An industry is a manufacturing unit which converts raw materials into usable goods. (Goods can be classified as final goods or Capital goods.) This is called the Secondary sector of the economy.
The industry is at the heart of a country’s economy; it includes the manufacturing of goods, extraction of metals, and provision of services. All the products available for use in the market are finished products and are the result of some industries.
These industries are set up based on economic activities known as Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary, and Quinary activities.
Primary Activities
- Directly dependent on environments such as land, water, vegetation, building materials, and minerals.
- Examples are hunting and gathering, pastoral activities, fishing, forestry, agriculture, and mining and quarrying.
- Red-Collar job
Secondary Activities
- Transforming raw materials into valuable/useful products.
- Examples- manufacturing, processing, and construction (infrastructure) industries.
- Blue-Collar job
Tertiary Activities
- It is the sector/activity that provides services to end consumers and to the primary and secondary sectors and is considered the most important sector in the chain.
- Examples are- Transportation, health care, food service, retail sales, advertising, entertainment, tourism, banking, law, etc. are all examples of tertiary-level sectors.
- White-collar jobs.
Quaternary Activities
- Although many economic models divide the economy into only three sectors, others divide it into four or even five sectors. These final two sectors are closely linked with the services of the tertiary sector. In these models, the quaternary sector of the economy consists of intellectual activities often associated with technological innovation. It is sometimes called the knowledge economy.
- Activities associated with this sector include government, culture, libraries, scientific research, education, and information technology. These intellectual services and activities are what drives technological advancement, which can have a huge impact on short- and long-term economic growth.
Quinary Activities
- Some economists further subdivide the quaternary sector into the quinary sector, which includes the highest levels of decision making in a society or economy.
- This sector includes top executives or officials in such fields as government, science, universities, nonprofits, health care, culture, and the media. It may also include police and fire departments, which are public services as opposed to for-profit enterprises.
- Economists sometimes also include domestic activities (duties performed in the home by a family member or dependent) in the quinary sector.
- These activities, such as child care or housekeeping, are typically not measured by monetary amounts but contribute to the economy by providing services for free that would otherwise be paid for.
- Gold collar professions.
Footloose Industries –
Footloose industries can be located in a wide variety of places. They are not dependent on any specific raw material, weight losing, or otherwise. They produce in small quantity and also employ a small labour force.
These are generally not polluting industries. The important factor in their location is accessibility by road network.
Classification of Industries
An industry can be classified on the basis of raw material, size and ownership –
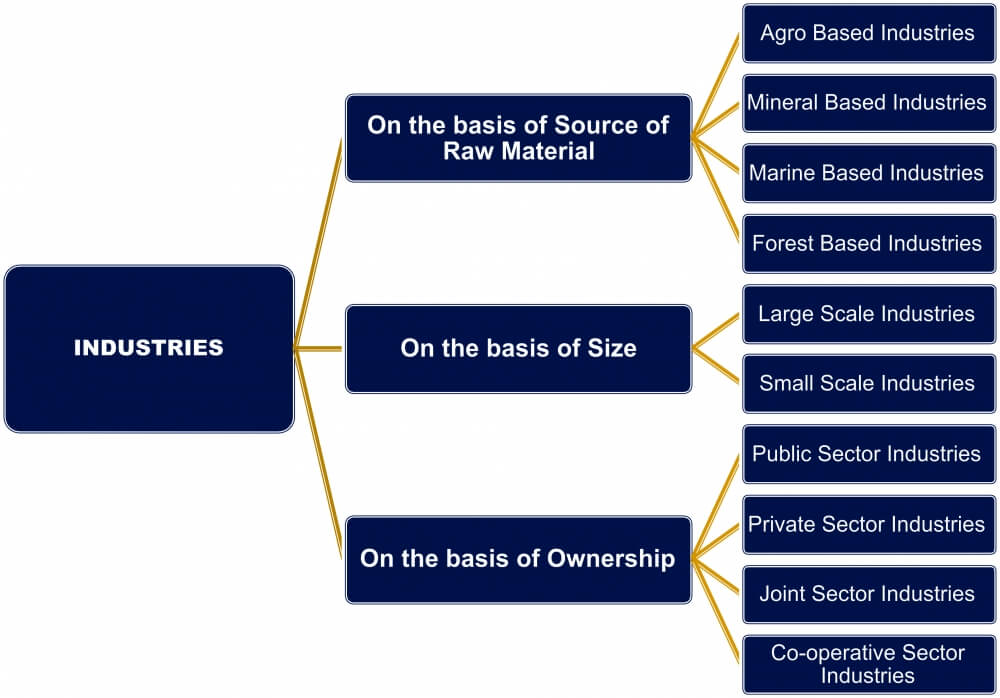
Based on Raw Material
- Any material that we get from our natural surroundings to be used by the industry is called raw material. Plant and animal-based products are used as raw materials in food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile, dairy, and leather products, which are all examples of agro-based industries.
