Islands of India (Indian Islands)
- India has a total of 1,382 off-shore identified islands.
- The major island groups of India are the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands were formed due to a collision between the Indian Plate and Burma Minor Plate [part of Eurasian Plate][Similar to the formation of Himalayas].
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a southward extension of the Arakan Yoma range [Myanmar][Arakan Yoma in itself is an extension of Purvanchal Hills].
- Lakshadweep Islands are coral islands. These islands are a part of Reunion Hotspot volcanism.
- Other than these two groups there are islands in the Indo-Gangetic Delta [they are more a part of delta than islands] and between India and Sri Lanka [Remnants of Adams Bridge or Rama’s Bridge or Rama Setu; formed due to submergence].
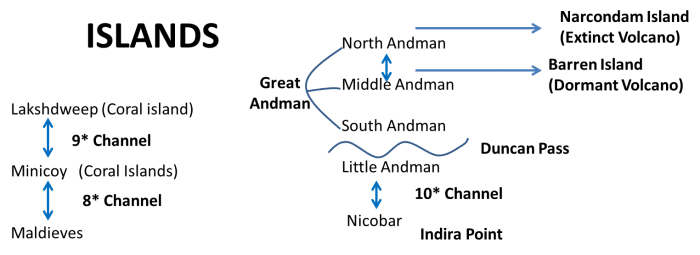
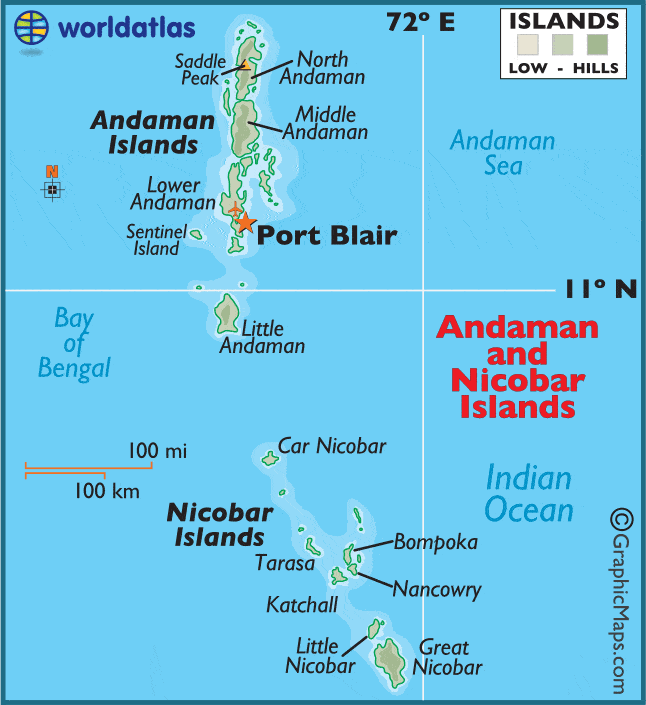
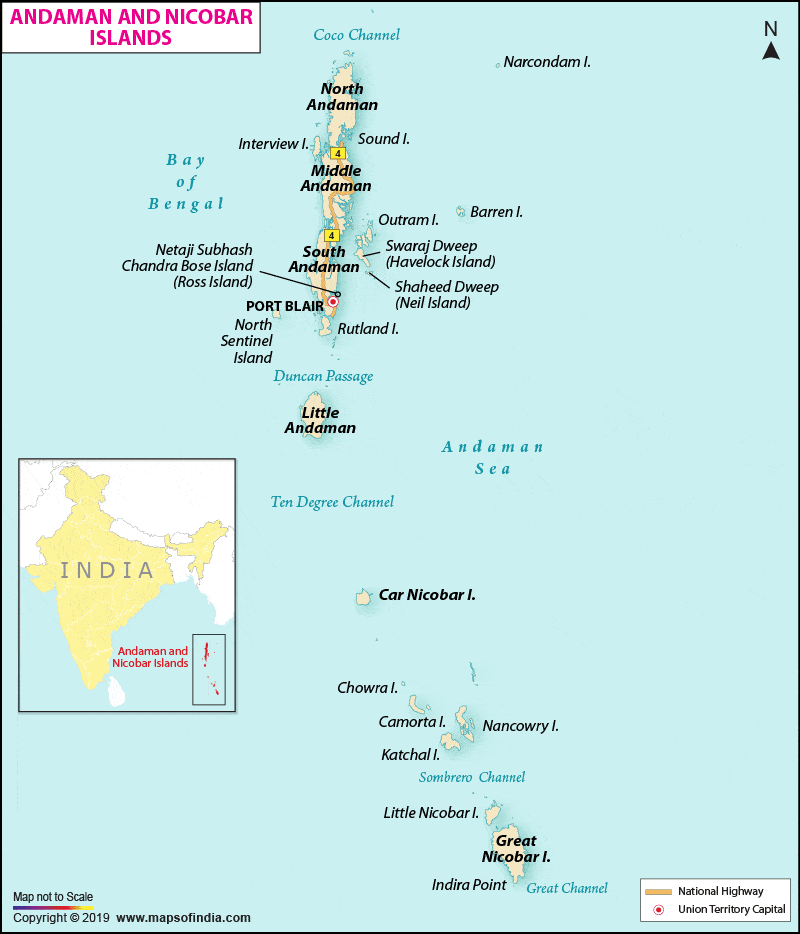
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands situated in the Bay of Bengal, run like a narrow chain in the north-south direction extending between 6° 45′ N to 13° 45′ N.
