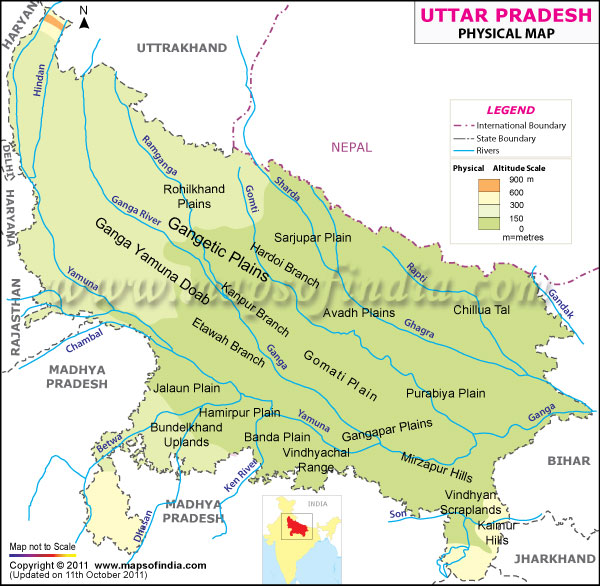
- Uttar Pradesh is well drained by a number of rivers except the Bundelkhand region. The state is drained by Himalayan as well as Peninsular rivers. The main river along with its tributaries create the drainage system or river basin.
- The major drainage regions of Uttar Pradesh can be broadly classified into four regions based on their respective river systems. These are:
- Ganga Basin: The Ganga basin is the largest drainage region in Uttar Pradesh, covering about two-thirds of the state’s area. It comprises the Ganga and its major tributaries like Yamuna, Ghaghara, and Gomti. This region is known for its fertile alluvial plains and is home to some of the most populous cities in the state, including Varanasi, Allahabad, and Kanpur.
- Betwa Basin: The Betwa basin is located in the southern part of Uttar Pradesh and covers the districts of Hamirpur, Jalaun, and Lalitpur. The main river in this basin is the Betwa, which is a major tributary of the Yamuna. This region is characterized by hilly terrain, with some areas being covered by forests.
- Son Basin: The Son basin is situated in the southeastern part of Uttar Pradesh and covers the districts of Sonbhadra and Mirzapur. The Son River, which originates in Madhya Pradesh and flows through this region, is the main river in this basin. The region is hilly and is home to a number of wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
- Gomti Basin: The Gomti basin is located in the central part of Uttar Pradesh and covers the districts of Lucknow, Sitapur, and Faizabad. The Gomti River, which flows through this region, is a major tributary of the Ganga. The region is characterized by fertile alluvial plains and is known for its rich cultural heritage.
- Ganga river basin is the major river basin in Uttar Pradesh. Ganga Basin in India is spread in approximately 861,404 sq km area. Out of this approximately 34.17% lies combinedly in Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- The Himalayan rivers in Uttar Pradesh follow a general flow pattern of north-west to south-east. Peninsular rivers flowing in the southern plateau region follow south to north relief.
- The rivers of Uttar Pradesh are divided into three categories:
- Himalayan Rivers
