Q. With reference to carbon nanotubes, consider the following statements:
- They can be used as carriers of drugs and antigens in the human body.
- They can be made into artificial blood capillaries for an injured part of the human body.
- They can be used in biochemical sensors.
- Carbon nanotubes are biodegradable.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Carbon nanotubes
- A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometer range (nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon.
- Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical large molecules consisting of a hexagonal arrangement of hybridized carbon atoms, which may by formed by rolling up a single sheet of graphene (single-walled carbon nanotubes, SWCNTs) or by rolling up multiple sheets of graphene (multiwalled carbon nanotubes, MWCNTs).
- Hence structurally, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) can be viewed as wrapped from graphene sheets.
- Carbon nanotubes were once considered to be resistant to chemical damage due to their rigid and perfect chemical structure, which rendered them immune to biodegradation. However, enzymes like peroxidase were found to play an important role in the process of biodegradation of carbon nanotubes.
- Carbon nanotubes can exhibit remarkable properties, such as exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity because of their nanostructure and strength of the bonds between carbon atoms.
- Carbon nanotubes are extremely robust and difficult to break, but they are still light. Because of their exceptional mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties, carbon nanotubes are one of the most investigated nanomaterials.
- Carbon Nanotubes Uses & Applications
- Carbon nanotubes are utilized in energy storage, device modelling, automotive parts, boat hulls, sporting goods, water filters, thin-film electronics, coatings, actuators, and electromagnetic shields.
- Because of their large surface area, CNTs have been successfully used in pharmacy and medicine to adsorb or conjugate a wide range of medicinal and diagnostic substances.
- CNTs have a number of unique chemical, size, optical, electrical, and structural properties that make them appealing as drug delivery and biosensing platforms for the treatment of a variety of diseases and noninvasive monitoring of blood levels and other chemical properties of the human body, respectively.
- Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have unique qualities, such as high surface-to-volume ratios, increased conductivity and strength, biocompatibility, ease of functionalization, optical properties, and so on.
Q. Consider the following activities:
- Spraying pesticides on a crop field
- Inspecting the craters of active volcanoes
- Collecting breath samples from spouting whales for DNA analysis
At the present level of technology, which of the above activities can be successfully carried out by using drones?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Notes
- A drone refers to an unmanned aerial vehicle. Different drones are capable of travelling varying heights and distances.
- The close-range drones have the ability to travel up to three miles and are mostly used by hobbyists.
- The short-range drones travel up to 90 miles and are used primarily for espionage and intelligence gathering.
- The Mid-range UAVs have a 400-mile distance range and could be used for intelligence gathering, scientific studies and meteorological research.
- The longest-range drones are called “endurance” UAVs and have the ability to go beyond the 400-mile range and up to 3,000 feet in the air.
- Some of the application of drones:
- Aerial photography for journalism and film
- Express shipping and delivery
- Gathering information or supplying essentials for disaster management
- Thermal sensor drones for search and rescue operations
- Geographic mapping of inaccessible terrain and locations
- Building safety inspections
- Precision crop monitoring
- Unmanned cargo transport
- Law enforcement and border control surveillance
- Storm tracking and forecasting hurricanes and tornadoes
Q. “The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to
(a) Voyager-2
(b) New horizons
(c) Lisa Pathfinder
(d) Evolved LISA
Answer: (d) Evolved LISA
evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (eLISA)
- The evolved Laser Interfermoter Space Antenna (eLISA) is a mission aiming at exploring the Gravitational Universe from space for the first time.
- It involves scientists from eight European countries ‒ Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, The Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, and the UK ‒ as well as the support of several US-based ones.
- The eLISA mission consists of a “Mother” and two “Daughter” spacecrafts. These will orbit the Sun in a triangular configuration.
- The three satellites will form a precision interferometer, with the two Daughter spacecrafts connected to the Mother one by 1 million km long laser beams. This interferometer will be capable of detecting gravitational waves at frequencies in the range of 0.1 mHz to 1 Hz.
- Such a frequency interval is not accessible on Earth due to arm length limitations and to noise caused by the terrestrial gravity gradient noise: in this sense, eLISA will complement the efforts of ground-based gravitational-wave detectors.
- eLISA is designed with orbits that allow the three satellites to maintain their near-equilateral triangular configuration. Indeed, because of their special orbits, they are seen to rotate about an axis passing through the centre of the triangle and normal to its plane. A passing gravitational wave alters the proper relative distance between the spacecraft, which will be sensed by detectors on each spacecraft.
- eLISA will coherently measure the frequency, phase, and polarisation of gravitational waves passing through it, allowing scientists to resolve overlapping signals and locating them on the sky.
