In this article, You will read Growing importance of Ports on National and Foreign trade and Sagarmala Project – UPSC.
Growing importance of Ports
- The Indian coastline which is 7516.6 km long covers 6100 km of mainland coastline along with the Andaman, Nicobar, and the Lakshadweep islands.
- The coastline of India touches 13 states and Union Territories. The western coastal plains are along the Arabian Sea whereas the eastern coastal plains are located along the Bay of Bengal. 20% of India’s population lives in coastal areas.
- The contribution of maritime states to India’s GDP is approximately 60%. The big and small ports along the Indian coastlines help in carrying out trade.
- There are 13 major ports and 200 minor ports.
- 95% of India’s foreign trade and 70% of the value is trade takes place through seaways.
- Over 7500 kilometers of coastline with 13 major and 60 operational non-major ports.
- 90% of the country’s trade by volume and 70% by value are moved through maritime transport.
- There are 13 major ports in India that handle approximately 58% of cargo traffic.
- Cargo handled at major ports is bulk (44% – iron ore, coal, and fertilizer), liquid (33% petrol, oil, and lubricants), and container (23%).
- Water transport has been playing an important role in the Indian economy since time immemorial. It is an easy, cheap, and energy-efficient means of exports and imports of heavy items. In this context role of ports become all the more important.
- Besides foreign trade, ports play an important role in internal trade. Many rivers are linked with major ports. These rivers carry important goods from ports to the hinterland to facilitate the transportation of these goods inside the country.
- Of the total sea-based trade of India, more than 85% is shared by Bombay, Calcutta, Cochin, Madras, and Vishakhapatnam due to both geographical and historical reasons. Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata have been centers of administration for a long time.
- With the increase in the population of these cities commercial and industrial activities also increase. During the later half of the 19th century, railways lines were constructed, consequently, from political centers they developed into great ports.
Rationale for Sagarmala Project
- Sagarmala project is for promoting port-led direct and indirect development and to provide infrastructure to transport goods to and from ports quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
- No cohesive institutional arrangement – There is the involvement of multiple agencies in the development of infrastructure in coastal areas which causes policy failure and ambiguity in the implementation of projects.
- Weak infrastructure at ports and beyond – Limited mechanization, lack of scale, deep draft, and other facilities at various ports in India is not up to the mark, which causes hurdles in port-led development in India.
- Lack of requisite infrastructure – For evacuation of goods from major and non-major ports to hinterland there is a lack of modal and mix modal transportation facilities.
- Limited hinterland linkages – Lack of infrastructure facilities mentioned above has led to the increase in the cost of transportation and cargo movement, limiting the hinterland linkages required for the development of coastal regions.
- Limited development of centers for manufacturing and economic activities in the hinterland also mandated an integrated project for port-led development.
Objectives of Sagarmala Project
- Port Led Development – It involves the development of Coastal Economic Zones with projects like port-based industrialization, coastal tourism, Logistics parks, warehousing, fisheries, etc.
- Port Infrastructure Enhancement –It includes the action points on transforming existing ports into world-class ports by developing deep drafts, mechanization of existing berths, creation of new capacity & greenfield ports.
- Efficient Evacuation – It includes expansion of rail/road network/inland waterways connected to ports & identification of congested routes.
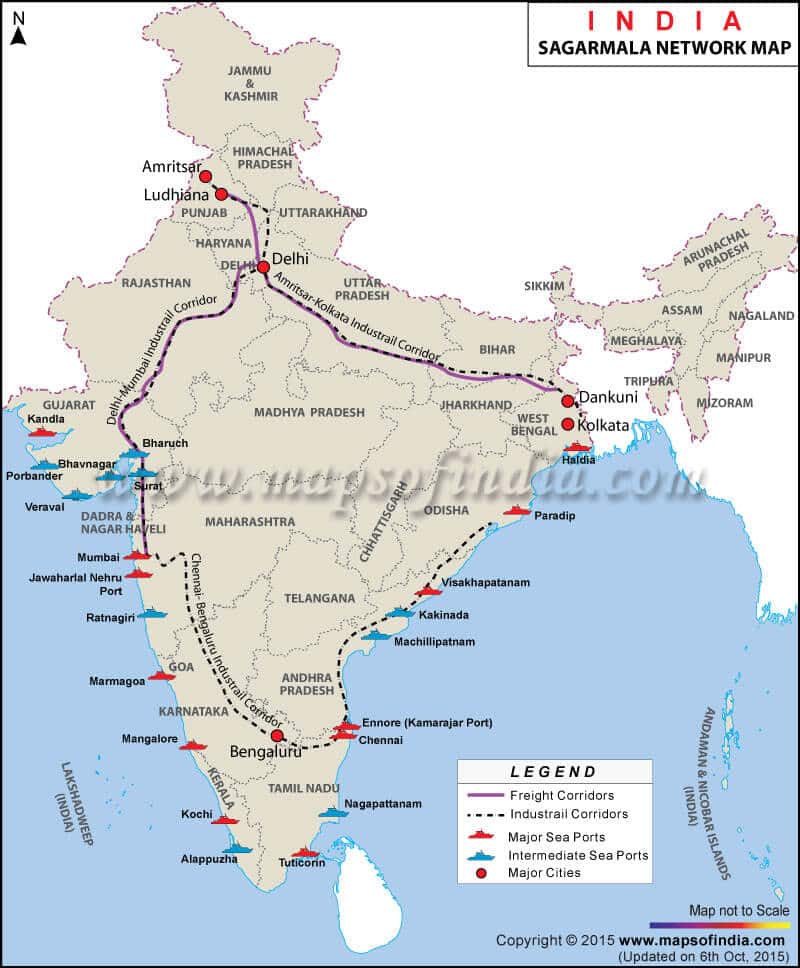
Sagarmala Vision
Sagarmala project aims to develop access to new development regions with intermodal solutions and promotion of the optimum modal split, enhanced connectivity with main economic centers and beyond through expansion of rail, inland water, coastal, and road services.
