History Optional Question Paper – 2019: Paper-1
SECTION – A
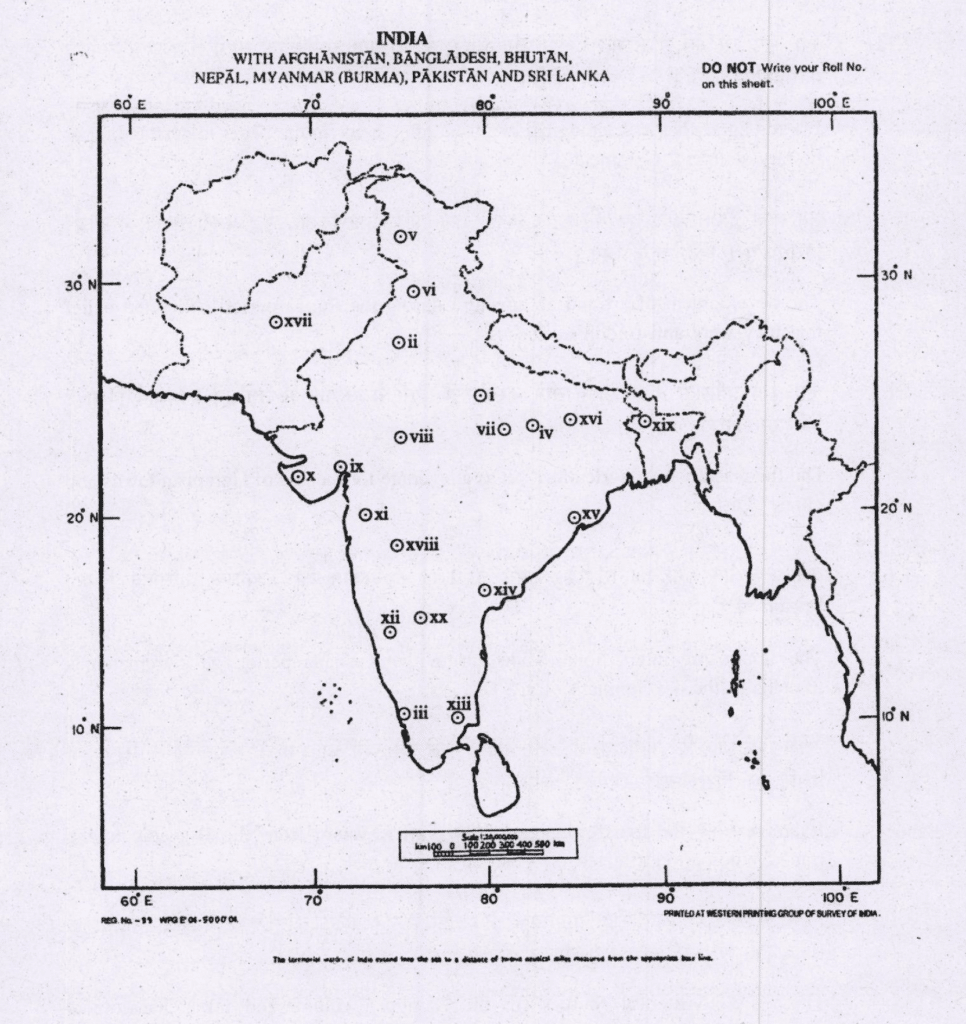
Q1. Identify the following places marked on the map supplied to you and write a short note of about 30 words on each of them in your Question-cum-Answer Booklet. Locational hints for each of the places marked on the map are given below seriatim.
- Brick temple site
- Early Harappan site
- Ancient seaport and trade centre
- Stone age site
- Neolithic site
- Archaeological site
- Ancient capital city
- Ancient capital
- Harappan site
- Ancient inscriptions site
- A Rock-cut cave site
- Ancient capital city
- Famous temple site
- Centre of School of art
- Ancient inscriptional site
- Ancient education centre
- Pre-Harappan site
- Chalcolithic period site
- Early inscriptional site
- Ancient petroglyphs site
Q2. (a) Do you agree that archaeological evidence often helps in the better understanding of literary sources ? Comment. 15 Marks
(b) The development of art and architecture during the Sunga period belies the belief that they were anti-Buddhist. Discuss. 15 Marks
(c) Did the mastery over agriculture act as a leverage for the rise of Harappan towns and cities ? Discuss.