- There is another type of industry that is based on the produce derived from forests. This is known as the forest-based industry and is responsible for producing paper, pharmaceuticals, furniture, equipment, and buildings.
Based in Ownership
- Industries are classified on the basis of ownership as well, i.e. privately owned, cooperative, or state-owned. A privately owned industry means it is owned by an individual or a group like the Tata group. State-owned or public sector means they are owned and operated by the government like Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL).
- A partnership between the state and an individual or a group is called the joint sector like Maharashtra Scooters Limited, which is a partnership between the Government of Maharashtra and the Bajaj Group.
- The cooperative sector was formed to play a major role in the advancement of agriculture and related industries. In this sector, the state facilitates the producers, suppliers, and even workers to own the enterprise like the Amul Dairy.
Based on Size
- Industries are classified as large-scale or small-scale depending, on the amount of capital invested, the number of people employed, and the volume of production.
- A small-scale industry needs a lesser amount of capital and technology inputs. A largescale industry has automated production, and is capital-and manpower-intensive requires heavy investment in plant and machinery.
Factors responsible for location of Industries:
- Availability of Raw Material
- Power Resources
- Availability of water
- Labour
- Transportation
- Availability of Market
- Capital
- Government Policies
According to a geographical theory, the location of an industry is largely influenced by the transportation cost of raw materials and finished products.
If an industry is a weight losing industry, i.e. the net weight of the product is less than the net weight of raw material, then the industry is located near the raw materials. E.g. Iron and steel industry, glass industry etc.
If there is no loss or gain in the net weight of raw material and product, then the industry can be placed anywhere between raw material and market. Other factors become more important. E.g. Cotton, leather, etc.
If an industry is a weight-gaining industry, i.e. the net weight of the final product increases, then the industry is located near the market. E.g. Automobile, heavy machinery, etc.
Industries are usually located in temperate areas, sea ports, and coal mines. When many industries are located close by, the place becomes known as an industrial region.
This is the reason why a government provides incentives like subsidized power, low transport cost, and infrastructure to industries located in the backward regions of the country.
The three steps involved in an industrial cycle are: Input, Processes and Output.
The first step is putting together the inputs, like raw material, labour, cost of land, transport, power, and other infrastructure. The second step is the process, which includes a wide range of activities that convert the raw material into finished goods like ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, and printing. The final step is the finished product or the output that we use.
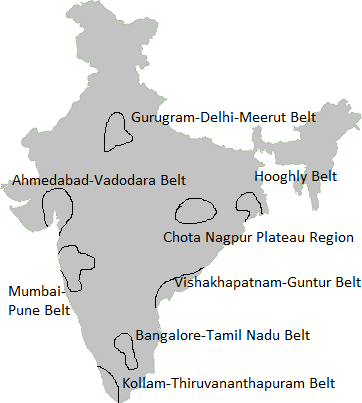
Major Industrial Regions of India-
- Mumbai-Pune Industrial Region
- Hugli Industrial Region.
- Bangalore-Tamil Nadu Industrial Region
- Gujarat Industrial Region
- Chotanagpur Industrial Region
- Vishakhapatnam-Guntur Industrial Region
- Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut Industrial Region
- Kollam-Thiruvananthapuram Industrial Region.