- This archipelago is composed of around 265 big and small islands [203 Andaman islands + 62 Nicobar Islands]
- The Andaman and Nicobar islands extend from 6° 45′ N to 13° 45′ N and from 92° 10′ E to 94° 15′ E for a distance of about 590 km.
- The Andaman islands are divided into three main islands i.e. North, Middle, and South.
- Duncan passage separates Little Andaman from South Andaman.
- The Great Andaman group of islands in the north is separated by the Ten Degree Channel from the Nicobar group in the south.
- The Grand Channel is between the Great Nicobar islands and the Sumatra islands of Indonesia.
- The Coco Strait is between the North Andaman islands and the Coco Islands of Myanmar.
- Port Blair, the capital of Andaman Nicobar Islands lies in the South Andaman.
- Among the Nicobar islands, the Great Nicobar is the largest. It is the southernmost island and is very close to Sumatra island of Indonesia. The Car Nicobar is the northernmost.
- Most of these islands are made of tertiary sandstone, limestone, and shale resting on basic and ultrabasic volcanoes [Similar to the Himalayas].
- The BARREN and NARCONDAM Islands, north of Port Blair, are volcanic islands [these are the only active volcanoes in India][There are no active volcanoes in mainland India].
- Some of the islands are fringed with coral reefs. Many of them are covered with thick forests. Most of the islands are mountainous.
- Saddle peak (737 m) in North Andaman is the highest peak.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Island has a tropical marine climate influenced by the seasonal flow of monsoon winds.
- The region is under dense tropical rain forests. The coastal regions have mangrove forests.
- Coconut fruit is the staple food of the people. Fisheries, piggery is also followed.
- The Islands are also famous for the largest and rarest species of crab, the Giant Robber Crab. It can climb the coconut trees and break the hard shell of the fruit.
- Many islands are uninhabited. The inhabited islands are also sparsely populated.
- The entire region is vulnerable to earthquakes as it is in the major earthquake zone.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are also known as the Emerald Islands.
- Andaman islands are home to the only known paleolithic people the Sentinelese. The Sentinelese are one of the last humans on earth who remain untouched by modern civilization.
- State Animal of Andaman is the dugong (sea mammal) really endemic to Indo-Pacific seacoast areas, especially to the Andaman Islands. [Sea-cow is a herbivorous marine mammal].
Ritchie’s Archipelago
- Ritchie’s Archipelago is a cluster of smaller islands which lie 20 km east of Great Andaman, the main island group of the Andaman Islands.
- Neil Island and Havelock Island is in Ritchie’s Archipelago.
- Ross Island was renamed Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose Dweep, Neil Island as Shaheed Dweep, and the Havelock Island as Swaraj Dweep.
- Ross Island is in the South Andaman region and 3km east of Port Blair.
