Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- VoIP is a technology that allowing you to make voice calls over a broadband Internet connection instead of an analog (regular) phone line.
- VOIP is an IP-enabled voice calling technology over the internet. Example: Skype, Yahoo messenger, MSN messenger.
- It requires broadband connectivity to make a call along with IP enables devices like Computers, smartphones, etc.
- The voice is converted into digital packets and transmitted to the destination over packet-switched network.
Some of the advantages of VOIP are:
- The cost of calling is cheaper than a normal phone.
- No need to carry a dedicated device for calling if you just have a computer with you.
- Its uses existing LANs so need for dedicated wiring features and hence reduces the complexity of calling.
- Call anywhere anytime; do not worry about Roaming Features and Cost.
- One payment, two services: voice calling and broadband data usage
Disadvantages of VOIP are:
- It is dependent on broadband network connectivity, no internet no calling.
- The quality of voice depends on broadband bandwidth and speed.
- Power shortage can hamper VOIP calling as it’s totally dependent on power-enabled devices.
- No emergency calling features like normal and Smartphone.
- The highest disadvantage of VOIP is security. It’s really tough to trace the source and identity if an imposter is at work.
- Threats like phishing, spoofing and sniffing, call tampering, etc. is very common.
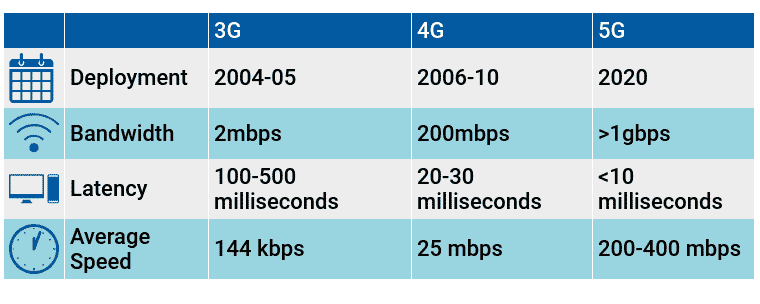
3G vs 4G
- 3G was completely a new innovation that transformed mobile telephony.
- For the first time, it provided voice and data connectivity on a single network.
- The true sense of smartphones came into existence by enabling data connectivity.
- The development accelerated new ideas like e-learning, e-governance, etc.
- It was also an improvement in bandwidth and speed of communication.
- 4G is a new technology highly concentrated on bandwidth enhancement and improved speed further. It will take 3G to next level.
- There are 2 existing technologies in 4G: 4G LTE and 4G WiMAX.
- In a nutshell, the difference between 3G and 4G is its difference in SPEED.
4G LTE vs 4G WiMAX
- LTE stands for Long Term Evolution. It’s a first-generation 4G technology termed as “true 4G”.
- WiMAX stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access.
- They differ in their bandwidth; LTE has higher bandwidth than WiMAX.
- LTE is compatible with the existing network but for WiMAX, we need an altogether new network.
- The cost of installation of LTE is more than WiMAX.
- Overall LTE is gaining popularity and hopes to exist 4G technology in coming years.
WIMAX
It is a wireless industry coalition dedicated to the advancement of IEEE 802.16 standards for broadband wireless access (BWA) networks.
- WiMAX can provide at-home or mobile Internet access across whole cities or countries.
- In many cases, this has resulted in competition in markets that typically only had access through an existing incumbent DSL (or similar) operator.
- Additionally, given the relatively low costs associated with the deployment of a WiMAX network (in comparison with 3G, HSDPA, xDSL, HFC, or FTTx), it is now economically viable to provide last-mile broadband Internet access in remote locations.
- WiMAX is competing with the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)’s Long-Term Evolution (LTE) in the 4G market.
IEEE 802.16 is a series of wireless broadband standards written by the Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
The IEEE Standards Board established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband for wireless metropolitan area networks.
The Workgroup is a unit of the IEEE 802 local area network and metropolitan area network
standards committee.
4G vs 5G
- The next (5th) generation wireless network will address the evolution beyond mobile internet to massive IoT (Internet of Things) for the horizon 2019/2020. The main evolution compared with today’s 4G and 4.5G (LTE advanced) is that beyond data speed improvements, new IoT and critical communication use cases will require new types of improved performance. For example, “low latency” is what provides real-time interactivity for services using the cloud: this is key to the success of self-driving cars for example. Also, low power consumption is what will allow connected objects to operate for months or years without the need for human assistance.
- Unlike current IoT services that make performance trade-offs to get the best from current wireless technologies (3G, 4G, WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, etc…), 5G networks will be designed to bring the level of performance needed for massive IoT. It will enable a perceived fully ubiquitous connected world.
5G Technology
- 5G networks are the next generation of mobile internet connectivity, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections on smartphones and other devices than ever before. Combining cutting-edge network technology and the very latest research, 5G should offer connections that are multitudes faster than current connections, with average download speeds of around 1GBps expected to soon be the norm.
- The next-generation telecom networks (5G) will hit the market by 2020. Beyond just speed improvements, 5G is expected to unleash a massive IoT ecosystem where networks can serve communication needs for billions of connected devices, with the right trade-offs between speed, latency, and cost.
- NGMN Alliance or Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance defines 5G network requirements as:
- Data rates of several tens of Mb/s should be supported for tens of thousands of users.
- 1 Gbit/s to be offered, simultaneously to tens of workers on the same office floor.
- Several hundreds of thousands of simultaneous connections to be supported for massive sensor deployments.
- Spectral efficiency should be significantly enhanced compared to 4G.
- Coverage should be improved.
- Signaling efficiency enhanced.
- Latency should be significantly reduced compared to LTE.
- Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance feels that 5G should be rolled out by 2020 to meet business and consumer demands. In addition to simply providing faster speeds, they predict that 5G networks will also need to meet the needs of new use-cases such as the Internet of Things as well as broadcast-like services and lifeline communications in times of disaster.
- 3GPP has set an early revision, Non-Standalone release of 5G called New Radio (NR). It will be deployed in two ways, Mobile and Fixed Wireless. The specification is subdivided into two frequency bands, FR1 (<6 GHz) and FR2 (mmWave) respectively.
Optical Fibre
- Optical fibre is the backbone of the digital infrastructure — the data is transmitted by light pulses travelling through long strands of thin fibre.
- Metal wires are preferred for transmission in optical fibre communication as signals travel with fewer damages.
- The optical fibre works on the principle of total internal reflection (TIR).
- Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data (In case of long straight wire without any bend).
- In case of a bend, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays inwards (using TIR).
LI FI Technology: LIGHT FIDELITY
As we all know that light reaches everywhere. Imagine if certain information is to be passed using light as a medium. Not only will the communication get fast but also the possibilities coming with it. Such a technique of using light as a medium is dubbed as the Li-Fi.
What is Wi-Fi?
- Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity.
- It uses a 2.4 to 5 GHz radiofrequency to deliver wireless Internet access around our homes, schools, offices, and in public places.
Main problem with the Wi-Fi
- Bandwidth is typically limited to 50-100 megabits per second (Mbps) today using the IEEE802.11n standard.
- It works fine with many of the internet connections. But it is unable to deliver High Definition Movies, music libraries, or video games.
- With the recent increase in the use of cloud computing (where you store your information on a certain web server & not on your local disk), Wi-Fi is not going to be useful in the future as it will not be able to cater to the need of the increasing bandwidth & speed.