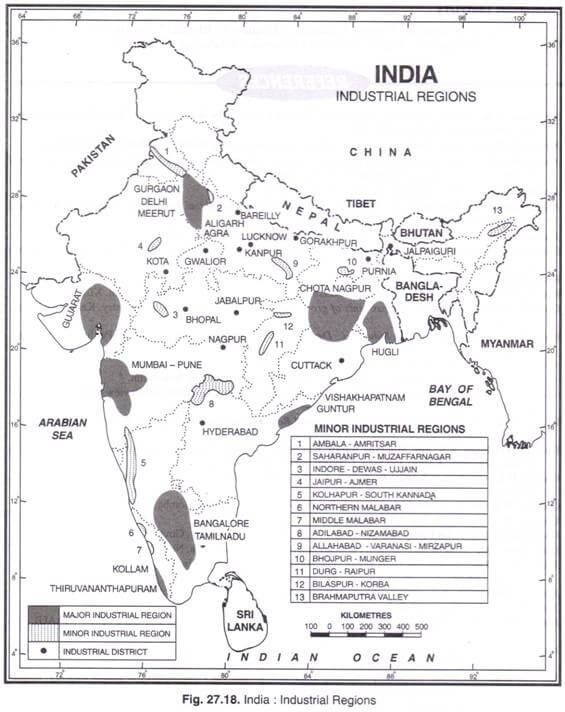
Minor Industrial Regions–
- Ambala-Amritsar in Haryana-Punjab.
- Saharanpur-Muzaffamagar-Bijnaur in Uttar Pradesh.
- Indore-Dewas-Ujjain in Madhya Pradesh.
- Jaipur-Ajmer in Rajasthan.
- Kolhapur-South Kannada in Maharashtra-Karnataka.
- Northern Malabar in Kerala.
- Middle Malabar in Kerala.
- Adilabad-Nizamabad in Andhra Pradesh.
- Allahabad-Varanasi-Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh.
- Bhojpur-Munger in Bihar.
- Durg-Raipur in Chhattisgarh.
- Bilaspur-Korba in Chhattisgarh.
- Brahmaputra Valley in Assam.
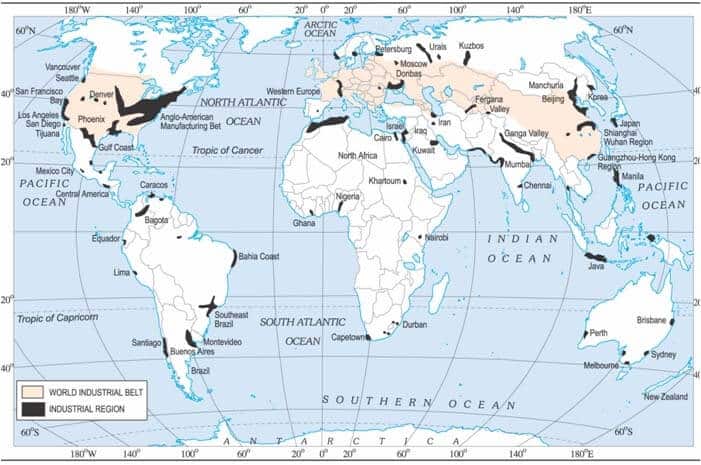
World Industrial Regions –
Industrial Disasters
Industrial workers are sometimes required to work in a dangerous environment. Any lapse in the regular maintenance of technical equipment or irresponsible handling of a hazardous material may lead to accidents. There are some risk reduction measures, which, if followed, can prevent large-scale disasters like:
- Industrial areas should be on the outskirts of a city or town or located far away from residential areas.
- People in the vicinity of the industrial area should be aware of the hazardous materials handled in these industries and their effects on humans in case of an accident.
- Improvement in the fire warning systems, firefighting systems, and pollution dispersion qualities, and limiting toxic storage capacity within these industries will reduce the risk of a large-scale disaster considerably.
Major Industries in India
Cement Industry
India is the second largest producer of cement in the world.
- As of July 2019, the production of cement stood at 28.08 million tonnes.
- The cement production capacity is estimated to touch 550 MT by 2020.
- Of the total capacity, 98 percent lies with the private sector and the rest with the public sector.
- Of the total 210 large cement plants in India, 77 are located in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu.
- Cement production in India increased from 230.49 million tonnes in 2011-12 to 297.56 million tonnes in 2017-18.