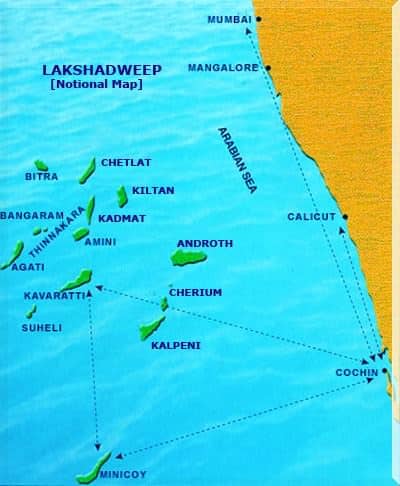
Lakshadweep Islands
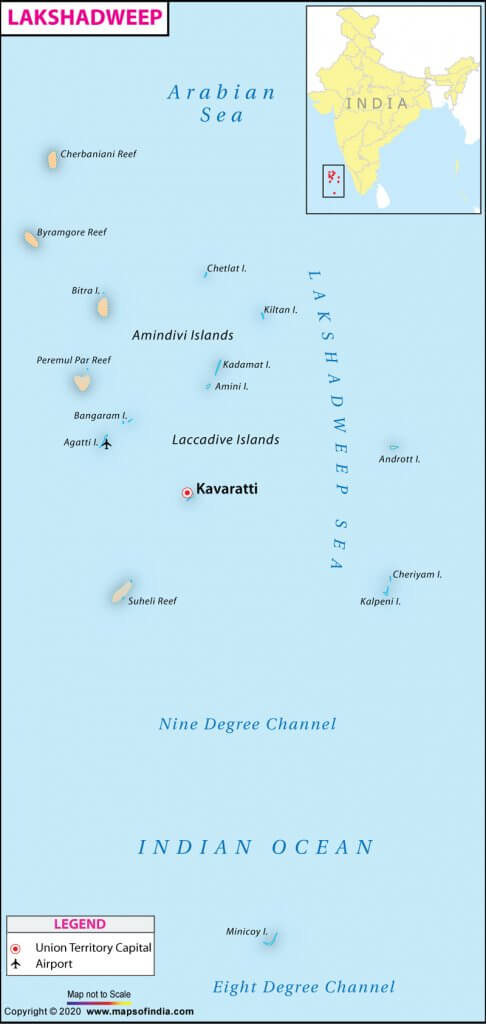
- Lakshadweep Islands situated in the Arabian Sea is a group of 36 islands having an area of 32 square kilometers and extending between 8 N and 12 N latitude.
- The main islands under the Lakshadweep Islands group are:
- Kavaratti
- Agatti
- Minicoy
- Amini
- These islands were earlier known as Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands.
- The name Lakshadweep was adopted on 1 November 1973
- These islands are separated from one another by very narrow straits.
- The Lakshadweep Islands group is a Union Territory administered by the President through a Lt. Governor.
- It is the smallest Union Territory of India.
- Kavaratti is the administrative capital of the Lakshadweep Islands. It is also the principal town of the Union Territory.
- It is a uni-district Union Territory and is comprised of 12 atolls, three reefs, five submerged banks, and ten inhabited islands.
- The name Lakshadweep in Malayalam and Sanskrit means ‘a hundred thousand islands‘.
- The Lakshadweep Islands are located at a distance of 280 km to 480 km off the Kerala coast.
- These islands are a part of Reunion Hotspot volcanism.
- The entire Lakshadweep island group is made up of coral deposits.
- Fishing is the main occupation on which livelihoods of many people depend.
- The Lakshadweep islands have storm beaches consisting of unconsolidated pebbles, shingles, cobbles, and boulders.
- Minicoy Island, located to the south of the nine-degree channel is the largest island among the Lakshadweep group.
- 8 Degree Channel ( 8 degrees north latitude) separates islands of Minicoy and Maldives.
- 9 Degree Channel ( 9 degrees north latitude) separates the island of Minicoy from the main Lakshadweep archipelago.
- In the Lakshadweep region, there is an absence of forests.
- Pitti Island is an important breeding place for sea turtles and for a number of pelagic birds such as the brown noddy, lesser crested tern, and greater crested tern. The Pitti island has been declared a bird sanctuary.
- Most of the islands have low elevation and do not rise more than five meters above sea level (Extremely Vulnerable to sea-level change).
- Their topography is flat and relief features such as hills, streams, valleys, etc. are absent.
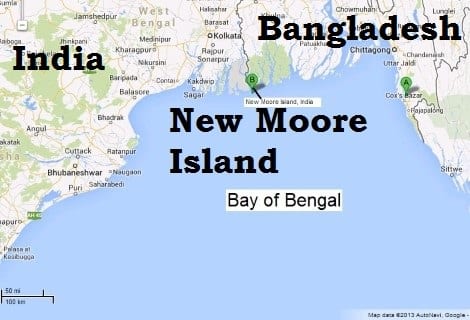
New Moore Island
- New Moore, also known as South Talpatti and Purbasha Island is a small uninhabited offshore sandbar landform (Marine Landforms) in the Bay of Bengal, off the coast of the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta region.