- Peninsular Rivers
- Rivers originating from Plains
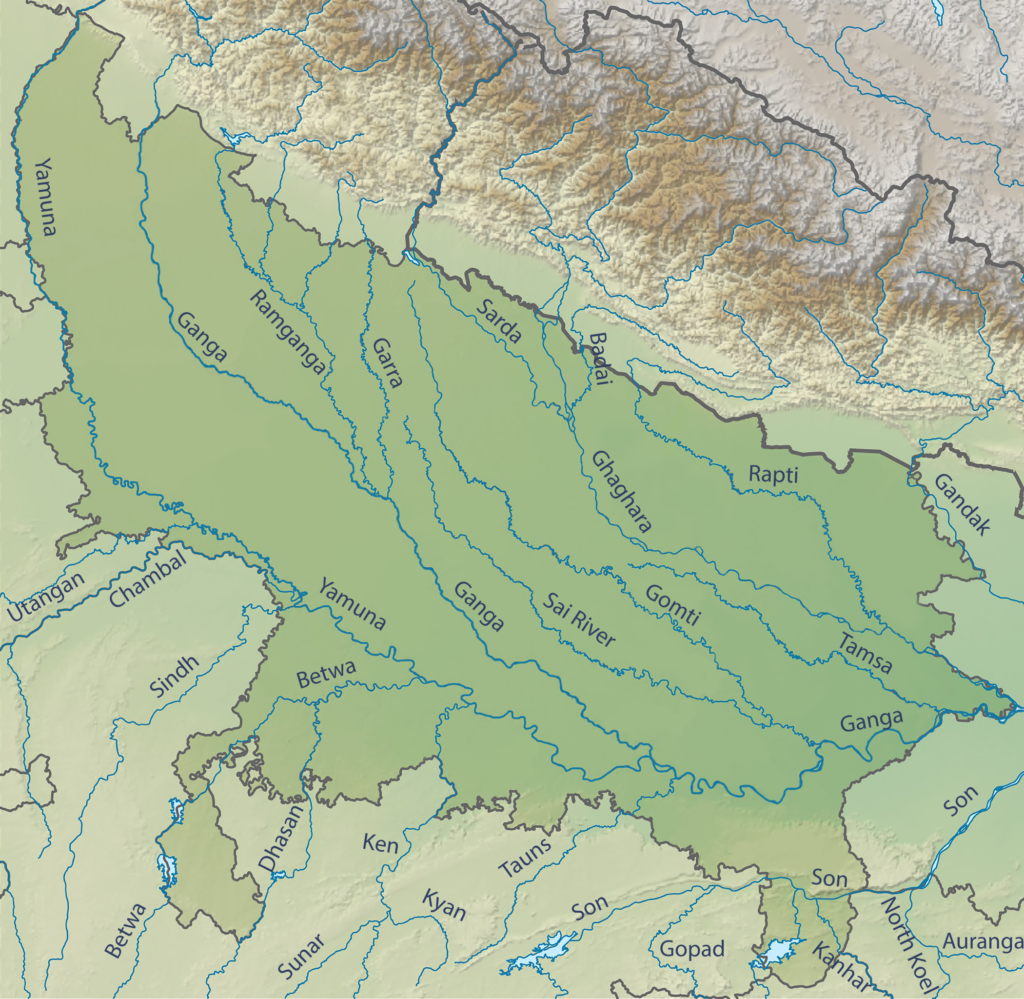
Himalayan Rivers
Himalayan rivers are perennial and receive their water from Himalayan glaciers. Among the Himalayan rivers, Ganga and its tributaries flow in Uttar Pradesh.
Ganga
- The Ganga originates from Gangotri glacier at Gaumukh in Uttarkashi District of Uttarakhand, as Bhagirathi.
- Bhagirathi is joined by Alaknanda at Devprayag and from there the river is known as Ganga.
- It has a total length of 2,525 km and approximately 1,000 km in Uttar Pradesh. It is the longest river of India as well as of Uttar Pradesh. It drains into the Bay of Bengal.
- Ganga appears in plains for the first time at Haridwar. It enters Uttar Pradesh through Bijnor. It flows through 28 districts of Uttar Pradesh and then enters Bihar through Balia.
- The longest waterway of India, National Waterway 1 or NW- 1 is situated on Ganga from Prayagraj to Haldia.
- Ganga was accorded the status of National River of India in 2008.
Panch Prayag
| Place of Confluence | Rivers |
|---|---|
| Vishnuprayag Nandprayag Karnprayag Rudraprayag Devprayag | Dhauli Ganga and Alaknanda Nandakini and Alaknanda Pinder and Alaknanda Mandakini and Alaknanda Bhagirathi and Alaknanda |
Tributaries of Ganga
| Left Bank (Northern) | Right Bank (Southern) |
|---|---|
| Kosi Gandak Sarayu Gomati Ramganga | Yamuna Tamasa Son Punpun Damodar |
Place of the Confluence of Ganga with its Tributaries
| Tributaries | Place of meeting |
|---|---|
| Ramganga Gomati Sarayu Gandak Kosi Son Yamuna Punpun Damodar | Kannauj Ghazipur Chhapra (Bihar) Hajipur (Bihar) Bhagalpur ( Bihar) Patna (Bihar) Prayagraj Fatuha (Near Patna) Shyampur, Howrah |
Yamuna
- The river Yamuna is also known as Kalindi. It is the longest and the most important tributary of Ganga. It originates from Yamunotri glacier near Bandarpunch Peak in Garhwal region of Uttarakhand.
- The river enters plains at Dakpathar in Uttarakhand. It gets highly polluted in its course through plains.
- Industrial effluents brought by Hindon are major contributor to the pollution of Yamuna. The Yamuna covers a total length of 1,376 kms and it joins Ganga at Prayagraj.
- Along with Ganga, it creates the highly fertile Ganga-Yamuna Doab region.