Iron and Steel Industry
India was the world’s second-largest steel producer in 2018 second to China. The growth in the Indian steel sector has been driven by the domestic availability of raw materials such as iron ore and cost-effective labour. Consequently, the steel sector has been a major contributor to India’s manufacturing output.
- India was the world’s second-largest steel producer in 2018 second to China. The growth in the Indian steel sector has been driven by the domestic availability of raw materials such as iron ore and cost-effective labour. Consequently, the steel sector has been a major contributor to India’s manufacturing output.
- India’s crude steel production in 2018 was at 106.5 MT, up by 4.9 percent from 101.5 MT in 2017.
- Indian steel industries are classified into three categories such as major producers, main producers, and secondary producers.
- The country is slated to surpass the USA to become the world’s second-largest steel consumer in 2019. In India, as per Indian Steel Association (ISA), steel demand to grow by over 7 percent in both 2019-20 and 2020-21
- In FY19, India produced 131.57 million tonnes (MT) and 106.56 MT of gross finished steel and crude steel, respectively.
- Exports and imports of finished steel stood at 2.45 MT and 3.35 MT, respectively, in FY20P (up to August).
- The Government has launched the National Steel Policy 2017 that aims to increase the per capita steel consumption to 160 kgs by 2030-31.
- National Mineral Development Corporation is expected to invest US$ 1 billion in infrastructure in the next three years to boost iron production.
- As per Economic Survey 2018-19, steel production will touch 128.6 million tonnes by 2021.
Textiles Industry
India’s textiles sector is one of the oldest industries in the Indian economy dating back several centuries.
India’s overall textile exports during FY 2017-18 stood at US$ 39.2 billion in FY18 and is expected to increase to US$ 82.00 billion by 2021 from US$ 31.65 billion in FY19.
- The Indian textiles industry, currently estimated at around US$ 150 billion, is expected to reach US$ 250 billion by 2019.
- India’s textiles industry contributed seven percent of the industry output (in value terms) of India in 2017-18.
- It contributed two percent to the GDP of India and employs more than 45 million people in 2017-18.
- The sector contributed 15 percent to the export earnings of India in 2017-18.
- The Indian government has come up with a number of export promotion policies for the textiles sector. It has also allowed 100 percent FDI in the Indian textiles sector under the automatic route.
- India is the world’s second-largest exporter of textiles and clothing.
Gems & Jewellery Industry
India’s gems & jewellery market size is expected to reach US$ 100 billion by 2025.
- The Gems and Jewellery sector play a significant role in the Indian economy, contributing around 7 percent of the country’s GDP and 15 percent to India’s total merchandise exports.
- It also employs over 4.64 million workers and is expected to employ 8.23 million by 2022.
- One of the fastest-growing sectors, it is extremely export oriented and labour intensive.
- The Indian government presently allows 100 percent Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the sector through the automatic route.
- India’s gems and jewellry sector are one of the largest in the world contributing 29 percent to global jewellery consumption.
- India is the world’s largest center for cut and polished diamonds in the world and exports 75 percent of the world’s polished diamonds. Today, 14 out of 15 diamonds sold in the world are either polished or cut in India.
Sugar Industry
The sugarcane is the raw material for this industry. Maharashtra is an important producer of sugarcane. Here the cultivation of sugarcane and the sugar industry are under the co-operative sector. India is one of the major sugar producers of the world.
Oil refining
India imports crude oil from a number of West Asian countries. In order to refine crude oil, several oil refineries have been set up in different parts of the country. The oldest refinery is Digboi in Assam. Others are at Noonmati, Haldia, Bongaigaon, Barauni, Mathura, Vishakhapatnam, Chennai, Cochin, Mumbai, and Koyali (Vadodara).
Petrochemical Industry
Many items are derived from crude petroleum, which provides raw materials for many new industries; hence, these are collectively known as petrochemical industries.
Petrochemical industries are categorized as polymers, synthetic fibers, elastomers, and surfactant intermediate industries.
Mumbai is the hub of the petrochemical industry.
Three organizations, which are working in the petrochemical sector under the administrative control of the Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals are −
- The Indian Petrochemical Corporation Limited (IPCL);
- The Petrofils Cooperative Limited (PCL);
- The Central Institute of Plastic Engineering and Technology (CIPET).