- It emerged in the Bay of Bengal in the aftermath of the Bhola cyclone in November 1970. It keeps on emerging and disappearing.
- Although the island was uninhabited and there were no permanent settlements or stations located on it, both India and Bangladesh claimed sovereignty over it because of speculation over the existence of oil and natural gas in the region.
- The issue of sovereignty was also a part of the larger dispute over the Radcliffe Award methodology of settling the maritime boundary between the two nations.
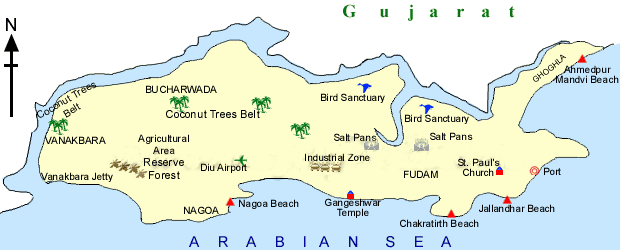
Diu Island
- It is located off the south coast of Kathiawar. Diu is an offshore island on the western coast, off the Gulf of Cambay, bordering the Junagarh district. It is separated from the Gujarat Coast by a tidal creek.
- The coast has limestone cliffs, rocky coves, and sandy beaches, the best of which are at Nagoa.
- Diu Island is famous for the historical Diu fort and beautiful beaches. A massive fort built by the Portuguese dominates the skyline.
- Nagoa beach is the most famous in Diu. Another beautiful beach is Ghoghla beach.
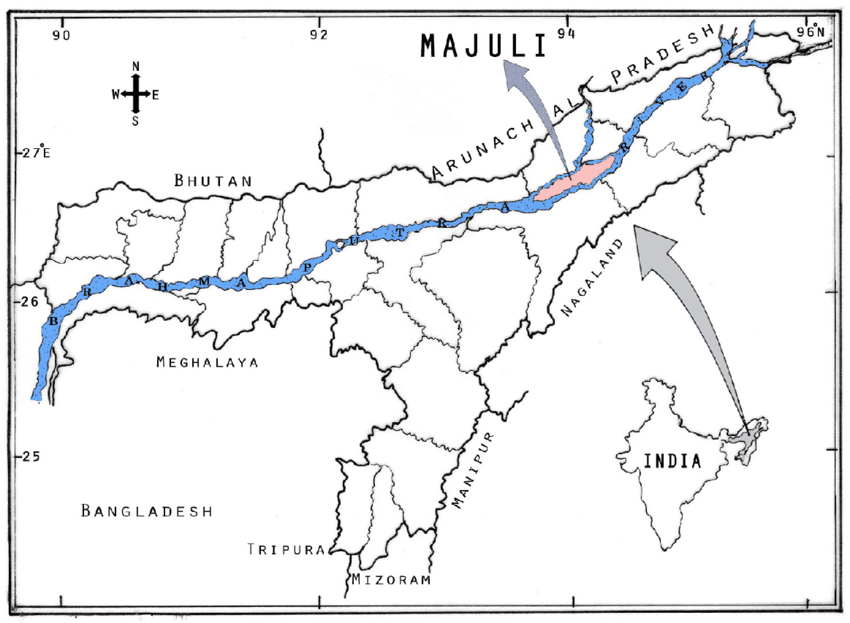
Mājuli Island
- Mājuli is a large river island in the Brahmaputra river, in Assam.
- It was formed due to course changes by the river Brahmaputra and its tributaries, mainly the Lohit.
- It was originally a piece of land between the Brahmaputra River (north) and Burhidihing river (south). Due to earthquakes back in medieval times, the change of the Brahmaputra river course caused the formation of the Majuli Island.
- Mājuli is also the abode of the Assamese neo-Vaisnavite culture.
- A wetland, Mājuli is a rich biodiversity spot and is home to many rare and endangered avifauna species including migratory birds that arrive in the winter season. Among the birds seen here are: the Greater Adjutant Stork, Pelican, Siberian Crane, and the Whistling Teal.
Islands Off Mumbai: Butcher Island
- Butcher Island (Jawahar Dweep) is an island off the coast of Mumbai.
- It has an oil terminal used by the port authorities to offload it from oil tankers.
- The crude oil is stored in oil containers on the island. From there they are piped to Wadala, in Mumbai where they are refined.
- This keeps the city relatively safe from a mishap. It is a restricted area and most of the island is covered with dense vegetation.