Other Problems with the Radio Spectrum
- Capacity (Costly & Expensive. Less bandwidth compared to other spectrums. Insufficient spectrum for increasing data)
- Efficiency (millions of base stations consume a huge amount of energy)
- Availability (Available within the range of Base Stations. Limited Availability. Unavailable in aircraft)
- Security (Less secure. It passes through walls)
Components of Electromagnetic Spectrum–
| Sr. No | Electromagnetic Spectrum | Description |
| 1 | Radio Waves | Expensive, Limited Bandwidth, less secure |
| 2 | Infrared | Only for Low power Applications |
| 3 | Visible | Which is not used so far. Sage to Use. Larger Bandwidth. |
| 4 | Ultra-violet | Dangerous for the human body. |
| 5 | X-rays | Used for hospitals |
| 6 | Gamma Rays | Is not used generally as it is very harmful. |
What is Li-Fi?
- Li-Fi is the latest communication technology that can transmit data using the spectrum of visible light.
- Other names for Li-Fi: Optical Wireless technologies / Visible Light Communication (VLC) but mostly called Li-Fi (Light Fidelity)
- Speed possible to Achieve: 10 Gbit/S (Giga bit per second). It is around 250 times faster than “superfast” broadband.
- The name “Li-Fi” was first coined by Edinburgh University’s Prof. Harald Hass in 2001.
How Li-Fi Technology works?
- It works by sending data over the light.
- For this purpose, a LED (Light Emitting Diode) light bulb, anyone at all, can be flicked on and off in order to be able to generate signals. A proper Light Receiver is made for receiving the LED signals.
- The LED bulb will hold a microchip that will do the job of processing the data.
- The light intensity can be manipulated to send data by tiny changes in amplitude.
- Properties of LED: (Fundamental property of Li-Fi):
- Intensity can be modulated into very high speeds and varying amplitudes.
- LED can be switched on and off with a very high speed.
- The question that comes to mind is that why would someone sit below a flickering light bulb? But this is not the thing. The technology is focusing on making sure that the light bulb is flickered up to billions of times a second! At that rate, the human eye simply cannot notice the light bulb being flicked on and off.
- The LIFI product consists of 4 primary sub-assemblies: Bulb, RF power amplifier circuit (PA), Printed circuit board (PCB) & Enclosure
- The PCB controls the electrical inputs and outputs of the lamp and houses the microcontroller used to manage different lamp functions.
- An RF (radio-frequency) signal is generated by the solid-state PA and is guided into an electric field about the bulb. The high concentration of energy in the electric field vaporizes the contents of the bulb to a plasma state at the bulb’s center; this controlled plasma generates an intense source of light. All of these sub-assemblies are contained in an aluminum enclosure.
1. It uses light as the medium for high-speed data transmission.
2. It is a wireless technology and is several times faster than ‘WiFi’.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Infrared Rays in remote control of TV
- Single data stream
- 10,000 or 20,000 bits per second
- Not usable for video streaming
Why Li-Fi
- For increasing Communication speed
- For increasing Flexibility
- For increasing Usability
- Reduced cost
- Greater efficiency
- It uses LED instead of bulbs & hence is indirectly helping the environment.
Drawback of Li-Fi
- The data receiver would have to be in sight of the transmitter-bulb as visible light does not penetrate solid materials. (Note: Some experts are considering it as an advantage as the hackers won’t be able to hack the Li-Fi network without being in sight.
- The presence of Light is required.
Difference between Wi-Fi & Li-Fi
| Sr. No. | Key | WiFi | LiFi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Definition | WiFi stands for Wireless Fidelity. | LiFi stands for Light Fidelity. |
| 2 | Invented | WiFi was invented by NCR corporation on 1991. | LiFi was coined by Prof. Harald Haas in 2011. |
| 3 | Operation | WiFi transmits data using radio waves using WiFi router. | LiFi transmits data using light signals using LED bulbs. |
| 4 | Device Compliance | WLAN 802.11/b/g/n/ac/d standard compliant devices. | IrDA compliant devices. |
| 5 | Data Transfer Speed | WiFi transfer speed ranges from 150 Mbps to 2 Gbps. | LiFi transfer speed is about 1 Gbps. |
| 6 | Frequency | 2.4Ghz, 4.9Ghz and 5Ghz. | 10,000 times radio frequency spectrum. |
| 7 | Coverage | WiFi coverage area is upto 32 meters. | LiFi coverage area is about 10 meters. |
| 8 | Components | Routers, Modems and access points. | LED bulb, LED driver and photo detector. |
| 9 | Applications | Used in internet browsing using WiFi hotspot. | Used in airlines, under sea explorations. |
Li-Fi and Wi-Fi
- The appearance of the Li-Fi cannot wipe off the need for Wi-Fi.
- Li-Fi is complementary.
Advantages of use of Visible Light over Radio Waves
- Visible light is more plentiful than radio waves. (more bandwidth)
- Visible light can achieve far greater data density.
- Can be used underwater without radio interference because salt conducts electricity
- Transmission can be blocked by walls so there is less risk for data leaking
- Can be safely used on planes because it does not interfere with radio equipment.
Uses of Li Fi
- It can be used in Hospitals where Radio Frequency signals are a threat to the medical equipment present in the hospital.
- It can be used in Mobiles to transfer data speedily.
- In Radio Frequency Restricted Environments
- In vehicles and traffic lights, reducing accidents and traffic congestion
- Street lamps (as free access points)
- In Aircraft cabins.
Spectrum Auction
What is Spectrum?
- The word spectrum refers to a collection of various types of electromagnetic radiations of different wavelengths.
- Spectrum or airwaves are the radio frequencies on which all communication signals travel.
- In India, the radio frequencies are being used for different types of services like space communication, mobile communication, broadcasting, radio navigation, mobile satellite service, aeronautical satellite services, defense communication, etc.
- Radiofrequency is a natural resource but unlike other resources, it will deplete when used. But it will be wasted if not used efficiently.
- The spectrum allocated to Indian telecom operators is most crowded and inadequate to accommodate the usage by 650 million mobile subscribers as on date. This has affected the quality of customer service and resulted in poor voice quality, call drop, and undelivered messages of mobile services in India.
What is mobile spectrum?
- Mobile or cellular spectrum is that part of the whole electromagnetic spectrum which is used by the Indian government to offer mobile services. Hence the name “Mobile Spectrum”.
- Generally, the following frequencies are used for this purpose – 800 Mhz (for CDMA), 900 Mhz (for 2G) & 1800 Mhz (for 3G/4G).
- But technically any frequency band can be used for any purpose. Like 900 Mhz frequency can be used to deliver 3g Services also.
Agencies allocating Spectrum
- For international purposes, the spectrum is allocated by the world body called the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- For domestic purposes, it is done by Wireless Planning and Coordination (WPC) Wing of the Ministry of Communications, created in 1952, is the National Radio Regulatory Authority responsible for Frequency Spectrum Management, including licensing and caters for the needs of all wireless users in the country. It issues licenses to operate wireless stations.
What is Reserve Price?
- It is the minimum amount set by the government from which the auction starts i.e. it is the starting amount or base price from which the auction starts.
Why auction of spectrum is done?
- Spectrum is a scarce resource. It needs to be managed efficiently.