LISA Pathfinder (LPF)
- LISA Pathfinder is the European Space Agency (ESA) precursor mission to the LISA space-based gravitational wave observatory that the agency is developing within the Cosmic Vision Programme.
- LISA Pathfinder has been developed within an international collaboration led by ESA and including the space agencies of France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, The Netherlands and United Kingdom, and NASA.
- The mission tested technologies needed for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA), an ESA gravitational wave observatory planned to be launched in 2037.
- The eLISA mission technology is being tested in space with LISA Pathfinder. LPF was placed in a low-earth transfer orbit. From there, the satellite used its propulsion module in order to reach the operational orbit around the Lagrange point L1.
- LISA Pathfinder placed two test masses in a nearly perfect gravitational free-fall, and controlled and measured their relative motion with unprecedented accuracy. The laser interferometer measured the relative position and orientation of the masses to an accuracy of less than 0.01 nanometres, a technology estimated to be sensitive enough to detect gravitational waves by the follow-on mission, the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA).
- LISA Pathfinder was a proof-of-concept mission to prove that the two masses can fly through space, untouched but shielded by the spacecraft, and maintain their relative positions to the precision needed to realise a full gravitational wave observatory.
Voyager-2
- Voyager 2 is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun’s heliosphere.
- As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, Voyager 1, on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune.
- Voyager 2 remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets, and was the third of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System.
- Voyager 2 successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space.
New horizons
- New Horizons is an interplanetary space probe launched as a part of NASA’s New Frontiers program.
- The spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow.
- It is the fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System.
Q. Consider the following statements:
- Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent.
- A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
- Human induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Gene Therapy
- Gene therapy refers to the method wherein a genetic defect is treated by inserting a functional gene or section of DNA in cells. The functional gene inserted into an individual or an embryo compensates for the non-functional gene present. The newly inserted DNA corrects the effect of the mutated gene.
- On the basis of types of cells involved in the gene transfer, gene therapy is of two types:
- Somatic gene therapy: Here the desired gene is transferred to a somatic cell. The gene is not transferred to the offspring.
- Germline gene therapy: Here the desired gene is introduced in the germ cell. The gene gets transferred from one generation to another generation.
Germline gene therapy
- Under this therapy, required DNA is transferred into the cells that produce reproductive cells, eggs or sperm, in the body.
- It allows for the correction of disease-causing gene variants that are certain to be passed down from generation to generation. This therapy removes a hereditary disorder from a family line forever.
Somatic cell gene therapy
- Somatic cell gene therapy is when therapeutic genes are transferred to a patient’s somatic cells.
- The somatic gene therapy targets body tissues. These cells do not produce sperm or eggs, therefore the gene is not transferred to the next generation.
- Somatic cell gene therapy would aim to cure a disease only in the patient, not in the patient’s descendants.
Human-induced pluripotent stem cells
- They have been hailed as an effective replacement for human embryonic stem cells and a prime candidate cell source for regenerative medicine aims.
- The researchers tried combining human induced pluripotent stem cells with pig embryos.
- Many of the embryos were much smaller than normal and seemed to grow more slowly.
- Hence, so far there has not been a success in growing human organs in pigs.
- But this experiment shows that human-induced pluripotent cells can be injected into pigs embryo.
Q. What is the importance of using Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in India?
- These vaccines are effective against pneumonia as well as meningitis and sepsis.
- Dependence on antibiotics that are not effective against drug-resistant bacteria can be reduced.
- These vaccines have no side effects and cause no allergic reactions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 2 only
Pneumococcal disease
- Pneumococcal disease is an infection caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae (also known as pneumococcus).
- It is caused by bacteria which can lead to infections in the lungs, blood, and brain.
- It causes health problems in children younger than 5 years of age.
- The greatest risk for infection is for children younger than 2, adults over 65, people with certain medical conditions, and cigarette smokers.
- These diseases also include pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis, blood infections, and ear infections.
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) prevents pneumococcal disease.
- The vaccine is a mix of several bacteria of the pneumococci family, which are known to cause pneumonia — hence ‘conjugate’ is included in the name of the vaccine.
- Conjugate vaccines are made using a combination of two different components.
- Most people who get a pneumococcal vaccine do not have any serious problems with it. With any medicine, including vaccines, there is a chance of side effects. These are usually mild and go away on their own within a few days, but serious reactions are possible.
Pneumonia vs Pneumococcal pneumonia
- Pneumonia is a lung disease.
- Pneumococcal pneumonia, a kind of pneumonia, can infect the upper respiratory tract and can spread to the blood, lungs, middle ear, or nervous system.
- Pneumococcal disease is a name for any infection caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumonia or pneumococcus.
- Most people carry pneumococcus in their nose and throat, where the bacteria do not cause any symptoms.
