- The two countries across the Arabian Sea are linked by geography, history and culture and enjoy warm and cordial relations, which are attributed to historical maritime trade linkages.
- While people-to-people contact between India and Oman can be traced back 5000 years, diplomatic relations were established in 1955 and the relationship was upgraded to Strategic partnership in 2008. Oman has been a key pillar of India’s West Asia Policy. Oman is an important interlocutor at the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) fora.
- The Sultanate of Oman is a strategic partner of India in the Gulf. Both nations are linked by geography, history and culture and enjoy warm and cordial relations.
- Oman became a British protectorate in 1891. It shook off the protectorate status during the decolonization of the Middle East (decolonization article link possible here) in the 1950s. During medieval times, Tipu Sultan even sent a diplomatic mission to Oman.
- Bilateral relations between both countries were formally established with signing of 1953 Indo-Oman Treaty of friendship, Navigation and Commerce. It was first between India and Arab country.
- In the 20th century, after India and Oman became independent, an Indian consulate was opened in Muscat in February 1955 which was upgraded to a consulate general in 1960 and later into a full-fledged embassy in 1971. The first ambassador of India arrived in Muscat in 1973.
- Similarly, Oman established its embassy in New Delhi in 1972 and a consulate general in Mumbai in 1976. This was the beginning of cordial diplomatic relations between the two countries.
- Sultan Qaboos is considered a major factor in consolidating and strengthening India’s ties with the country, which was influenced by his educational history in the Indian city of Pune.
- The historical India-Oman bilateral ties culminated into a strategic partnership in 2008 which continues to provide the base for current cooperation. This can also be seen in the recent announcement of the program of cooperation.
Areas of Cooperation
Political Relations:
- Visits at the highest level have been exchanged frequently between India and Oman. Ministerial level visits have taken place regularly.
- The Sultanate of Oman is a strategic partner of India in the Gulf and an important interlocutor at the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) fora.
Defence Cooperation:
- Oman is the first nation in the Persian Gulf to have formal defence relations with India. Both countries conducted joint military exercises in 2006 and later signed a defence agreement.
- The Ministries of Defence of both countries review their relations annually under the aegis of Joint Military Cooperation Committee meeting.
- India and Oman conduct regular biennial bilateral exercises between all three services.
- Army exercise: Al Najah
- Air Force exercise: Eastern Bridge
- Naval Exercise: Naseem Al Bahr
- Since 2008, Oman has been extending its support to Indian Navy’s anti-piracy missions and Indian Naval Ships are regularly welcomed by Oman for Overseas Deployments.
- Oman also sought India’s assistance in fencing the border it shared with Yemen due to the growing unrest over there.
Economic & Commercial Relations:
- India accords a high priority to expanding its economic and commercial ties with Oman. Institutional mechanisms like Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) and Joint Business Council (JBC) oversee economic cooperation between India and Oman.
- The bilateral trade and investment between India and Oman remain robust and buoyant.
- India is among Oman’s top trading partners. The value of trade between the two nations rose from $ 3.8 billion in 2015-2016 to $ 4 billion in 2016-2017. There are 2900 Indian enterprises and establishments who have invested close to $ 4.5 billion in Oman.
- For Oman, India was the 3rd largest (after UAE and China) source for its imports and 3rd largest market (after UAE and Saudi Arabia) for its non-oil exports in 2018.
- Major items of India’s exports to Oman include mineral fuels, mineral oils and products of their distillation; boilers, machinery and mechanical appliances; articles of iron or steel; electrical machinery and equipment, textiles and garments, chemicals, tea, coffee, spices etc
- Main items of India’s imports from Oman include fertilizers; mineral fuels, mineral oils and products of their distillation; bituminous substances etc.
- Indian financial institutions such as State Bank of India, Public Sector Undertakings such as Air India, Life Insurance Corporation(LIC), have presence in Oman. Indian companies have invested in Oman in sectors like iron and steel, cement, fertilizers, textile etc.
- India-Oman Joint Investment Fund (OIJIF), a JV between State Bank of India and State General Reserve Fund (SGRF) of Oman, a special purpose vehicle to invest in India, has been operational.