- Also, the spectrum can’t be used by many people. It has to be allocated to some persons who can manage the services under it. Hence it is auctioned.
- Government auctions it because the spectrum is a resource & the ownership rights for it are vested in the Government of India. It is not private property. So, government auctions it.
- Also, a lot of revenue is generated by selling the spectrum. That money can be used for developmental programs in India.
Reasons for superiority of 900 Mhz and 1800 Mhz band
- According to the laws of Physics, for any wave, the higher the frequency of the wave, the lesser will be the distance traveled by it. So naturally, frequencies of 900 Mhz will cover more distance than the frequencies of 1800 Mhz & hence mobile operators are more interested in the 900 Mhz frequency.
- More investment needed by the companies who buy the 1800 Mhz frequency spectrum: the 1800 Mhz frequency has poor coverage than the 900 Mhz frequency. So, for matching the existing coverage mobile operators have to install additional base stations (i.e. mobile towers) to give the same effect as the frequencies under 900 Mhz.
- Also, hardware equipment required for carrying out the operation of 1800 Mhz frequency is costly. The main reason behind it is that the 900 Mhz frequency band has been in use for mobile communications globally for over 20 years and as a result technology standards have been better developed compared with the 1800 Mhz band, which has been in use only recently.
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is a wireless broadband technology designed to support roaming Internet access via cell phones and handheld devices. Because LTE offers significant improvements over older cellular communication standards, some refer to it as a 4G (fourth generation) technology along with WiMAX.
LTE, an acronym for Long Term Evolution, commonly marketed as 4G LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals.
Long Term Evolution or LTE is the first step towards true 4G technologies. To be a truly 4G technology, download speeds of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s should be available from moving (i.e. in a car) or pedestrian points respectively. It was however widely decided across the world that companies could market LTE as “4G LTE” due to some having already taken that step and to avoid further consumer confusion with the terms 3.5G or 3.9G that were starting to surface.
LTE offers maximum download speeds of 299.6 Mb/s although there has been controversy over the speeds some operators running LTE networks are providing, sometimes being lower than the supposedly ‘inferior’ HSPA (plus) technology. Commercially available speeds vary wildly and using the (at the time of writing) recently launched UK LTE network, tests have shown anywhere in between 8-50 Mb/s in available areas. LTE requires brand new network technology and masts/radios. This also means that the devices that support LTE will also need to have a compatible receiver.
What is Multiplexing? What are its types?
- Any information i.e. voice/date in this case can be sent to another party only by the use of communication channel.
- In this case, the communication channel is the Radio Waves.
- But the spectrum under these radio waves is limited i.e. limited users can use these communication channels. Hence communication channels have to be used efficiently.
- For efficient use, the communication channel is allotted to the users in number of ways which is called Multiplexing.
- Types of Multiplexing: a) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) b) Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) c) Time-Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
- FDMA: In FDMA, the goal is to divide the frequency spectrum into slots and then to separate the signals of different users by placing them in separate frequency slots.
- TDMA: In TDMA, the goal is to divide time into slots and separate the signals of different users by placing the signals in separate time slots.
- CDMA: In CDMA, signals are sent at the same time in the same frequency band. Signals are either selected or rejected at the receiver by recognition of a user-specific signature waveform, which is constructed from an assigned spreading code.
Advantages of CDMA techniques:
- Efficient practical utilization of fixed frequency spectrum.
- Flexible allocation of resources.
- Many users of CDMA use the same frequency, TDD or FDD may be used
- Multipath fading may be substantially reduced because of large-signal bandwidth
- No absolute limit on the number of users, Easy addition of more users.
- Impossible for hackers to decipher the code sent
- Better signal quality
- No sense of handoff when changing cells
- The CDMA channel is nominally 1.23 MHz wide.
- CDMA networks use a scheme called soft handoff, which minimizes signal breakup as a handset passes from one cell to another.
- CDMA is compatible with other cellular technologies; this allows for nationwide roaming.
- The combination of digital and spread-spectrum modes supports several times as many signals per unit bandwidth as analog modes.
Difference between GSM & CDMA
You may have heard that mobile phones are available in GSM or CDMA. Even when you go to a mobile recharge shop, you are asked by the shopkeeper, “Do you want to recharge for GSM or CDMA?” What exactly is he asking to you is the type of technology being used by your mobile. A recharge voucher meant for GSM mobiles can’t work for CDMA mobiles & vice versa.
| Sr. No. | Parameter | CDMA | GSM |
| 1 | Stands for | Code Division Multiple Access | Global System for Mobile Communication |
| 2 | Storage Type | Internal Memory | SIM (Subscriber identity module) Card |
| 3 | Global Market share | 25% | 75% |
| 4 | Dominance | Dominant standard in the US | Dominant standard worldwide except the US |
| 5 | Network | There is one physical channel and a special code for every device in the coverage network. Using this code, the signal of the device is multiplexed, and the same physical channel is used to send the signal. | Every cell has a corresponding network tower, which serves the mobile phones in that cellular area. |
| 6 | International roaming | Less Accessible | Most Accessible |
| 7 | Frequency band | Single (850 MHz) | Multiple (850/900/1800/1900 MHz) |
| 8 | Network service | Handset specific | SIM specific. User has option to select handset of his choice. |
What is GPRS?
GPRS is a system used to transmit data at speeds of up to 60 Kbits per second and is a battery-friendly way to send and receive emails and to browse the internet but in these days of broadband connectivity, it will be seen as slow by some.
What is EDGE?
EDGE (Exchanged Data rates for GSM Evolution) is a recent development based on the GPRS system and has been classified as a ‘3G’ standard due to the fact that it can run at up to 473.6 Kbits per second. If a smartphone is EDGE compliant it can be used for heavy mobile data transmission such as receiving large email attachments and browsing complex web pages at great speed.
What is HSDPA?
HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access) is a technology-based on the 3G network which can support speeds of up to 7.2 Mbits per second. In reality, you will most likely get a top speed of around 3 Mbits but this is useful for mobile TV streaming and other high-end data transmissions. To use HSDPA your phone must be able to support the technology and of course, you will need to be located within range of a cell site that has been upgraded to offer the service.
What is HSPA (Plus)?
- This is an evolution of the HSPA (HSDPA & HSUPA) standard and allows for faster speeds. The maximum download speed allowed by the standard is 168 Mbit/s although in reality networks that support HSPA (plus) will offer 21 Mbit/s downloads. This is because the existing 3G network architecture operators would have deployed and made compatible was never designed to handle such massive bandwidth.
- The operators need additional spectrum to improve the quality of services. The Government should formulate a spectrum policy that will promote efficient use of spectrum by developing market incentives and differential pricing of spectrum in congested areas. An open and transparent auction format will ensure that the government realizes the best price for spectrum as per the market forces and at the same time the telecom operators minimize and efficiently use the spectrum.