Q. In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of
(a) Digital security infrastructure
(b) Food security infrastructure
(c) Health care and education infrastructure
(d) Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Answer: (a) Digital security infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure
- The Public Key Infrastructure is a technology for authenticating users and devices in the digital world. It is the framework of encryption and cybersecurity that protects communications between the server and the client. It is based on digital certificates that verify the identity of the machines and/or users that ultimately proves the integrity of the transaction through encryption and decryption.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) can protect the identities involved as well as the private information used in situations where digital security is necessary, such as smart card logins, SSL signatures, encrypted documents, and more.
- There are three key components:- digital certificates, certificate authority, and registration authority.
- Digital Certificates– It is a form of electronic identification for websites and organizations. Secured connections between two communicating machines are made available through PKI because the identities of the two parties can be verified by way of certificates.
- Certificate Authority– It is used to authenticate the digital identities of the users, which can range from individuals to computer systems to servers. It can prevent falsified entities and manage the life cycle of any given number of digital certificates within the system.
- Registration Authority- It is authorized by the Certificate Authority to provide digital certificates to users on a case-by-case basis. All of the certificates that are requested received, and revoked by both the Certificate Authority and the Registration Authority are stored in an encrypted certificate database.
- The PKI is best utilized for situations that require digital security. It performs encryption directly through the keys that it generates and it works by using two different cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key.
- PKI secures sensitive electronic information by using a two-key encryption system as it is passed back and forth between two parties. It then provides each party with a key to encrypt and decrypt the digital data.
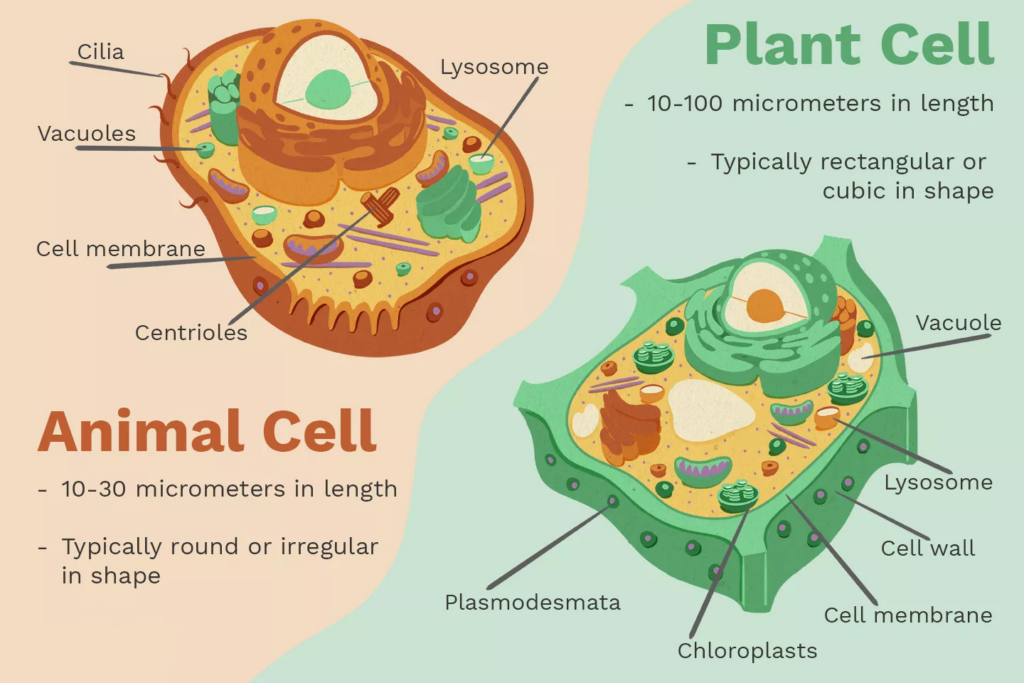
Q. Which of the following statements are correct regarding the general difference between plant and animal cells?
- Plant cells have cellulose cell walls whilst animal cells do not.
- Plant cells do not have plasma membranes unlike animal cells which do.
