In this article, You will know Major Grasslands of the World for UPSC Geography.
What are Grasslands?
A grassland ecosystem is a dry area of land dominated by grasses. Huge trees and shrubs are very rarely found in these regions, which is mainly because of the climatic conditions and other environmental factors, which do not withstand the plant’s requirements.
Grasslands are also called transitional landscape. In a grassland ecosystem, the vegetation is dominated by herbs and grass. These ecosystems are mainly found in regions, where there is a scarcity of water and not enough and regular rainfall to support the growth of plants and forests. The grassland ecosystem lies between the deserts and the forest ecosystems.
Savanna grasslands and temperate grasslands are some examples of grassland ecosystems. There are many other types of grassland around the world, which go by many names. Grasslands of South America are known as pampas and central Eurasian grasslands are referred to as steppes and so on.
Types of Grasslands
Grasslands are subdivided into two types, namely:
Tropical Grasslands
Tropical grasslands have dry and wet seasons that remain warm all the time. These regions are warm throughout the year, followed by dry and wet seasons. Tropical Grasslands are the ones which receive 50 cm to 130 cm rain.
Also, the tropical grasslands contain quite short plants which makes it an excellent hunting ground. For instance, the African savanna is one of the tropical grasslands.
In conclusion, the tropical grassland is a home for elephants, giraffes, lions, cheetahs, zebras, and other spectacular species.
Tropical Grasslands are:
- East Africa- Savanna
- Brazil- Campos
- Venezuela- Llanos
Temperate Grasslands
These grasslands are similar to tropical grasslands, except for the climatic conditions. They have cold winters and warm summers with 25 cm and 75 cm. of annual rainfall. Shrublands are the best example of temperate grasslands.
Moreover, these grasslands suffer extreme climates. In the cold season, the temperature can reach up Flooded Grasslands to 0 degrees Fahrenheit. While in the summer season it reaches up to 90 degrees in some areas. The precipitation in these grasslands is mostly in the form of dew and snow.
For instance, some vegetation that grows here are, cacti, sagebrush, perennial grasses, buffalo grass clovers, and wild indigos, etc.
Temperate Grasslands are:
- Argentina- Pampas
- America- Prairie
- South Africa- Veld
- Asia- Steppe
- Australia- Down

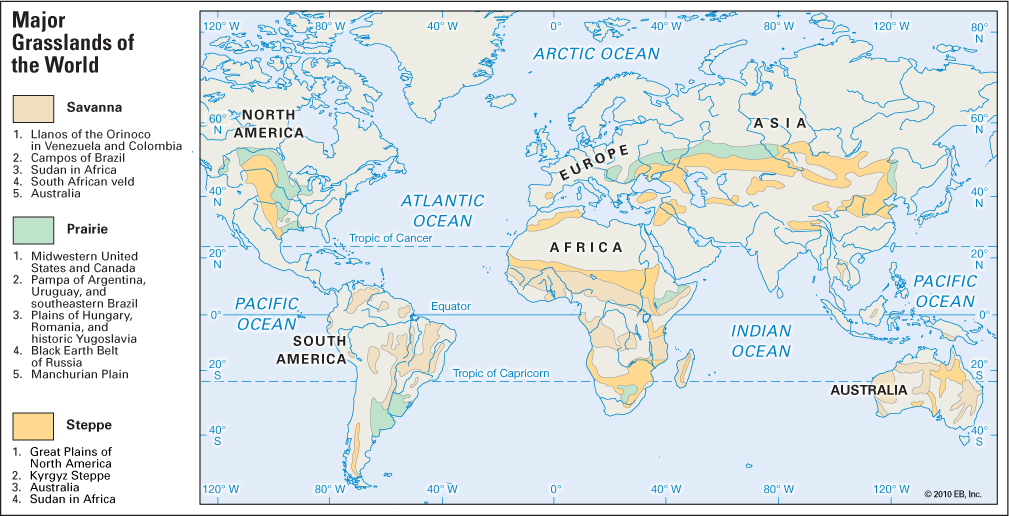
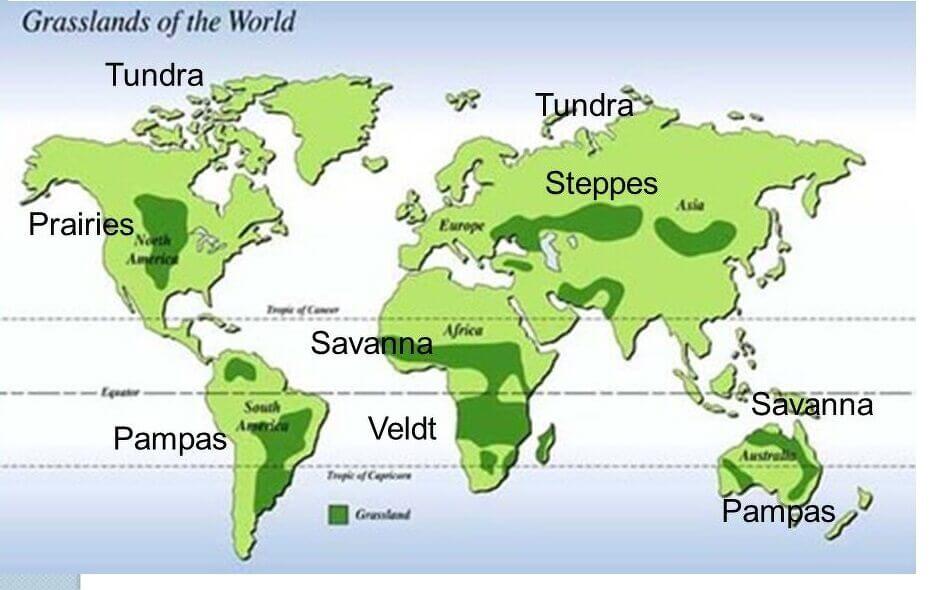
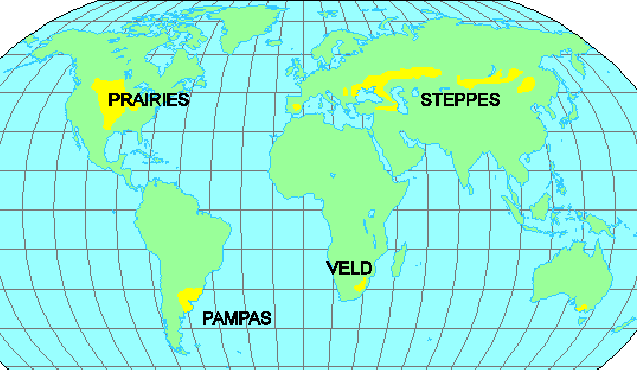
Grasslands of the World
| Grasslands | Region |
| Steppe | Europe and North Asia |
| Pustaz | Hungary |
| Prairies | USA |
| Pampas | Argentina |
| Veld | South Africa |
| Downs | Australia |
| Canterbury | New Zealand |
| Savannah | Africa and Australia |
| Taiga | Europe and Asia |
| Grassland | Major Economic Activity |
| Prairies | Wheat Granaries Extensive Ranching |
| Pustaz | Rich black soil Abundant wheat production Sugar from Sugar beet [Beta vulgaris, is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose] Countries like Hungary, Ukraine, Romania, etc. |
| Pampas | Alfalfa: nutrient-rich grass. Ranching, cattle rearing; Dairy products Extensive wheat-producing region Economy depends on wheat and beef export |
| Downs and Canterbury | Sheep and Cattle rearing, Merino sheep: wool production |
| Veldts | Maize farms Sheep and Cattle rearing |

thank you so much for your great efforts. it was very difficult for me to prepare geography as a optional notes but when I saw your website then everything become clear for me. Thank you so much once again and keep it up
Sure, Most Welcome
Thank you so much for this notes.
Thanks, Sir, Appreciated
Most Welcome
Well explained, thanks a lot.
its a nector water for us ,god bless u all
Thanks……. It’s really helpful for us….
Thanks for this note. It is very nicely explained and helpful.
very important important information
Loving the way, this is explained.
thanks for the notes
Helped me alot.
thank you very very much sir
very very useful
Thanks
A obvious good thing for us, thanks a lot 🙂
Thankyou so much god bless you
Very well explained. Thank you
Hi! Thank you for your effort. I am a little confused about the types of grasslands. Are steppe, pampas, prairie and veld are all same type but have names specific to the region they are found? Are different names come from different languages? or Do they have distinctive features and be considered as different types of temperate grasslands? Thank you very much in advance.
Highly appreciated. Very nicely described.
thank you! that was about of help
thx
Kya ye gs 1 ke liye hai
Tqu for it, it’s very useful and easy
Simple and Lucid manner 😀
Thanks 👍
Keep it up..