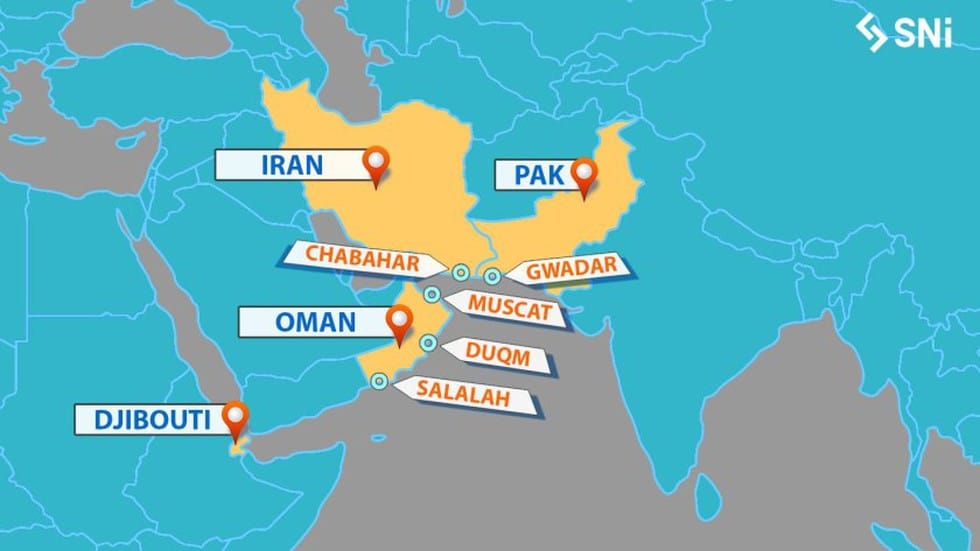
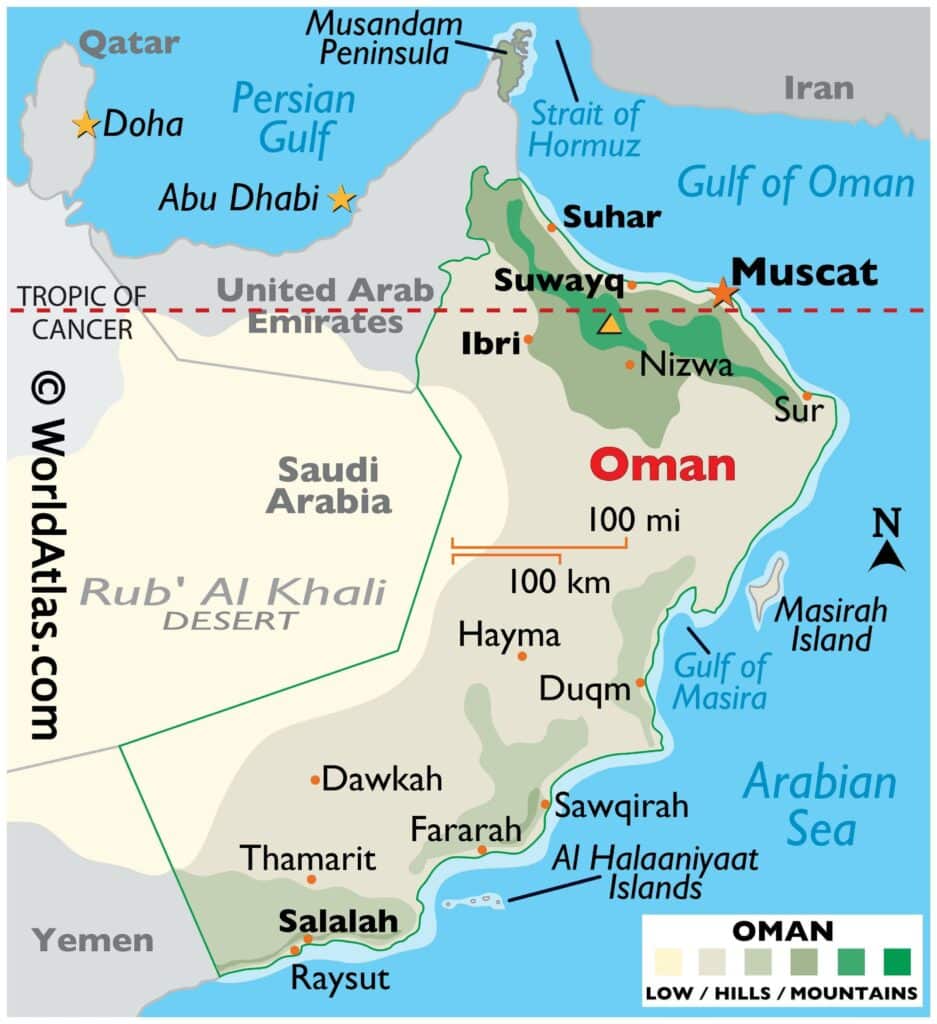
- Access to Duqm Port: Oman has allowed India, including its navy, access to its Duqm port, about 550 km south of the capital Muscat. The Port of Duqm SEZ is earmarked to be the Indian Ocean’s largest deep-sea port.
- An agreement to develop Little India, an integrated tourism complex project in Duqm worth 748 million USD, has been signed between the two countries.
- Energy: India has been considering the construction of a 1,100-km-long underwater natural gas pipeline from Oman called the South Asia Gas Enterprise (SAGE).