- A hillock rises from the center of the island. It is located 8.25 kilometers (5.13 mi) from the Gateway of India.
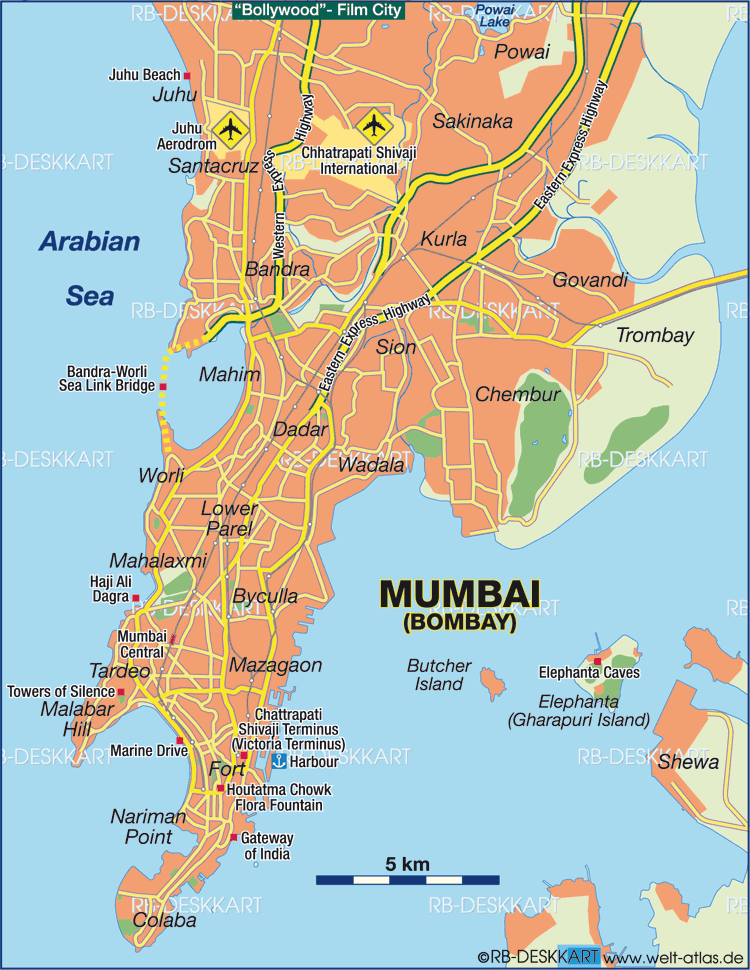
Islands Off Mumbai: Elephanta Island
- Elephanta Island or Gharapuri Island is in Mumbai Harbour. It is home to the Elephanta Caves that have been carved out of the rock.

Islands Off Mumbai: Oyster Rock
- Oyster Rock is an island in the Mumbai harbour, Mumbai, India. It is fortified, and owned by the Indian Navy.
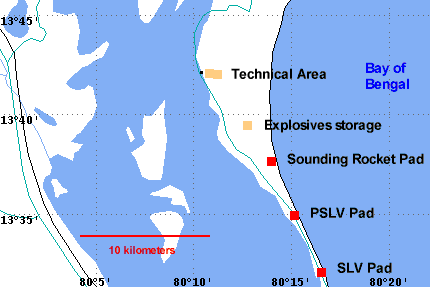
Islands off andhra pradesh: Sri Harikota
- Sriharikota is a barrier island off the coast of Andhra Pradesh.
- It houses India’s only satellite launch center in the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (also known as SHAR) and is used by the Indian Space Research Organization to launch satellites using multi-stage rockets such as the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle.
- Sriharikota separates the Pulicat Lake from the Bay of Bengal and is home to the town of Pulicat.
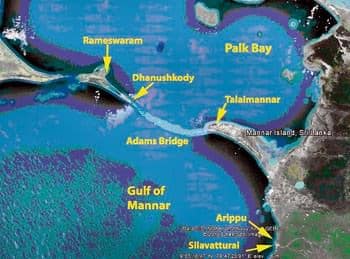
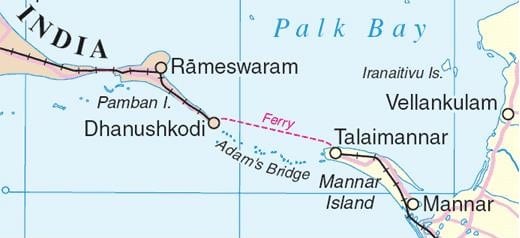
Islands Off Tamil Nadu: Pamban Island
- It is located between India and Sri Lanka in the Gulf of Mannar and in the Ramanathapuram district of the state of Tamil Nadu.