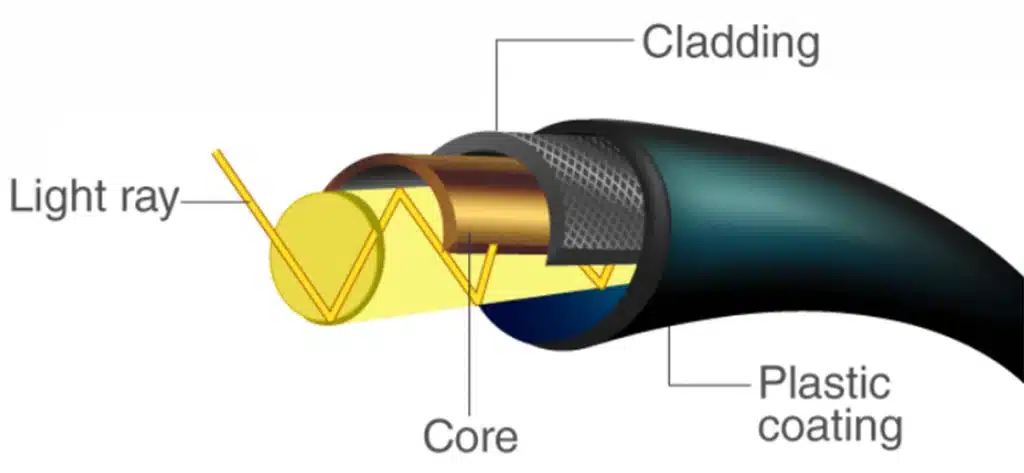
OPTICAL FIBRE Technology
- Fibre-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information.
- Fibre is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long-distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required.
- Optical fibre is made up of semiconducting materials and usually has a cylindrical structure. In inner core, there is the material of higher refractive index than in the outer core resulting in Total Internal Reflection (TIR).
Free-Space optical communication (FSO)
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. “Free-space” means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable.
It is a Line of Sight (LOS) technology. It consists of an optical transceiver at both ends to provide full duplex (bidirectional) capability.
It is capable of sending up to 1.25 Gbps of data, voice, and video communications simultaneously through the air.
Advantages: low initial investment, flexible network that delivers better speed than broadband, security due to line of sight operation, etc.
Challenges: misalignment errors, geometric losses, background noise, weather attenuation losses and atmospheric turbulence.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID)
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically-stored information.
Passive tags collect energy from a nearby RFID reader’s interrogating radio waves. Active tags have a local power source (such as a battery) and may operate hundreds of meters from the RFID reader.
Unlike a barcode, the tag need not be within the line of sight of the reader, so it may be embedded in the tracked object. RFID is one method for Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC).
RFID can be used in a variety of applications, such as:
- The electronic key for RFID based lock system
- Access management
- Tracking of goods
- Tracking of persons and animals
- Toll collection and contactless payment
- Machine-readable travel documents
- Smartdust (for massively distributed sensor networks)
- Airport baggage tracking logistics
- Timing sporting events
- Tracking and billing processes
RFID provides a way for organizations to identify and manage stock, tools, and equipment (asset tracking), etc. without manual data entry.
RFID is used for item-level tagging in retail stores. In addition to inventory control, this provides both protection against theft by customers (shoplifting) and employees (“shrinkage”) by using electronic article surveillance (EAS), and a self-checkout process for customers.
Yard management, shipping and freight, and distribution centers use RFID tracking. In the railroad industry, RFID tags mounted on locomotives and rolling stock identify the owner, identification number, and type of equipment and its characteristics. This can be used with a database to identify the lading, origin, destination, etc. of the commodities being carried.
BIG DATA
Big data is a term used to refer to the study and applications of data sets that are so big and complex that traditional data-processing application software is inadequate to deal with them. Big data challenges include capturing data, data storage, data analysis, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source.
There are a number of concepts associated with big data: originally there were three concepts volume, variety, velocity. Other concepts later attributed to big data are veracity (i.e., how much noise is in the data) and value.
Big data can be described by the following characteristics:
- Volume – The quantity of generated and stored data. The size of the data determines the value and potential insight, and whether it can be considered big data or not.
- Variety – The type and nature of the data. This helps people who analyze it to effectively use the resulting insight. Big data draws from text, images, audio, video; plus it completes missing pieces through data fusion.
- Velocity – In this context, the speed at which the data is generated and processed to meet the demands and challenges that lie in the path of growth and development. Big data is often available in real-time.
- Veracity – The data quality of captured data can vary greatly, affecting the accurate analysis.
Applications–
Government –
Big data is being increasingly used by the government in policy formation. The use and adoption of big data within governmental processes allow efficiencies in terms of cost, productivity, and innovation, but does not come without its flaws.
International development –
Research on the effective usage of information and communication technologies for development (also known as ICT4D) suggests that big data technology can make important contributions but also present unique challenges to International development. Advancements in big data analysis offer cost-effective opportunities to improve decision-making in critical development areas such as health care, employment, economic productivity, crime, security, and natural disaster and resource management.
Manufacturing–
A conceptual framework of predictive manufacturing begins with data acquisition where different type of sensory data is available to acquire such as acoustics, vibration, pressure, current, voltage, and controller data. The vast amount of sensory data in addition to historical data construct big data in manufacturing. The generated big data acts as the input into predictive tools and preventive strategies such as Prognostics and Health Management (PHM).
Healthcare–
Big data analytics has helped healthcare improve by providing personalized medicine and prescriptive analytics, clinical risk intervention and predictive analytics, waste and care variability reduction, automated external and internal reporting of patient data, standardized medical terms, and patient registries and fragmented point solutions.
Education–
A McKinsey Global Institute study found a shortage of 1.5 million highly trained data professionals and managers and a number of universities including the University of Tennessee and UC Berkeley, have created master’s programs to meet this demand. Private boot camps have also developed programs to meet that demand, including free programs like The Data Incubator or paid programs like General Assembly.
Media–
- Targeting of consumers (for advertising by marketers)
- Data capture
- Data journalism: publishers and journalists use big data tools to provide unique and innovative insights and infographics.
Insurance–
Health insurance providers are collecting data on social “determinants of health” such as food and TV consumption, marital status, clothing size and purchasing habits, from which they make predictions on health costs, in order to spot health issues in their clients. It is controversial whether these predictions are currently being used for pricing.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Big data and the IoT work in conjunction. Data extracted from IoT devices provides a mapping of device interconnectivity. Such mappings have been used by the media industry, companies, and governments to more accurately target their audience and increase media efficiency. IoT is also increasingly adopted as a means of gathering sensory data, and this sensory data has been used in medical, manufacturing, and transportation contexts.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE)
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a system of communication where only communicating users can read the messages. In principle, it prevents potential eavesdroppers – including telecom providers, Internet providers, and even the provider of the communication service – from being able to access the cryptographic keys needed to decrypt the conversation.
