In this article, You will read Cross Border terrorism in India – for UPSC IAS.
The term ‘cross-border’ implies a movement or an activity across a border between the two countries. Cross-Border Terrorism is a form in which the soil of one country is used to create terror in bordering countries. As a grey zone conflict, it is an undeclared war and considered to be the highest form of strategy to bleed a nation for a prolonged period by small efforts.
Cross Border terrorism
- A common definition of terrorism is the systematic use or threatened use of violence to intimidate a population or government for political, religious, or ideological goals.
- India is a physiographical diverse country and is a part of Indian sub-continent. India is sharing its border with seven international countries. Therefore, providing the porous borders.
- The different types of administration, radical and linguistic diversity exists simultaneously and diverse religion create different types of ideology, customs and trade which was first studied by cultural geographers like Carl O Snover.
- Cross border terrorism is a new approach identified by political geographers due to identification of international borders and frontiers.
- When the soil of one country is used to create terror or engage in terrorism against its neighbouring countries across the border for political, religious, or ideological goals, then it is termed as Cross border terrorism.
- In Cross border terrorism a person of ethnic group illegally enters without the permission of government, with the aim of violence and to create the instability in geographical region.
- According to geographers centripetal forces are responsible for the creation of borders, which is necessary for maintaining, identity and sovereignty.
- Geographers identified various reasons responsible for cross border terrorism like strategic location of the place, regional aspiration, radicalism, or climate or economic geology of a place.
- For e.g. the cross border terrorism in North East India is guided by the demand of separation especially by Nagaland people. The cross border terrorism from Pakistan and Bangladesh has radical thinking while the intrusion from Nepal is guided by Maoist ideology.
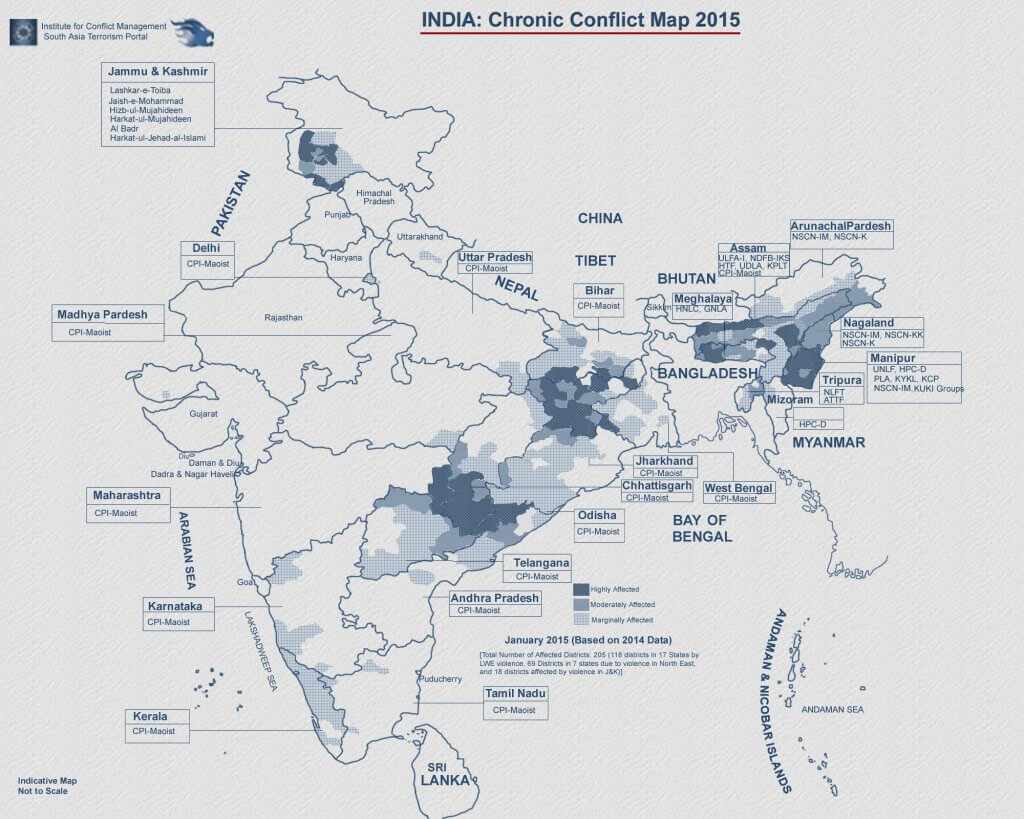
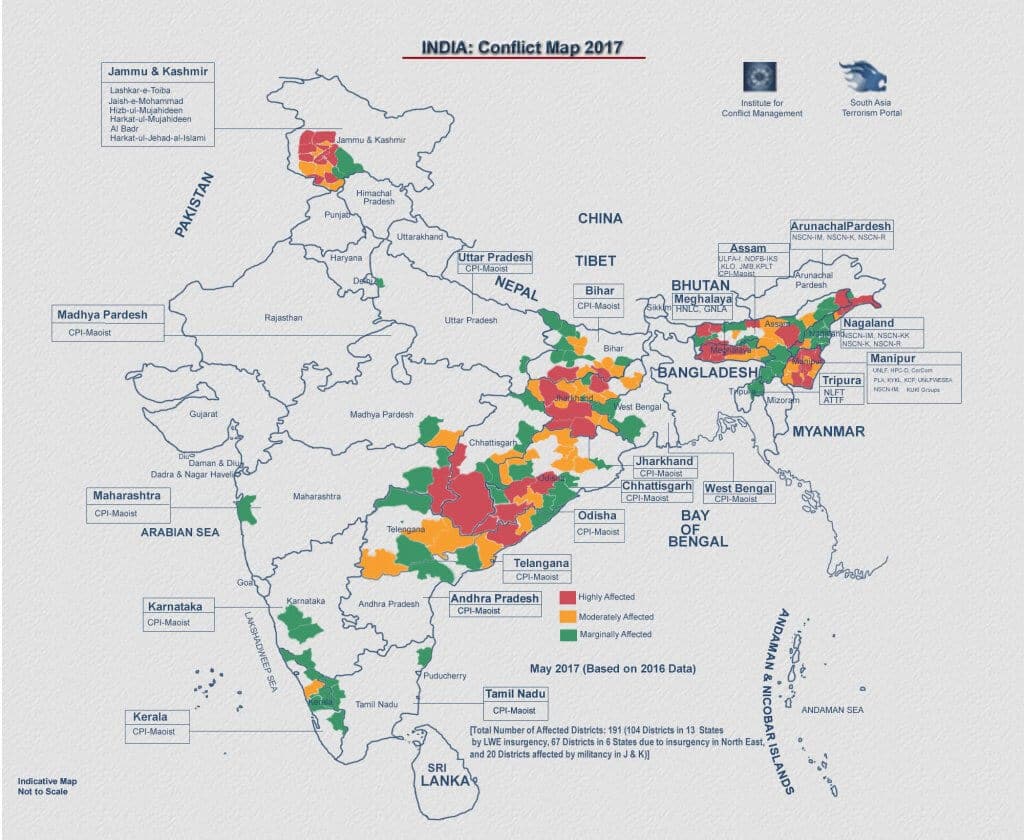
| Indian Border |
| India has 15,106.7 kms of land border and a coastline of 7,516.6 kms including island territories. |
| Out of the total 29 states of India except for six states (Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Telangana, Delhi, and Haryana), the rest all states have either maritime boundary or land border with other nations. |
| India has land borders with countries: Pakistan, Afghanistan (PoK), China, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and Bangladesh. |
| India has maritime borders with seven countries: Bangladesh, Indonesia, Myanmar, Pakistan, Thailand, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. |
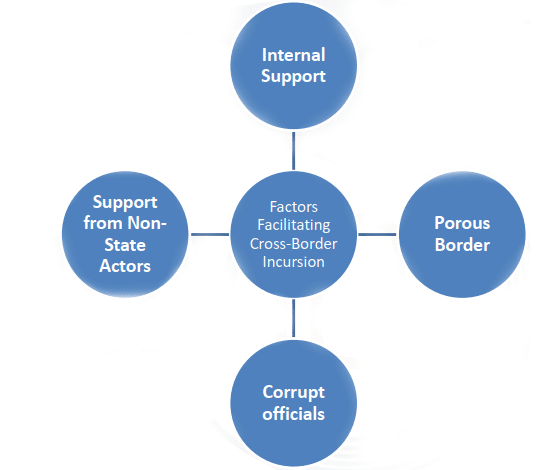
- Other causes of cross border terrorism:
- Technological advancement especially in terms of communication links which led to the availability of more sophisticated weapons, cell phones and high speed internet connections to the radical groups.