Some of the visions of the project is mentioned below.
- Changing the way how India moves logistically
- The project aims to increase the competitiveness of core industry and manufacturing by savings the input cost of power and steel by up to 5% through modernization of port infrastructure.
- Utilization of National resources by the increasing volume of trade by inland waterways and coastal shipping by 50 MTPA.
- The project aims to implement the IT-enabled National multimodal logistics to plan to streamline the implementation process of the Sagarmala project.
- The project also aims to construct the coastal roads through the maritime state, connecting them with at least two-lane Highways.
- Creating world-class port institutions:
- Sagamala Development Company: The Sagarmala Development Company Limited (SDCL) has been incorporated (on 31st August 2016) under the Companies Act, 2013. The Objectives of SDCL are:
- Develop & formulate projects emanating from the National Perspective Plan (NPP)
- Assist project SPVs set up by Central Line Ministries / State Governments/State Maritime Boards/Ports etc. for projects in alignment with Sagarmala objectives
- Provide funding window for residual projects that cannot be funded by any other means/mode
- Prepare the Detailed Master Plans for the Coastal Economic Zones (CEZs) identified as part of the National Perspective Plan
- Raise funds from multi-lateral and bilateral agencies as debt/equity (as long term capital), as per the project requirements
- Sagarmala Coordination and Steering Committee:
- At the national level, the government will constitute a Sagarmala Coordination and Steering Committee (SCSC) under Cabinet Secretary with Secretaries of the Ministries of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways, Tourism, Defence, Home Affairs, Environment, Forest & Climate Change, Departments of Revenue, Expenditure, Industrial Policy, and Promotion, Chairman, Railway Board and CEO, NITI Aayog as members.
- This committee would provide coordination between various ministries, state governments, and agencies connected with implementation and review the progress of implementation of the National Perspective Plan, Detailed Master Plans, and individual projects
- The project aims to implement a World-class PPP program in port, waterways, and connectivity projects that will attract the best domestic and international investors.
- Maritime services clusters will be set up for boosting port infrastructure, for e.g. construction of facilities for shipbuilding.
- Sagamala Development Company: The Sagarmala Development Company Limited (SDCL) has been incorporated (on 31st August 2016) under the Companies Act, 2013. The Objectives of SDCL are:
- Boosting development through ports & shipping
- For the establishment of 2-3 port-based smart cities & marine clusters/Coastal Economic Zones, over 10,000 acres of land will be accrued which will help in creating 50,000 direct jobs.
- Launching of 100 Early bird projects (including PPP) with Rs. 100,000 crores of investment.
- The addition of a port capacity of 1200-1500 MTPA will be done by strengthening existing ports and by launching 3-4 new mega ports.
- The establishment of a world-class transshipment port will be done under the project.
- Empower coastal communities
- Skill development in coastal communities will be carried out under the project (e.g., fisheries) which will help in creating 20 million jobs in maritime states.
- Comprehensive coastal community development potential from tourism in islands, lighthouses & cruises would increase the GDP contribution of maritime states and sectors in the Indian economy.