Point-to-point encryption (P2PE)
Point-to-point encryption (P2PE) is a standard established by the PCI Security Standards Council. Payment solutions that offer similar encryption but do not meet the P2Pe standard are referred to as end-to-end encryption (E2Ee) solutions. The objective of P2Pe and E2Ee is to provide a payment security solution that instantaneously converts confidential payment card (credit and debit card) data and information into indecipherable code at the time the card is swiped to prevent hacking and fraud. It is designed to maximize the security of payment card transactions in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
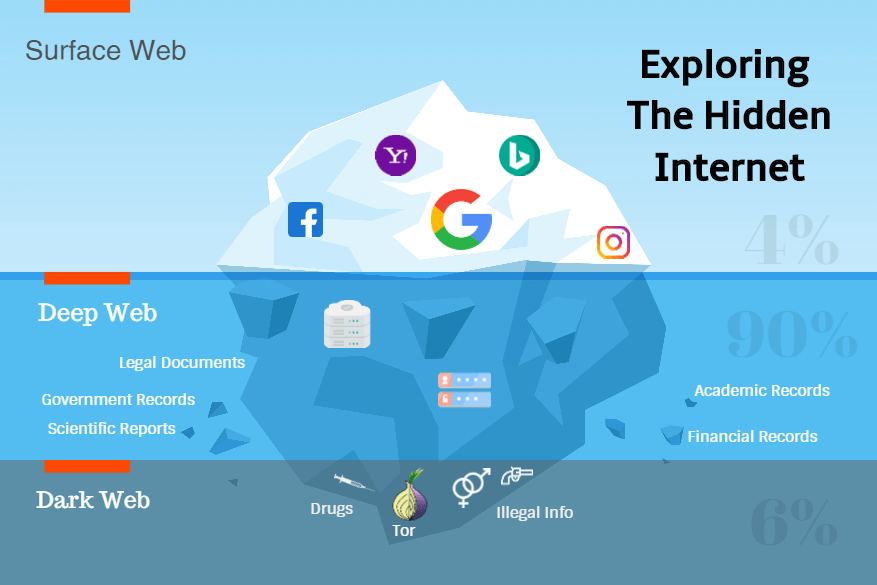
DEEP WEB
The deep web, invisible web, or hidden webs are parts of the World Wide Web whose contents are not indexed by standard web search engines for any reason. The opposite term to the deep web is the surface web, which is accessible to anyone using the Internet. Computer scientist Michael K. Bergman is credited with coining the term deep web in 2001 as a search indexing term.
The content of the deep web is hidden behind HTTP forms and includes many very common uses such as webmail, online banking, and services that users must pay for, and which is protected by a paywall, such as a video on demand, some online magazines, and newspapers, and many more.
Content of the deep web can be located and accessed by a direct URL or IP address and may require a password or other security access past the public website page.
DARK WEB
The dark web is the World Wide Web content that exists on darknets, overlay networks that use the Internet but require specific software, configurations, or authorization to access. The dark web forms a small part of the deep web, the part of the Web not indexed by web search engines, although sometimes the term deep web is mistakenly used to refer specifically to the dark web.
The darknets which constitute the dark web include small, friend-to-friend peer-to-peer networks, as well as large, popular networks like Tor, Freenet, I2P, and Riffle operated by public organizations and individuals. Users of the dark web refer to the regular web as Clearnet due to its unencrypted nature.
The Tor dark web may be referred to as Onionland, a reference to the network’s top-level domain suffix. onion and the traffic anonymization technique of onion routing.
WANNACRY
The WannaCry ransomware attack was a May 2017 worldwide cyberattack by the WannaCry ransomware cryptoworm, which targeted computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system by encrypting data and demanding ransom payments in the Bitcoin cryptocurrency.
It propagated through EternalBlue, an exploit in older Windows systems released by The Shadow Brokers a few months prior to the attack.
While Microsoft had released patches previously to close the exploit, much of WannaCry’s spread was from organizations that had not applied these or were using older Windows systems that were past their end-of-life. WannaCry also took advantage of installing backdoors onto infected systems.
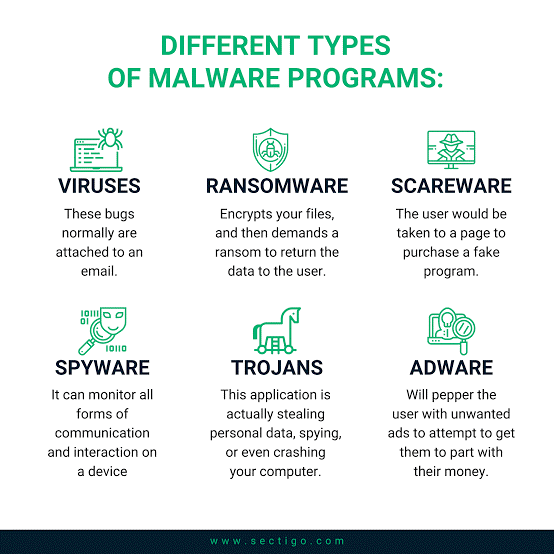
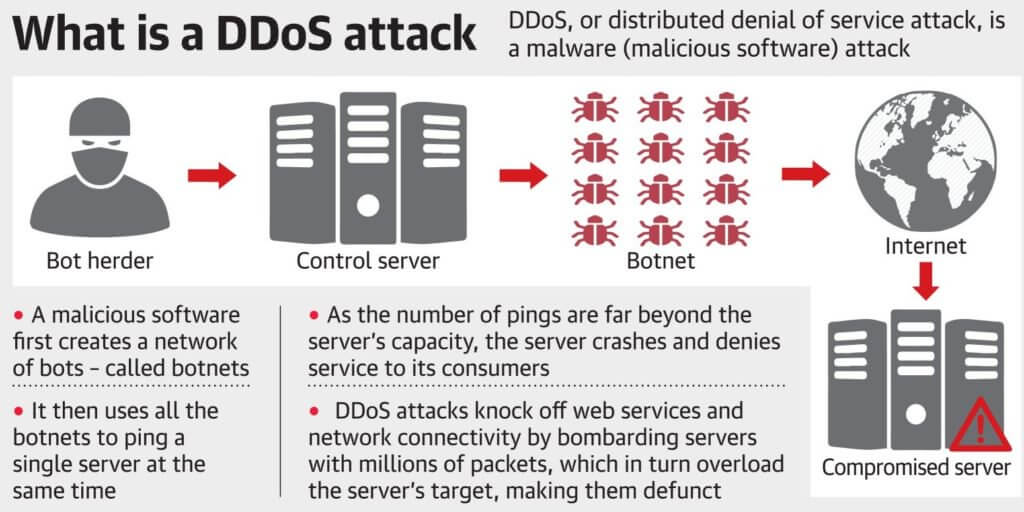
BOTNET
A botnet is a number of Internet-connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), steal data, send spam, and allows the attacker to access the device and its connection. The owner can control the botnet using command and control (C&C) software. The word “botnet” is a combination of the words “robot” and “network”. The term is usually used with a negative or malicious connotation.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attack
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack is an illegal large-scale cyber campaign where a big number of devices are used to create traffic to a certain server.
If the number of devices involved is big enough, the overwhelming traffic would be more than what the targeted server is capable of handling.
The malware first creates a network of bots — called a botnet — and then uses the botnet to ping a single server at the same time.
In such a case, the server would get overburdened which would lead to crashes. After a successful DDoS attack, the customers of the service that had its servers targeted would not be able to use/access the said service due to the server crash triggered by the DDoS attacks.
Reaper is a highly evolved malware capable of not only hacking devices like WiFi routers and security cameras, but also able to hide its own presence in the bot — a device taken over by malware.
Spectrum Pooling
Spectrum pooling is a spectrum management strategy in which multiple radio spectrum users can coexist within a single allocation of radio spectrum space. One use of this technique is for primary users of a spectrum allocation to be able to rent out use of unused parts of their allocation to secondary users. Spectrum pooling schemes generally require cognitive radio techniques to implement them.
Cognitive Radio
A cognitive radio (CR) is a radio that can be programmed and configured dynamically to use the best wireless channels in its vicinity to avoid user interference and congestion. Such a radio automatically detects available channels in wireless spectrum, then accordingly changes its transmission or reception parameters to allow more concurrent wireless communications in a given spectrum band at one location. This process is a form of dynamic spectrum management.