- Noida, Agra, Mathura and Etawah are major cities of Uttar Pradesh situated on its bank.
- Chambal, Betwa, Ken and Hindon are its major tributaries. The State Government has formulated a 30-year plan to revive the Yamuna river basin.
Tributaries of Yamuna
| Left Bank (None Peninsular) | Right Bank (Peninsular) |
|---|---|
| Hindon Tons Giri Rishi Ganga Hanuman Ganga Sasur Khaderi | Chambal Betwa Ken Sindh Bhagain |
Ramganga
- Ramganga is the first major left-bank tributary of Ganga. It originates from the Doodhatoli range in Garsain of Uttarakhand.
- It enters the plains at Kalagarh near Bijnor. A dam for irrigation and hydroelectricity purpose is built at Kalagarh.
- The river has an approximate length of 596 km and flows through the famous Jim Corbett National Park. Ramganga joins Ganga near Kannauj.
- Bareilly, Badaun, Moradabad, Rampurand Shahjahanpur are major cities situated on its banks.
- Ban, Khoh, Gangan and Bahugul are major tributaries.
Saryu or Ghagra
- It was earlier known as Ghagra. The State Government has decided to change its name to Saryu as mentioned in ancient scriptures.
- It is the largest left bank tributary of Ganga. It originates from Mapchachungo Glacier. It enters India after flowing through Nepal. It is known as Karnali in Nepal.
- Sharda, Rapti, Tedhi, Bisuhi and Chhoti Gandak are its main tributaries in plains. Its total length is 1,080 kms.
- It flows through Bahraich, Sitapur, Gonda, Barabanki, Ayodhya, Ambedkarnagar, Mau, Basti, Gorakhpur, Balia and Lakhimpur Kheri.
- Ayodhya is situated on its right bank. Rapti joins it at Barhaj in Deoria. It joins Ganga at Chhapra near Balia.
Sharda or Kali
- It originates from Milam Glacier in Kumaon Hills. It is known as Gori Ganga in Kumaon and Kali Ganga in the plains.
- Dharma and Leesad are its major tributaries. Its total length is 350 km and it flows along the Eastern Boundary with Nepal.
- The river enters into Uttar Pradesh from Pilibhit. The river merges with Saryu (Ghagra ) near Behramghat in Sitapur.
- The river has a huge potential for hydroelectric power. Mahakali Treaty was signed between India and Nepal for integrated development of the river.
- Upper Sharda Barrage, Lower Sharda Barrage and Tanakpur Barrage are situated on this river.
- Pancheshwar Multipurpose project is a proposed joint venture between India and Nepal.
Rapti
- It originates from Rukumkot of Nepal. The river is 640 km long.
- Rohini and Budhi Gandak are its major tributaries.
- It flows through Gorakhpur, Shravasti, Basti and Bahraich.
- Rohini joins its left bank at Gorakhpur. It merges with Ghagra near Barhaj in Deoria district.
- It is called sorrow of Gorakhpur.
Gandak
- It was known as Sadanira during Vedic times. It is also known as Shaligram and Narayani. It originates between Dhaulagiri, Annapurna and Mount Everest.
- It enters the plains in Champaran district of Bihar. Thereafter it flows towards the south-east. It forms the eastern boundary of Uttar Pradesh with Bihar. It flows along the borders of Maharajganj and Kushinagar districts of Uttar Pradesh.
- The river is known for frequent shifts in its course. It merges with Ganga at Hajipur in Bihar.
- Trishuli and Kali Gandaki are its major tributaries.