- It is also known as Rameswaram Island.
- Most of Pamban Island is covered with white sand.
- The chain formed by Pamban Island, the shoals of Adam’s Bridge, and Mannar Island of Sri Lanka separate Palk Bay and the Palk Strait in the northeast from the Gulf of Mannar in the southwest.
- Pamban Island extends for around 30 kilometers in width from the township of Pamban in the west to the remains of Dhanushkodi towards the south-east.
Other Islands of India
- Abdul Kalam Island/ Wheeler Island- Abdul Kalam Island is located off the Odisha coast. It is India’s most advanced missile testing site. The island was earlier named after an English commandant Lieutenant Wheeler.
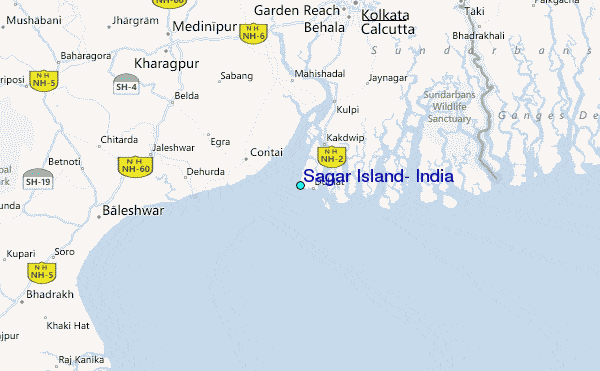
- Sagar Island-It is located in the Ganga delta in the Bay of Bengal. It is a large island. It is also an important place of Hindu pilgrimage.
- Halliday Island-It is located in the state of West Bengal and is part of the Sunderbans region. It is located in the river Malta. It is also designated as a wildlife sanctuary.
- Phumdis/Floating Islands-They is located in the state of Manipur. It is part of the Keibul Lamjao National Park. It is famous for the Eld’s deer/ Sangai.
- Munroe Island – is an inland island group located at the confluence of Ashtamudi Lake and the Kallada River, in Kollam district, Kerala, South India. It is a group of eight small islets comprising a total area of about 13.4 km².
Offshore Islands
- There are numerous islands in the delta region of Ganga and in the Gulf of Mannar.
- Among the Western coast islands Piram, Bhaisala (Kathiawar}, Diu, Vaida, Nora, Pirtan, Karunbhar (Kachchh coast), Khadiahet, Aliabet (Narmada·Tapi mouths), Butchers, Elephanta, Karanja, Cross (near Mumbai), Bhatkal, Pegioncock, St. Mary {Mangalore coast), Vypin near Kochi, Pamban, Crocodile, Adunda (Gulf of Mannar), Sri Harikota (mouth of Pulicat Lake, Pairkud (mouth of Chilka Lake), Short, Wheeler (Mahanadi·Brahmani mouth), and New Moore, and Ganga-Sagar and Sagar (Ganga Delta).
- Many of these islands are uninhabited and administered by the adjacent states.
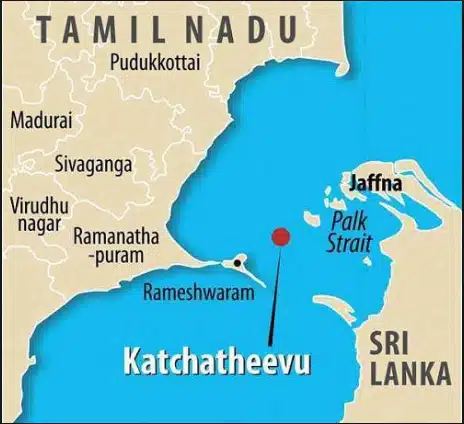
Katchatheevu Island
- It is an uninhabited off-shore island in the Palk Strait originally owned by a king of Ramnad (present-day Ramanathapuram, Tamil Nadu).
- The island is used by fishermen to dry their nets.
- During the British rule, it was administered jointly by India and Sri Lanka.
- In the early 20th century, Sri Lanka claimed territorial ownership over the islet, so in 1974 Indiaceded the island to Sri Lanka, through a joint agreement.
- Two years later through another accord, India further gave up its fishing rights in the region.

Amazing info…thanx so much
I want to buy notes but first I would like to see some part of the notes if you can then please send me.thanku
Please contact on Telegram/Whatsapp.
Thank you so much sir ❤️