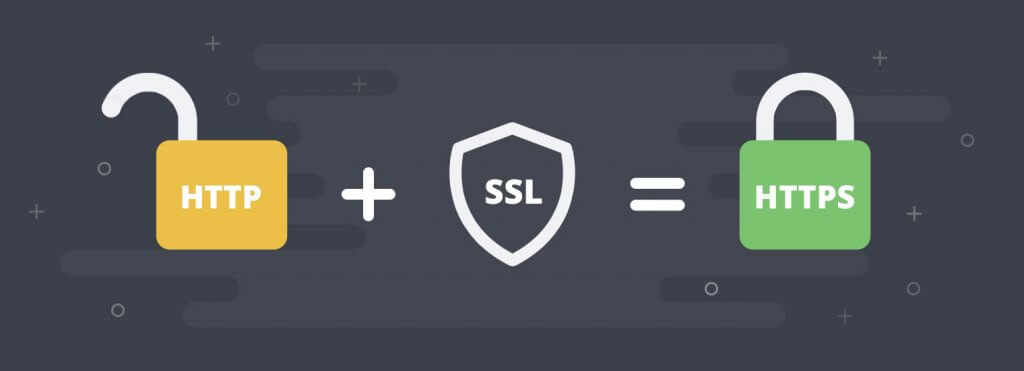
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for secure communication over a computer network and is widely used on the Internet.
The principal motivation for HTTPS is authentication of the accessed website and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks.
The bidirectional encryption of communications between a client and server protects against eavesdropping and tampering of the communication. In practice, this provides a reasonable assurance that one is communicating without interference by attackers with the website that one intended to communicate with, as opposed to an impostor.
QUANTUM COMPUTER
Quantum computing is computing using quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement. A quantum computer is a device that performs quantum computing. Such a computer is different from binary digital electronic computers based on transistors.
Whereas common digital computing requires that the data be encoded into binary digits (bits), each of which is always in one of two definite states (0 or 1), quantum computation uses quantum bits or qubits, which can be in superpositions of states. The qubit is the basic unit of quantum computing and the subatomic equivalent of the binary system comprising 0s and 1s that we use today.
It uses binary properties of particles, electron spin (up and down), photon polarization (positive and negative), etc, but, much like Schrödinger’s cat, can actually be in both states simultaneously, a phenomenon called superposition.
Physicists have observed that when one particle is observed, it seems to affect the state of the completely different, opposite particle in a phenomenon called entanglement. This is the basis of quantum computing and communication.
QUANTUM SUPREMACY
- Quantum supremacy is the ability to use a quantum computer to perform a single calculation that no conventional computer, even the biggest supercomputer, can perform in a reasonable amount of time.
- Google researchers claim to have achieved a major milestone in computer science known as “quantum supremacy.”.
- The Google research involved checking whether the output of an algorithm for generating random numbers was truly random. The researchers were able to use a quantum computer to perform this complex mathematical calculation in three minutes and 20 seconds, according to the paper.
- It is claimed that it would have taken Summit 3—an IBM-built machine that is the world’s most powerful commercially-available conventional computer—about 10,000 years to perform the same task.
Sycamore – Sycamore is Google’s state-of-the-art quantum computer that was used for Quantum
Supremacy.
Quantum-Enabled Science & Technology (QuEST) Programme
India is starting work on building infrastructure and acquiring human resources in the first phase of its push to develop quantum computers under the Department of Science & Technology’s (DST’s) -Quantum-Enabled Science & Technology (QuEST) program.
Currently, QuEST is being funded by the DST, which has put in Rs 80 crore for Phase 1. After three years, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), and the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) are expected to jointly fund Phase 2 with Rs 300 crore.
Blockchain
Blockchains are basically digital ledgers or decentralized database of financial transactions that are immutable and instantly updated across the world.
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way”. For use as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is typically managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for inter-node communication and validating new blocks.
Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority.
Although blockchain records are not unalterable, blockchains may be considered secure by design and exemplify a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance. Decentralized consensus has therefore been claimed with a blockchain.
Blockchain was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 to serve as the public transaction ledger of the cryptocurrency bitcoin. The invention of the blockchain for bitcoin made it the first digital currency to solve the double-spending problem without the need for a trusted authority or central server.
The bitcoin design has inspired other applications, and blockchains that are readable by the public are widely used by cryptocurrencies. Private blockchains have been proposed for business use. Some marketing of blockchains has been called “snake oil”.
BITCOIN
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, a form of electronic cash. It is a decentralized digital currency without a central bank or single administrator that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries.
Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. Bitcoin was invented by an unknown person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto and released as open-source software in 2009. Bitcoins are created as a reward for a process known as mining. They can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services.
Bitcoin has been criticized for its use in illegal transactions, its high electricity consumption, price volatility, thefts from exchanges, and the possibility that bitcoin is an economic bubble. Bitcoin has also been used as an investment, although several regulatory agencies have issued investor alerts about bitcoin.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
AI, is the “science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs”. AI enables intelligent machines that can execute functions, similar to human abilities like speech, facial, object or gesture recognition, learning, problem-solving, reasoning, perception and response.
AI enables machines to think intelligently, somewhat akin to the intelligence human beings employ to learn, understand, think, decide, or solve a problem in their daily personal or professional lives. Intelligence is intangible.
The present wave of enthusiasm in AI is backed by the industry, with Apple, Amazon, Google, Facebook, IBM, Microsoft, and Baidu in the lead. Automotive industry is also unleashing benefits of AI for self-driving cars, led by Tesla, Mercedez-Benz, Google, and Uber.
Real-world examples from around us:
- AI-empowered cars are already under rigorous testing and they are quite likely to ply on the roads soon.
- The social humanoid robot Sophia became a citizen of Saudi Arabia in 2017.
- Apple’s intelligent personal assistant, Siri, can receive instructions and interact with human beings in natural language.
- Autonomous weapons can execute military missions on their own, identify and engage targets without any human intervention.
- Facial detection has instated deep interest from law enforcement and security agencies.
- China is known to be building a massive facial recognition system, connected with its surveillance camera networks, to assist in detecting criminals and fugitives.
- AI is also changing the ways militaries command, train, and deploy their forces.
Applications of AI
The gaming industry, where AI-empowered computers can think of a large number of possible positions in games such as chess, poker, and go. These computers can test the skills of the human beings who are playing against these AI-enabled computers, in games or simulations which require the greater mathematical and strategic depth.
Computers with natural language processing capability can understand and generate human language, including speech, imitating human capabilities of listening, comprehending, thinking, and responding.
Law enforcement or internal security requirements for detecting and recognizing individuals or criminals, with multitudes of data streaming from police databases or the network of surveillance cameras.
Healthcare industry to design optimized treatment plans, assistance in repetitive jobs, data management for medical records, or even assistance in clinical decision making with better analysis of diagnostics and interpretation of clinical laboratory results.
Banking and financial services for fraud detection using advanced algorithms to identify patterns in transactions and consumer behaviors that are risk-prone.
The automotive industry is already using AI algorithms to enhance fuel efficiency and safety in vehicles to build features such as automatic braking, collision avoidance systems, alerts for pedestrians and cyclists, and intelligent cruise controls.
DEEP LEARNING
It is an aspect of artificial intelligence (AI) that is concerned with emulating the learning approach that human beings use to gain certain types of knowledge. At its simplest, deep learning can be thought of as a way to automate predictive analytics.