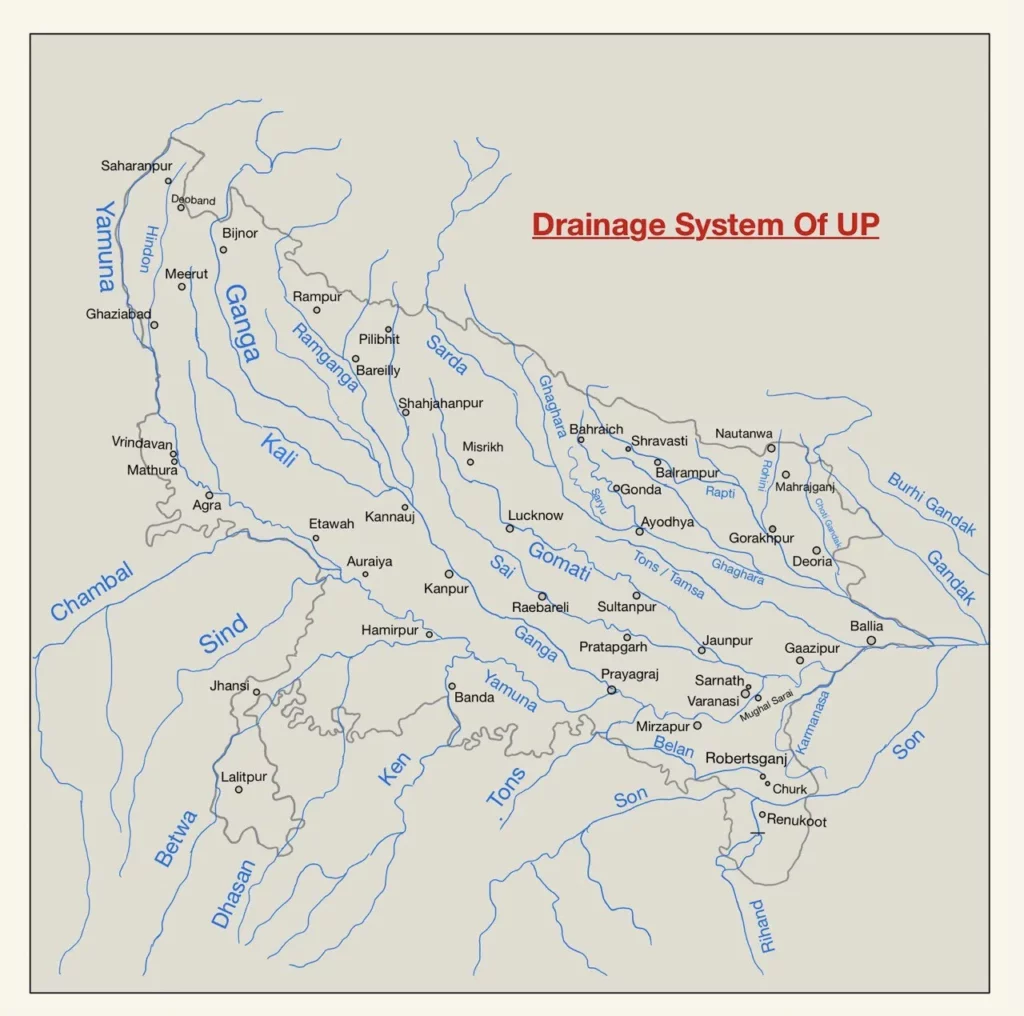
Peninsular Rivers
These rivers originate from the peninsular plateau region. These rivers are older than Himalayan rivers. Chambal, Betwa, Ken, Son are the major peninsular rivers in Uttar Pradesh.
Chambal
- The river originates from the Janapav Hills near Mhow in Malwa plateau. The river flows in north and north-east directions and passes through Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- It merges with the Yamuna in Etawah district of Uttar Pradesh. The total length of the river is 1,050 km.
- National Chambal River Sanctuary is established on 425 km stretch of Chambal close to the trijunction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- The Gandhi Sagar Dam, Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam and Kota Barrage are some important river projects on Chambal.
- Parvati, Kali-sindh and Banas are its major tributaries.
Ken
- It originates from the northern slope of Kaimur Hills near Katani in Madhya Pradesh and flows northwards. It has a total length of 427 km. It flows through Bundelkhand region and joins the Yamuna at Bhojha in Banda.
- It is also known as Karnavati. It flows through the Panna National Park and makes Rahen falls in Chhatarpur of Madhya Pradesh.
- Bawas, Devar, Kaith, Baink and Bearma are its major tributaries.
- Banda is an important city situated on its banks. Ken is known for the semi-precious stone Shazar which is used by locals for stone craft.
- Shazar is recognized as a product of Banda under ODOP scheme of Uttar Pradesh Government.
- Ken-Betwa river linking project is signed between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh to divert the water of Ken river into Betwa river.
Chambal Ravines
- Chambal river is infamous for badland topography in its lower course. The rivers flow causes excessive erosion in a wide area and gives rise to undulating floodplain, gulliesand ravines. These ravinesare locally known as Beehad.
- The semi-arid region of Chambal valley and poorly cemented bedrock creates ideal conditions for ravine formation. Every year the river vertically erodes loosely bound soil and light vegetation,and creates more Beehad region.
- Along with Chambal and its tributaries, the Yamuna and its tributaries also give rise to the Beehad region. The Beehad region is not suitable for farming and is known for frequent droughts, infertile land and water scarcity.