- Present terrorist groups are more diffused in their structure with increase in their sleeper cells and various local groups.
- State sponsorship to various terrorist organisation and discriminating terrorists organisations as good terrorist and bad terrorists. E.g. good and bad Taliban.
- Extreme sense of fundamentalism and ideological leaning towards fundamental groups.
- Bad governance and deprivation.
- According to some political geographers, the developing nature of India and as per the model provided by Rostov, India is converting from developing to developed stage and is guided by high investment and manufacturing activities.
- India is optimising for regional power in Asia which is in clash with some other emerging nations, who are responsible for cross border terrorism to create economic and cultural instability in India.
- Indian political thinkers recognised two types of cross border terrorism, which are cross border terrorism at micro level and cross border terrorism at macro level. According to them international borders result into international cross border terrorism, while the cultural and ethnic diversity of country and quasi-federal nature of administration are responsible for micro or national cross border terrorism.
- For example the Al-Qaeda attack on Pune bakery is an example of international cross border terrorism, while the violence in Chhattisgarh and Assam are example of micro level cross border terrorism.
Consequences Of Cross Border Terrorism
- Geographers identified numerous consequences associated to cross border terrorism which are as follows:
- Threat to the national integrity
- Hurdles in the implementation of regional planning
- Strengthening of cultural regions and notion of regionalism.
- Loss of property, human resource, flora and fauna, and overall diversity.
- Cross border terrorism also disturbs the demographic dividend and attributes for any given geographical region and causes the push factor for migration. Therefore, some regions are underutilised and some are over utilised
Strategies To Control Cross Border Terrorism
- Political geographers suggested some of the political and geographical strategies to control cross border terrorism which are as follows:
- Effective implementation of international laws on borders and frontiers
- Satisfying the economic needs of region specific people,
- Effective implementation of UNCLOS
- Best utilisation of recent technology in form of Indian Space Program and related satellite like RISAT-1 and GSAT-1.
- Regional cooperation between SAARC nation, Indian Ocean RIM countries and national agencies like NCTC, IB, RAW.
- India is also a member of FATF (Financial Action Task Force) whose aim is to establish international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS) has replaced manual surveillance/patrolling of the international borders by electronic surveillance to enhance detection and interception capabilities.
Way Forward
- There is a need to reassess our policies on number of issues pertaining to the management of India’s international borders such as intelligence apparatus, internal security and border management.
- Impose tight control over immigration.
- Promote more effective domestic coordination and international cooperation to combat the financing of terrorism.
- Military should also look at alternative means to strike at the terror camps across the LoC and LAC through mechanisms like Precision Engagement Capability.
- Technical solutions are necessary to augment and complement the traditional methods of border guarding.
- Maintain close and effective coordination between intelligence and security agencies at the centre and state level.
Conclusion
- Borders, in recent years are the symbol of peace and prosperity by providing due care to regional identity and cultural diversity. Cross border terrorism is the threat to this identity and cultural diversity. Therefore, it is responsibility of geographers and political thinkers to examine the geography of a region, demographic attributes and cultural diversity of the region, and advocate the policies which are in the high interest of the people of India.

Really Helpful….thanks for it!!😇