While traditional machine learning algorithms are linear, deep learning algorithms are stacked in a hierarchy of increasing complexity and abstraction. To understand deep learning, imagine a toddler whose first word is the dog. The toddler learns what a dog is (and is not) by pointing to objects and saying the word dog. The parent says, “Yes, that is a dog,” or, “No, that is not a dog.” As the toddler continues to point to objects, he becomes more aware of the features that all dogs possess. What the toddler does, without knowing it, is clarify a complex abstraction (the concept of dog) by building a hierarchy in which each level of abstraction is created with knowledge that was gained from the preceding layer of the hierarchy.
MACHINE LEARNING
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning focuses on the development of computer programs that can access data and use it to learn for themselves.
The process of learning begins with observations or data, such as examples, direct experience, or instruction, in order to look for patterns in data and make better decisions in the future based on the examples that we provide. The primary aim is to allow the computers to learn automatically without human intervention or assistance and adjust actions accordingly.
The key difference between AI and ML are:
| ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE | MACHINE LEARNING |
|---|---|
| AI stands for Artificial intelligence, where intelligence is defined acquisition of knowledge intelligence is defined as an ability to acquire and apply knowledge. | ML stands for Machine Learning which is defined as the acquisition of knowledge or skill |
| The aim is to increase the chance of success and not accuracy. | The aim is to increase accuracy, but it does not care about the success |
| It works like a computer program that does smart work | It is a simple concept machine that takes data and learns from data. |
| The goal is to simulate natural intelligence to solve a complex problem | The goal is to learn from data on a certain task to maximize the performance of the machine on this task. |
| AI is decision making. | ML allows the system to learn new things from data. |
| It leads to developing a system to mimic human to respond to behave in circumstances. | It involves creating self-learning algorithms. |
| AI will go for finding the optimal solution. | ML will go for the only solution for that whether it is optimal or not. |
| AI leads to intelligence or wisdom. | ML leads to knowledge. |
Project Brainwave
Microsoft has launched “Project Brainwave”, a deep learning acceleration platform for real-time artificial intelligence (AI).
It uses the massive field-programmable gate array (FPGA) infrastructure.
The system architecture allows very high throughput, with the FPGA processing requests as fast as the network can stream them.
Significance: Real-time AI is becoming increasingly important as cloud infrastructures process live data streams, whether they be search queries, videos, sensor streams, or interactions with users.
Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot is a robot with its body shape built to resemble the human body. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of al locomotion, or for other purposes.
In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some forms of humanoid robots may model only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans.
Features of Humanoid Robots –
- Self-maintenance
- Autonomous learning
- Avoiding harmful situations to people, the property, and itself
- Safe interacting with human beings and the environment
Humanoid Robot Sophia became the world’s first robot citizen as Saudi Arabia granted citizenship to her in a bid to promote artificial intelligence.
Sophia
Sophia is a social humanoid robot developed by Hong Kong-based company Hanson Robotics. Sophia was activated on April 19, 2015. She is able to display more than 50 facial expressions.
In November 2017, Sophia was named the United Nations Development Programme’s first-ever Innovation Champion, and the first non-human to be given any United Nations title.
Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL)
Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) is a pioneer initiative of India to prevent misappropriation of the country’s traditional medicinal knowledge at International Patent Offices on which healthcare needs of more than 70% population and livelihood of millions of people in India is dependent. Its genesis dates back to the Indian effort on the revocation of the patent on wound healing properties of turmeric at the USPTO.
Besides, in 2005, the TKDL expert group estimated that about 2000 wrong patents concerning Indian systems of medicine were being granted every year at the international level, mainly due to the fact that India’s traditional medicinal knowledge which exists in local languages such as Sanskrit, Hindi, Arabic, Urdu, Tamil, etc. is neither accessible nor comprehensible for patent examiners at the international patent offices.
Traditional Knowledge Digital Library has overcome the language and format barrier by scientifically converting and structuring the available contents (till date 0.29 million medicinal formulations) of the ancient texts on Indian Systems of Medicines i.e. Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, and Yoga, into five international languages, namely, English, Japanese, French, German and Spanish, with the help of information technology tools and an innovative classification system – Traditional Knowledge Resource Classification (TKRC).
TKRC has structured and classified the Indian Traditional Medicine System in approximately 25,000 subgroups for Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha, and Yoga. TKRC has enabled the incorporation of about 200 subgroups under A61K 36/00 in International Patent Classification instead of a few sub-groups earlier available on medicinal plants under A61K 35/00 thus enhancing the quality of search and examination of prior-art with respect to patent applications filed in the area of traditional knowledge.
TKDL has also been able to set international specifications and standards for setting up to TK databases based on TKDL specifications. This was adopted in 2003 by the Committee in the fifth session of the
Intergovernmental Committee (IGC) of WIPO on Intellectual Property and Genetic Resources, Traditional Knowledge and Expression of folklore.
TKDL technology integrates diverse disciplines and languages such as Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha, Yoga, Sanskrit, Arabic, Urdu, Persian, Tamil, English, Japanese, Spanish, French, German, modern science &
modern medicine.
Till date, TKDL is based on 359 books of Indian Systems of Medicine, which are available at a cost of approx US$ 1000, in the open domain, and can be sourced by any individual/organization at the national/international level. TKDL acts as a bridge between these books (Prior-art) and International patent examiners. It is the TKDL technology that has created a unique mechanism for a Sanskrit verse to be read in languages like German, Japanese, English, Spanish and French by an examiner at any International Patent Office on his computer screen.
At present, as per the approval of the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, access of TKDL is available to nine International Patent Offices (European Patent Office, United State Patent & Trademark Office, Japan Patent Office, United Kingdom Patent Office, Canadian Intellectual Property Office, German Patent Office, Intellectual Property Australia, Indian Patent Office, and Chile Patent Office), under TKDL Access (Non-disclosure) Agreement. Negotiations are underway to conclude the Access Agreement with the Intellectual Property Office of Russia and Malaysia.
As per the terms and conditions of the Access Agreement, examiners of the patent office can utilize TKDL for search and examination purposes only and cannot reveal the contents of TKDL to any third party unless it is necessary for the purpose of citation. TKDL Access Agreement is unique in nature and has in-built safeguards on Nondisclosure to protect India’s interest against any possible misuse.
In addition, pre-grant oppositions are being filed at various International Patent Offices, along with prior-art evidence from TKDL. A significant impact has already been realized. So far about 200 patent applications of the pharmaceutical companies of the United States, Great Britain, Spain, Italy, China, etc. have either been set aside/ withdrawn/ amended, based on the Prior art evidences present in the
TKDL database without any cost and in few weeks/months of time, whereas APEDA had to spend
about seven crores towards legal fee only for getting few claims of Basmati rice patent revoked. A similar
outcome is expected in about 1200 more cases, where TKDL has filed pre-grant opposition.
TKDL is proving to be an effective deterrent against bio-piracy and is being recognized as a global leader in the area of traditional knowledge protection. In 2011, an International Conference was organized by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in collaboration with CSIR on ‘Utilization of Traditional Knowledge Digital Library as a Model for Protection of Traditional Knowledge’, at New Delhi. Pursuant to this, WIPO in collaboration with CSIR and DIPP (Ministry of Commerce and Industry) organized an ‘International Study Visit To TKDL’ for 19 countries interested in the replication of TKDL.