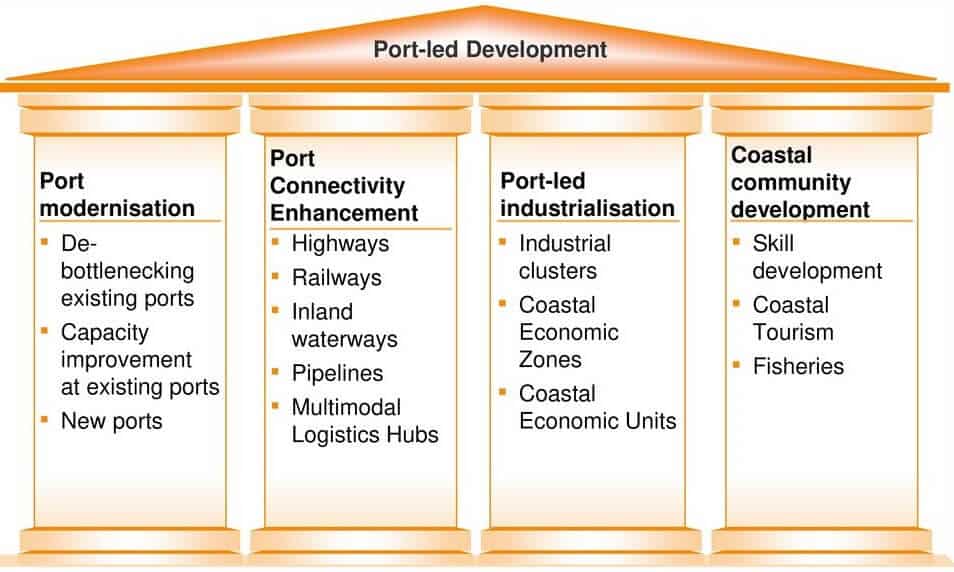
Potential Benefits of Sagarmala Project
- Under this port-led development framework government hopes to increase its cargo traffic three-fold in the next 5 years. It will benefit around 14 percent of the country’s overall population from at least 13 States and Union Territories.
- The project will be integrating the coastal economy with the ports through the development of Coastal Economic Regions & projects with synergies to coastal Industrial Corridors.
- The project will be led to the development of port-based smart cities and other urban infrastructure to improve standards of living.
- There will be the implementation of skill development/livelihood generation projects for coastal community development through the Sagamala project.
- Modernization/capacity expansion of existing ports and the creation of Greenfield ports will reduce the bottlenecks for future growth.
- Development of port evacuation (road/rail/inland waterways) and logistics infrastructure will reduce the overall logistic cost and will increase cargo movement to-and-from the hinterland.
- The project will help in the development of the maritime sector leading to new economic activity in the region – E.g. Ship Building and Repair Cluster.
- Easing of policy and institutional bottlenecks for obtaining project approvals, accessing project funding and implementation partners will help in proper Project implementation and monitoring.
- Some other benefits:
- It will help in ease of doing business.
- It will reduce farm to factory timing of the products as well as raw materials.
- It will lead to employment generation.
- In the future, India may become the major destination of port-led trade among major economies of east and west.
Six mega ports are planned under Sagarmala project
Coastal Economic Zones
- Coastal Economic Zone (CEZ) refers to designated coastal areas with special economic regulations such as tax incentives and lower tariffs to make it friendly for foreign direct investment.
- It is similar to Special Economic Zone (SEZ) but focuses on coastal development projects such as the development of port-proximate industrial clusters, promoting port-led development, reduction of logistics cost, and time for movement of goods.
- CEZ will be developed as part of the plan for developing 14 such industrial clusters to spur manufacturing and generate jobs. The plan envisages a total investment of Rs 15,000 crore in the first phase and the creation of more than 1.5 lakh jobs.
Coastal Economic Zones Planned under Sagarmala
| S.No. | CEZ | State | Linkage Ports |
| 1 | Kachch | Gujarat | Deen Dayal, Mundra |
| 2 | Saurashtra | Gujarat | Pipavav, Sikka |
| 3 | Suryapur | Gujarat | Dahej, Hazira |
| 4 | North Konkan | Maharashtra | JNPT, Mumbai |
| 5 | South Konkan | Maharashtra, Goa | Dighi, Jaigarh, Mormugao |
| 6 | Dakshin Kanara | Karnataka | New Mangalore |
| 7 | Malabar | Kerala | Cochin |
| 8 | Mannar | Tamil Nadu | VOCPT (Tuticorin) |
| 9 | Poompuhar | Tamil Nadu | Cuddalore |
| 10 | VCIC South | Tamil Nadu | Chennai, Kamarajar, Katupalli |
| 11 | VCIC Central | Andhra Pradesh | Krishnapatnam |
| 12 | VCIC North | Andhra Pradesh | Vizag, Kakinada |
| 13 | Kalinga | Odisha | Paradip, Dhamara |
| 14 | Gaud | West Bengal | Kolkata, Haldia |

excellent job lotusrise team. Heart full thanks.
Can you please share whole notes in Evernote or Onenote, it will be easy to read and highlight.
Sorry, I have not complete notes on Evernote/Onenote. I am using both handwritten with digital notes on Onenote. So, You can also make your own notes on Onenote.
I must say, your website is much better than Drishti, Insight, Byju etc. You give complete information! Please keep on giving complete information like this only!
Hello
please tell me
india’s trade relations with japan
thank u so much…