- Beehad region extends in Etawah, Fatehpurand Kanpur Dehat of Uttar Pradesh. As per the UP Agricultural Department, there was 12.3 lakh hectare of Beehad in the state in 1993.
- The state Government has launched several programmes for the ravine reclamation. The UP Bhumi Sudhar Nigam launched a pilot project of ravine reclamation in collaboration with the world bank under UPSLR-III in 2009-10 for reclamation of 5,000 ha land in Fatehpur and Kanpur Dehat districts.
- Techniques of Contour Bunding, Peripheral Bunding and Check Dams were employed in ravine reclamation.
- The Union Government has also decided to convert more than 3 lakh sq.km Beehad area in Gwalior Chambal region into cultivable land through a world bank assisted scheme.
- The Chambal Beehad region was also infamous for dacoits. Presence of rugged topography and dacoits kept large scale human settlements and industries at bay in this region and the region remained as one among the very few as safe-havens for many endangered wildlife species including Gharials, Turtle, Mugger, Indian Skimmer, etc.
Son
- The river originates from Amarkantak Plateau in Madhya Pradesh. It has a length of 784 km.
- It flows through Sonbhadra and Mirzapur districts of Uttar Pradesh and joins Ganga at Danapur near Patna.
- Son valley is an extension of Narmada rift valley and known for its coal deposits.
- The important tributaries of the Son river are the Johilla, Gopat, Rihand, Kanhar, Karmnasha, Pandu and North Koel. Almost all the tributaries join it on its right bank.
Rihand
- It is a tributary of Son river and originates from Matiranga Hills in the Manipat plateau of Chattishgarh. It is also known as Renu or Renuka river.
- Morana, Meur and Gagar are its tributaries. It flows through Sonbhadra district of Uttar Pradesh and finally joins Son.
- Rihand dam is built on this river for Hydropower generation in Pipari of Sonbhadra.
- Its reservoir Govind Ballabh Pant Sagar is the largest artificial reservoir of India.
Ton or Tamasa
- Tons is a right bank tributary of Ganga. It meets Ganga at Sirsa near Prayagraj. It has a total length of 150 km.
- It originates from Tamsakund in Kaimur range. Belan is its important tributary.
- The river creates many falls in its journey like Vihaar falls, Chachai falls, Keoti falls, Odda falls, Purwa falls, etc.
Betwa
- The river is also known as Vetravati. It has a total length of 590 km. It originates from Vindhyas in Raisen District of Madhya Pradesh.
- It flows through the Bundelkhand region and finally joins the Yamuna in Fiamirpur.
- Lalitpur, Jhansi, Auraiya and Jalaun are situated on its banks.
- Matatila Dam is built upon the river in Lalitpur. Parichha dam is built near Jhansi.
- Sindhu, Dhasan and Bina are its major tributaries,
Rivers Emerging from Gangetic Plains
Gomati
- The river originates from Gomati Taal or Fulhar Jheel in Pilibhit. It has a length of 900 km.
- It flows through the area lying between Ramganga and Sharda in upper stretches and through the area lying between Ganga and Ghagra at the lower stretches.
- Sai is its major tributary.
- Lucknow, Pilibhit, Shahjahanpur, Jaunpur, Sultanpur, etc. are situated on its bank.
- It merges with Ganga at Ghazipur where the famous Markandey Mahadev temple is situated.
- The river is in pathetic condition due to environmental pollution.
Varuna
- It originates near Phulpur in Allahabad.
- It flows approximately 100 km before joining Ganga in Varanasi.
Other Rivers
Hindon
- It is a tributary of Yamuna. It has a length of 400 km. It originates from the Shivalik range in Saharanpur.
- It is a monsoon fed river with approximately 7000 sq.km catchment area.
- The Hindon Air Force base lies on the bank of this river.
- Many anecdotes related to Mahabharata are associated with this river.
Karmanasa
- It is a tributary of Ganga, originating in Kaimur district in Bihar. Chandraprabha is its main tributary.
- It runs along the boundary of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. It passes through Mirzapur, Chandauli and Ghazipur in Uttar Pradesh.
- It merges with Ganga in Ghazipur. Karmnasa and its tributaries form Chhan Pathar fall and Devdari fall.
Manwar/Manorma
- The river originates near Gonda and flows eastwards.
- It passes through Mankapur Gonda and Basti. It finally joins Kuwano River in Lalganj.
- The river is dying a slow death due to silting and water hyacinth.