- The National Organic Chemicals Industries Limited (NOCIL), established as a private sector in 1961.
Information Technology (IT)
The information technology industry deals in the storage, processing, and distribution of information. Today, this industry has become global. This is due to a series of technological, political, and socio-economic events. The main factors guiding the location of these industries are resource availability, cost, and infrastructure. The major hubs of the IT industry are Silicon Valley, California, and Bangalore, India.
Cottage Industries
A cottage industry is a small-scale, decentralized manufacturing business often operated out of a home rather than a purpose-built facility. Cottage industries are defined by the amount of investment required to start, as well as the number of people employed. hey often focus on the production of labor-intensive goods but face a significant disadvantage when competing with factory-based manufacturers that mass-produce goods.
Cottage Industries –
- Provide jobs to millions of people
- Check migration of rural people to urban areas
- Can be started with low investment
- Helps to earn additional income for rural people
- Use local raw material → Optimum utilization of national resources
- Earn a lot of foreign exchange for the country
- Generate seasonal as well as perennial employment for labour
- Play a significant role in our national economy.
Tea plantation Industry
Labour availability
- Weeding, manure, pruning and plucking → tedious job + need skill + patience
- Cheap female labour force is essential (same factor like sericulture)
- Since tea has to be grown in hill slopes, mechanization not possible
- Even while drying, rolling, fermentation, grading and packaging of tea, skilled manpower needed
- Therefore, tea plantation is done near areas with high population density
Raw material
- Tea leaves to tea, involves considerable weight loss
- Hence tea processing is done in the estate/plantation itself
- Further blending/repacking could be done at break of the bulk location
- For e.g. port cities like London
- [Break of the bulk] → Place where mode of transportation changes e.g. waterway to railways
Climate
- Frost damages the leaves hence tea is not grown beyond Northern China / Honshu
- Very long winter retards plant growth hence decreases yield
Topography
- Doesn’t like stagnant water
- Hence, has to be grown on highland or hill slopes
- for e.g. hills of Darjeeling, Jalpaiguri (West Bengal) & Nilgiri (Tamil Nadu)
Coffee Plantation → Karnataka + Kerala (India)
| Region | The Western Ghats + Nilgiri Hills region Suited for both Tea + coffee |
| Soil | Red soil → best suited Hill areas of → No stagnant water |
| Temp | Coffee is grown on the Northern and Eastern slopes of the Ghat (Because coffee hates direct sunlight) Moderating effect of Lakshadweep sea Temp stays ~25 throughout the year |
| Transport | Via Kochi port |
| Market | Kochi port to (mostly) Italy Local demand in South India |
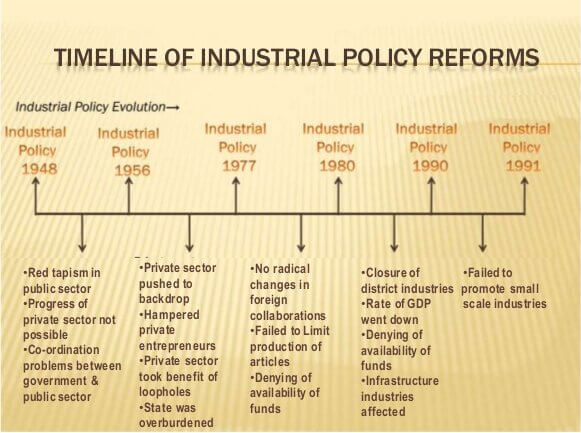
Industrial Policy
- The new Industrial Policy was implemented in 1991.
- The new industrial policy has three main dimensions − liberalization, privatization, and globalization.
- Within this new industrial policy, measures initiated are − abolition of industrial licensing; free entry to foreign technology; foreign investment policy; access to capital market; open trade; abolition of phased manufacturing program; and liberalized industrial location program.
- Globalization means integrating the economy of the country with the world economy.

Too much helpful, Thank for your thankless efforts.
Thank u from the depth of my heart ….really thanku thank u sooo much🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻🙏🏻 may god bless u
Most Welcome, Keep reading.
Good👍👍👍👍👍👍
Amazingly put together!
Thank you so much sir ❣️❣️❣️❣️
Thanks a Lot .Sir