15 Marks
Q3 (a) The flourishing international trade during the Kushana period gave tremendous impetus to the development of art. Discuss. 15 Marks
(b) Examine how the transformation of the Varna system from the Rigvedic to the Later-Vedic period affected the position of women. 15 Marks
(c) There are no literary sources for the Harappan culture and non archaeological evidence for the vedic period Explain the phenomenon . 20 Marks
Q4(a) Explain how Ashoka used religion as a tool of political, aggrandizement ? 15 Marks
(b) Do you agree that the system of land grants from the Gupta-Vakataka Period was connected with the decentralisation of state in any way ? 20 Marks
(c) The discovery of monsoons by Hippalus gave a new direction to Indo-Roman trade during the Satavahana period. Comment. 15 Marks
SECTION – B
Q5. Answer the following questions in about 150 words each :
(a) Discuss how Vijayanagara empire became the cultural capital of the south ? 10 Marks
(b) Examine the status of Sanskrit in Mughal India. 10 Marks
(c) Assess the rule of Zainul Abedin in Kashmir. 10 Marks
(d) The economic measures of Alauddin Khalji were aimed at greater political control. Discuss. 10 Marks
(e) Examine the European impact on Mughal paintings. 10 Marks
Q6(a) Assess the statement that ‘the philosophy of Shankaracharya revolutionised religious thoughts in India’. 20 Marks
(b) Delineate the state of agriculture during the Sultanate period. 15 Marks
(c) Sufi and Bhakti thoughts ennobled Indian psyche amidst the vagaries of time. Elucidate. 15 Marks
Q7(a) The emergence of early capitalism in the Mughal period was primarily due to urbanisation and commercialisation. Comment. 20 Marks
(b) Internal strife and conflict beset with personal ambitions was enough of an invitation for the Ghurids to invade India. Discuss. 15 Marks
(c) The Mughals built like Titans and embellished like jewellers. Comment. 15 Marks
Q8(a) Critically analyse whether the success of the Mughals is to be credited to their robust Jagirdari and Mansabdari system. 15 Marks
(b) It was as much the court intrigues as also the defiance of the provincial powers that hastened the decline of the Mughals in the 18th century. Comment. 20 Marks
(c) Shivaji was not merely a military conqueror but also was an enlightened ruler. Discuss. 15 Marks
History Optional Question Paper – 2019: Paper-2
(SECTION – A)
Q1. Critically examine the following statements / Answer the following in about 150 words each: 10×5=50
(a) “Tipu Sultan was trying to build in Mysore a strong centralized and militarized state, with ambitious territorial designs.” 10 Marks
(b) “Not until independence, when economic development became a conscious and pursued policy, did the Railways begin to realize their potential for assisting in the transformation of the Indian economy.” 10 Marks
(c) “Two important intellectual criteria which informed the reform movements were rationalism and religious universalism.” 10 Marks
(d) ” … the Kol Insurrection was mainly a war of the tribal inhabitants of Chotanagpur against the non-tribal settlers and service-holders.” 10 Marks
(e) “The Cripps Mission was plagued throughout, and ultimately torpedoed.” 10 Marks
Q2.(a) How far was the drain theory a focal point of nationalist critique of colonialism? 20 Marks
(b) Examine the forces at work for the introduction of western education in India. Analyse the thrust given to it by the Christian Missionaries. 20 Marks
(c) Do you subscribe to the view that the Anglo-French tussle in Carnatic demonstrated the internal decay of the provincial chieftains of South India? 10 Marks
Q3(a) How would you explain the major trends of the Swadeshi Movement in Bengal? 20 Marks
(b) Is it justified to say that the Government of India Act of 1935 had all brakes, but no engine ? 20 Marks
(c) How far was the widow remarriage movement effective in arousing social concern for Indian women ?
10 Marks
Q4(a) Why is the Quit India Movement characterized as a ‘Spontaneous Revolution’? Did it accelerate the process of Indian independence? 20 Marks
(b) Assess the role of Subhas Chandra Bose in India’s struggle for independence. 20 Marks
(c) How did the introduction of Community Development Programme and Panchayati Raj promote welfare of rural India? 10 Marks
SECTION – B
Q5. Critically examine the following statements in about 150 words each: 10×5=50
(a) “The arguments of the free traders were a curious mixture of economic hard-headedness, social benevolence, cosmopolitan idealism and class prejudice.” 10 Marks
(b) “There are many ways in which the war of 1914 – 18 was unprecedented, and in human history, entirely novel.” 10 Marks
(c) “The ineffectiveness of the League of Nations to prevent or to check Japanese aggression against China was the first serious blow to its prestige as an agency for providing security.” 10 Marks
(d) “Non-alignment came to symbolize the struggle of India and other newly independent nations to retain and strengthen their independence from colonialism and imperialism.” 10 Marks
(e) How would you explain the nature of pre-Marxian Socialism? 10 Marks
Q6(a) How did the policies of governments facilitate the process of industrialization in Europe? 20 Marks
(b) How was Italy transformed from ‘a geographical expression’ to nation state? 20 marks
(c) How far did the Napoleonic preferential stance to help out the French economy result in embroiling France in continental conflicts? 10 Marks
Q7(a) Which factors would you attribute to the British colonial intervention in Malaya in the 19th century?
How did Malays react to British colonial rule? 20 marks
(b) Explain why Latin America was beset with chronic political instability and endemic military conflicts throughout most of the 19th century. 20 Marks
(c) Do you agree with the view that the formation of NATO marked a revolution in American attitude to the world’s problems? 10 Marks
Q8. (a) Do you subscribe to the view that Greek War of Independence was mired in contrasts of the best and the worst episodes? How did affect the Concert of Europe? 20 Marks
(b) Was Czechoslovakia served on a dish to Hitler at Munich? What were its implications? 20 Marks
(c) Analyse the role of Egypt after the Second World War in bringing about Arab unity. 10 Marks