Important Rivers of Uttar Pradesh
Rivers from Himalayas
| Rivers | Origin | Total Length (km) |
|---|---|---|
| Ganga Yamuna Sharda Ramganga Sarayu Gandak Rapti | Uttarakhand Uttarakhand Uttarakhand Uttarakhand Tibet Nepal Nepal | 2,525 1 ,384 350 696 1,080 630 814 |
Rivers from Plateau Region
| Rivers | Origin | Total Length (km) |
|---|---|---|
| Chambal Betwa Ken Son Kanhar Sindh Riband Tons | Madhya Pradesh Madhya Pradesh Madhya Pradesh Madhya Pradesh Chhattisgarh Madhya Pradesh Chhattisgarh Madhya Pradesh | 965 590 427 784 100 416 250 264 |
Rivers from Gangetic Plain
| Rivers | Origin | Total Length (km) |
|---|---|---|
| Gomti Varuna Sai | Pilibhit ( UP) Phulpur ( UP) Hardoi (UP) | 910 100 563 |
Other Important Rivers
| Rivers | Origin |
|---|---|
| Kuwano Manwar Hindon Karmanasa Terhi Gambhir | Bahraich (UP) Gonda (UP) Saharanpur (UP) Bihar Behraich Rajasthan |
Cities Located on River Banks
| River | City |
|---|---|
| Ganga | Sherpur (Ballia), Ghazipur, Saidpur (Gazi), Varanasi, Mirzapur, Sirsa (Prayagraj), Prayagraj, Shringverpur (Prayagraj), Kalakankar (Pratapgrah), Dalmau ( Raebareli), Baxur (Unnao), Kanpur, Bithur ( Kanpur), Fatehgarh (Farrukhabad), Kachla Ghat ( Badaun), Anupshahar (Bulandshahar), Garmukteshwar (Hapur). |
| Ramganga | Moradabad and Bareilly. |
| Yamuna | Prayagraj, Kaushambi, Hamirpur, Etawah, Kalpi, Bateshwar, Agra, Mathura, Vrindavan, Bagpat |
| Gomti | Jaunpur, Sultanpur, Lucknow |
| Saryu | Ayodhya, Gola, Barhalganj, Behraich |
| Rapti | Gorakhpur and Bahraich |
| Ken | Banda |
| Betwa | Hamirpur |
| Sai River | Pratapgarh |
| Son River | Sonbhadra |
| Hindon | Ghaziabad, Noida and Greater Noida |
List of Rivers in Uttar Pradesh
| River Name | Length (km) | Originates From | Joins With |
| Ganga | 2,525 | Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand | Bay of Bengal |
| Yamuna | 1,376 | Yamunotri Glacier in Uttarakhand | Ganga in Allahabad |
| Ghaghara | 1,080 | Near Mapchachungo Glacier in Tibet | Ganga in Bihar |
| Gomti | 900 | Gomat Taal in Pilibhit | Ganga in Varanasi |
| Betwa | 590 | Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh | Yamuna in Hamirpur |
| Chambal | 960 | Janapav Hill in Madhya Pradesh | Yamuna in Etawah |
| Ken | 427 | Near village Ahirgawan in Madhya Pradesh | Yamuna in Banda |
| Rapti | 525 | Sisarma Hill in Nepal | Ghaghara in Uttar Pradesh |
| Sharda | 350 | Milam Glacier in Uttarakhand | Ghaghara in Bahraich |
| Saryu | 540 | Near Sarmool in Tibet | Ghaghara in Uttar Pradesh |
| Son | 784 | Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh | Ganga in Patna |
| Varuna | 30 | Near Bhurh Jheel in Varanasi | Ganga in Varanasi |
| Tons | 250 | Bandarpunch Range in Uttarakhand | Yamuna in Yamunanagar |
| Dhasan | 318 | Lalitpur Hills in Madhya Pradesh | Betwa in Hamirpur |
| Sai | 213 | Ajgain Hills in Madhya Pradesh | Yamuna in Etawah |
| Gerua | 150 | Kannauj district in Uttar Pradesh | Ganga in Kannauj |
| Kali | 350 | Pithoragarh district in Uttarakhand | Sharda in Bahraich |
| Kuwana | 130 | Katerniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary in Uttar Pradesh | Ghaghara in Uttar Pradesh |
| Rihand | 600 | Sonbhadra district in Uttar Pradesh | Son in Sonbhadra district |
| Gori Ganga | 150 | Milam Glacier in Uttarakhand | Kali Ganga in Pithoragarh district |