TKDL has made waves around the world, particularly in TK-rich countries by demonstrating the advantages of proactive action and the power of strong deterrence. The idea is not to restrict the use of traditional knowledge, but to ensure that wrong patents are not granted due to lack of access to the prior art for Patent examiners.
For entering into TKDL Access Agreement by a Patent Office, Head, CSIR Traditional Knowledge Digital Library Unit may be contacted.
Digiceuticals
What if an app could replace a pill? That’s the big question behind an emerging trend known as “digital therapeutics.” The idea: software that can improve a person’s health as much as a drug can, but without the same cost and side-effects.
Digital therapeutics, or “digiceuticals,” as some call them, have become a Holy Grail in some quarters of Silicon Valley, where investors see the chance to deliver medicine through your smartphone.
Some digiceuticals will work better alongside conventional drugs, rather than on their own– opening up possibilities for alliances between tech and pharma firms. Voluntis, a startup, develops companion software for specific medications or medical devices. These programs can monitor side-effects, help manage symptoms and connect patients with doctors and nurses.
CIMON (CREW INTERACTIVE MOBILE COMPANION)
- It is a 3D-printed artificial intelligence system, described by its creators as a “flying brain”.
- It is made up of plastic and metal, created using 3D printing
- It is being developed by Airbus; an aeronautics company based in the Netherlands
- It will be the first AI-based mission and flight assistance system
- It will join the crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to assist astronauts.
- It is designed to support astronauts in performing routine work.
Cryptojacking
- Cryptojacking is defined as the secret use of your computing device to mine cryptocurrency.
- Cryptojacking used to be confined to the victim unknowingly installing a program that secretly mines cryptocurrency
- Attackers employ malware to force an entry into the computers of remote users and then using their hardware to mine for coins.
- This form of distributed computing can be profitable since it eliminates the cost burden of owning a mining rig with hundreds of processors.
- Cryptojackers usually target popular websites that draw audiences numbering in the millions every day.
Haptic Communication
Haptic communication is a technology that transmits the sensation of touch over the Internet, had been developed by engineers in the Virtual Reality Laboratories at the University at Buffalo (UB).
The breakthrough leads to the creation of haptic technologies that convey the sense of touch and taught users how to master skills and activities — such as surgery, sculpture, playing the drums or even golf – that require the precise application of ‘touch’ and movement.
DigiShala
DigiShala, a free Doordarshan DTH channel is launched to educate and inform people about the various modes of digital payments. DigiShala will be available through GSAT15 (DD Direct DTH), 93.5 degree East, Receive frequency: 11590 Mhz
The channel will help people understand the use of a unified payments interface (UPI), USSD, aadhar-enabled payments system, electronic wallets, debit, and credit cards.
A website was also launched which will serve as a repository of knowledge regarding digital payments.
Both the channel and website were launched as a part of the ‘Digi Dhan Abhiyan’, a campaign conceptualized by the IT ministry to enable every citizen, small trader and merchant to adopt digital payments in their everyday financial transactions.
Significance:
- DigiShala will enable and empower every citizen of the country, especially farmers, students, Dalits and women in rural areas to learn the usefulness and benefits of digital payment in our everyday life to adopt the same on a mass scale.
- The provision of digital literacy to the semi-urban and rural sectors of the economy has become the major focus area for the government.
COMPUTER FIREWALL
A firewall is a system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. You can implement a firewall in either hardware or software form, or a combination of both. Firewalls prevent
unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets.
All messages entering or leaving the intranet (i.e., the local network to which you are connected) must pass through the firewall, which examines each message and blocks those that do not meet the specified security criteria.
In protecting private information, a firewall is considered a first line of defense; it cannot, however, be considered the only such line. Firewalls are generally designed to protect network traffic and connections, and therefore do not attempt to authenticate individual users when determining who can access a particular computer or network.
CYBER-ATTACKS
Cyber-attacks involve the unauthorized access of private or confidential information contained on computer systems or networks, but the techniques and methods used by the attacker further distinguish whether the attack is an active cyber-attack, a passive type attack, or some combination of the two.
According to Symantec, both active and passive cyber-attack types are defined by unique characteristics and techniques, and each type of attack presents unique challenges to victims, system users, system administrators, and cybersecurity professionals.
Knowing the difference between passive and active cyber-attacks can help system users and administrators identify when an attack is taking place so that action can be taken to try and contain the attack.
Active Cyber Attacks
Active cyber-attacks are often aggressive, blatant attacks that victims immediately become aware of when they occur. Active attacks are highly malicious in nature, often locking out users, destroying memory or files, or forcefully gaining access to a targeted system or network. Viruses, worms, malware, Denial of Service attacks, and password crackers are all examples of active cyber-attacks. Usually, hackers that use active attacks are not much concerned with their activities being detected because by the time the attack is detected the damage is already done or is underway.
Passive Cyber Attacks
Passive cyber-attacks often employ non-disruptive and covert methods so that the hacker does not draw attention to the attack. The purpose of the passive attack is to gain access to the computer system or network and to collect data without detection. Many data security breaches involving the exposure of credit card and debit card payment information are the result of passive attacks, as are data breaches where the targeted data collected during the attack is user name, passwords, and other personal identifying information.
Passive attacks are usually data-gathering operations, which means they usually employ some sort of malware or hack that eavesdrops on system communications (i.e., scrubs email for personal identifying information) or records system communications (i.e., keystroke recording malware). Information that is gathered in a passive cyber-attack is usually sold on the black market and dark web for the financial
the gain of whoever perpetrated the passive attack.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
A Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) is a secure digital key that certifies the identity of the holder, issued by a Certifying Authority (CA). It typically contains your identity (name, email, country, APNIC account name, and your public key).
- Digital Certificates use Public Key Infrastructure meaning data that has been digitally signed or encrypted by a private key and can only be decrypted by its corresponding public key. A digital certificate is an electronic “credit card” that establishes your credentials when doing business or other transactions on the Web.
- Digital Signatures are legally admissible in a Court of Law, as provided under the provisions of IT Act, 2000.
Open-source software (OSS)
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software with its source code made available with a license in which the copyright holder provides the rights to study, change, and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner.
- The main occurrence of open-source sharing goes back to even before the primary PC was created. In 1911, progressive automaker Henry Ford was instrumental in propelling the Motor Vehicle Manufacturers Association. This affiliation propelled an open-source activity that saw real US vehicle makers sharing innovation licenses straightforwardly without looking for any money related advantages consequently.
Software-defined Radio
- Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by means of software on a personal computer or embedded system.
- A basic SDR system may consist of a personal computer running SDR software that interfaces with analog-to-digital converter over USB or ethernet, preceded by some form of RF front end with RF amplifiers, filters, and attenuators.
LIDAR-(Light Detection and Ranging)
- LIDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth.
- A LIDAR instrument principally consists of a laser, a scanner, and a specialized GPS receiver. Airplanes and helicopters are the most commonly used platforms for acquiring LIDAR data over broad areas.
- Two types of LIDAR are topographic and bathymetric.
- Topographic LIDAR typically uses a near-infrared laser to map the land, while bathymetric lidar uses water-penetrating green light to also measure seafloor and riverbed elevations.

Sir is this Available in pdf format
thank you
Thank you for the content