Maritime Cooperation
- Oman is at the gateway of Strait of Hormuz through which India imports one-fifth of its oil imports.
- Oman also actively participates in the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- India signed a pact with the country in 2018 to access the Duqm port of Oman.
- The Indian Navy is able to use the facilities at Duqm port in Oman following the signing of a pact between the two countries
- The port will act as India’s entry point for wider West Asia and Eastern Africa, a welcome development at a time when China has deployed strategic assets in the Indian Ocean Region.
Port of Duqm
The Port of Duqm is situated on the southeastern seaboard of Oman, overlooking the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean. It is strategically located, in close proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran.
Cultural Cooperation:
- India and Oman have close cultural relations. The vibrant Indian expatriate community in Oman regularly hosts cultural performances and invites celebrity artists and singers from India.
- Yoga is quite popular in Oman, especially among expatriates and local youth.
- The Embassy organised many events in 2019 to celebrate the 150th Birth Anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi and the 550th Birth Anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev ji.
Indian Community in Oman:
- There are about 7,00,000 Indians in Oman, of which about 5,67,000 are workers and professionals (June 2020). There are Indian families living in Oman for more than 150-200 years.
- The large, diverse and highly regarded expatriate Indian community in Oman is spread over the entire spectrum of professions. Thousands of Indians are working as doctors, engineers etc.
- There are many Indian schools offering CBSE syllabus catering to the educational needs of about 45,000 Indian children.
What is the Programme Of Cooperation (POC)?
The POC for Cooperation in Science and Technology for the period 2022 – 2025 was signed in pursuance of the Agreement for Cooperation in Science and Technology concluded in 1996 between the two countries. India and Oman will work together in areas like sustainability and scientific harnessing of resources under a Programme of Cooperation (POC) in the fields of Science and Technology.
- The Department of Science & Technology, Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India, and the Office of Science, Knowledge & Technology Transfer, Foreign Ministry, Government of Oman, will supervise, coordinate and implement the POC in their respective countries.
- Under POC, both countries will establish joint scientific projects. They will be based on mutual interest and developed jointly by the Indian and Omani institutions.
- The exchange of scientists, researchers, experts, and specialists for the implementation of selected joint projects will be encouraged.
- The aim will be to develop applicable technology.
Key Areas Of POC
The areas of cooperation identified based on the POC for the period 2022– 2025 are as follows:
- Medicinal Plants and processing
- Real-time Air Quality Monitoring
- Development of an electronic platform for knowledge sharing
- Technical expertise for Small and medium enterprises in the field of sustainability (Eco-Innovate) Accelerator
- Plastic Bio-fuel and Bio-diesel Research
- Software development for Graduate Programs – Linking Industry with Academia
- Blockchain and FinTech solutions
- Training programs – Big data, coding & testing
- STEM teaching
- Other areas of S&T cooperation added by mutual consent.
Significance of Oman for India
- Oman is India’s closest defense partner in the Gulf region and an important anchor for India’s defense and strategic interests.
- It is the only country in the Gulf region with which all three services of the Indian armed forces conduct regular bilateral exercises and staff talks, enabling close cooperation and trust at the professional level.
- It also provides critical operational support to Indian naval deployments in the Arabian sea for anti-piracy missions.
Duqm port and its strategic imperative
- In a strategic move to expand its footprint in the Indian Ocean region, India has secured access to the key Port of Duqm in Oman for military use and logistical support.
- This is part of India’s maritime strategy to counter Chinese influence and activities in the region.
- The Port of Duqm is strategically located, in close proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran.
- With the Assumption Island being developed in Seychelles and Agalega in Mauritius, Duqm fits into India’s proactive maritime security roadmap.
- In recent years, India had deployed an attack submarine to this port in the western Arabian Sea.
Deterrent in ties: Chinese influence in Oman
- China started cultivating ties with the Arab countries following the former Soviet Union’s invasion of Afghanistan.
- Beijing has cultivated close ties with Oman and the latter was, in fact, the first country to deliver oil to China.
- As of today, 92.99 per cent of Oman’s oil exports go to China, making China Oman’s largest oil importer.
- Oman and China signed an agreement to establish an Oman-China Industrial Park at Duqm in 2016.
- China has identified Oman as a key country in the region and has been enhancing defence ties with it steadily.
Way forward
- India does not have enough energy resources to serve its current or future energy requirements. The rapidly growing energy demand has contributed to the need for long term energy partnerships with countries like Oman.
- Oman’s Duqm Port is situated in the middle of international shipping lanes connecting East with West Asia. India needs to engage with Oman and take initiatives to utilise opportunities arising out of the Duqm Port industrial city.
- India should also work closely with Oman to enhance strategic depth in the region and add heft to its Indo-Pacific vision in the Western and Southern Part of Indian Ocean.
