nipurnika.
thankyou so much
Thank u so much….and please, if possible then extend ur notes to other subjects also…..
Sure
Thanks 🙏
I think that these vital information is really required to Crack the any exam ,,,I need geo optional too…I will, try to purchase paid pdf with accurate fact and data with conceptualize too..thanks to lotus arise …keep running it …
thank you brother
thank u so much…
Whoever you are, you are literally a saviour. Thank you so much 😩😩🙏🙏🙏
Tell us if we can contribute in any way.
sir why list of all concept in geography optional removed only option is to buy notes we are adding some infornmation from the free reading content
Please Support this initiative
https://www.instamojo.com/@lotusarise/