- Mature plant cell has one large vacuole whilst an animal cell has many small vacuoles.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell
| Animal Cell | Plant Cell | |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Present | Present |
| Cilia | Present | It is very rare |
| Shape | Round (irregular shape) | Rectangular (fixed shape) |
| Chloroplast | Animal cells don’t have chloroplasts | Plant cells have chloroplasts because they make their own food |
| Cell Wall | Animal cells do not have a cell wall. | Plant cells have a cell wall. |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough) | Present | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Lysosomes | Animal cells contain lysosomes for breaking down the molecules with enzymatic action. | Plant cells rarely have lysosomes that are meant for molecule degradation. |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
| Vacuole | One or more small vacuoles (much smaller than plant cells). | One large central vacuole taking up 90% of cell volume. |
| Centrioles | Meant to assist in cell division, centrioles are present in animal cells. | They are absent in plant cells. |
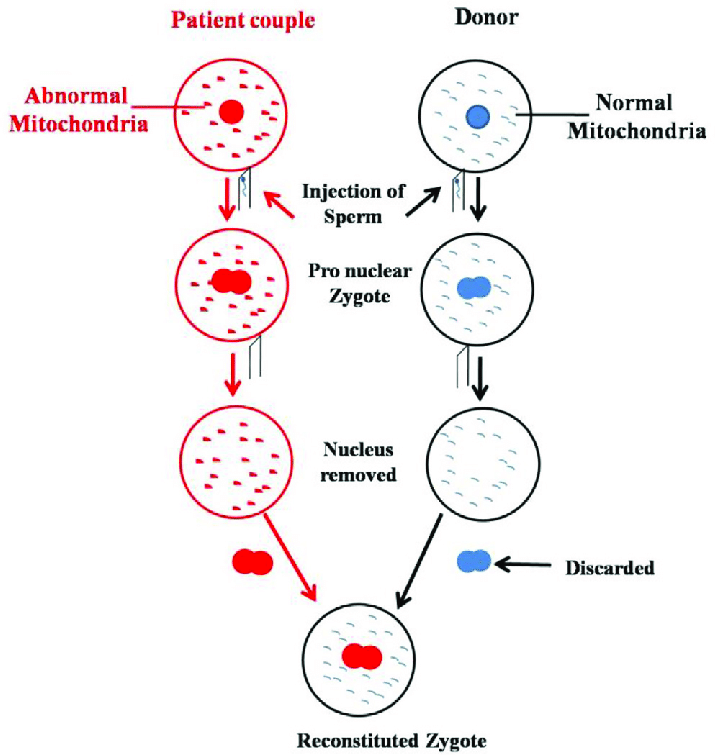
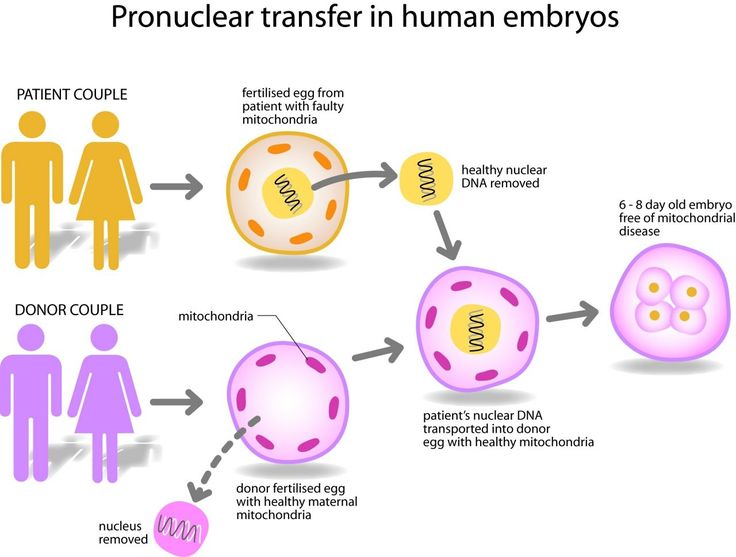
Q. In the context of recent advances of human reproductive technology, “Pronuclear Transfer” is used for
(a) fertilization of egg in vitro by the donor sperm
(b) genetic modification of sperm producing cells
(c) development of stem cells into functional embryos
(d) prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring
Answer: (d) prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring
Pronuclear Transfer
- In pronuclear transfer, the mother’s egg is first fertilized with the father’s sperm, producing a zygote. The pronuclei of the egg and sperm are then removed from the zygote and inserted into a donor egg that has been fertilized and has had its own nucleus removed.
- Pronuclear Transfer
- It involves the transfer of pronuclei from one zygote to another.
- This technique first requires fertilisation of healthy donated egg/eggs provided by the mitochondrial donor with the intending male parent sperm.
- The intending mother’s affected oocytes are fertilised with the intending father’s sperm.
- Thereafter, both sets of fertilised oocytes are allowed to develop to the early zygote stage where the pronuclei are visible.
- The pronuclei of zygotes formed from donated oocytes are removed within a karyoplast using micromanipulation equipment, and then it is discarded.
- The resulting zygotes contain nuclear DNA from each of the intending parents and a donor’s mtDNA.
- The zygote is then implanted into the mother’s uterus.
- This offspring produced from the genetic material of one man and two women are also referred to as Three-parent baby.
- There are various approaches that could help women to overcome infertility and could prevent the transmission to their offspring of potentially debilitating mitochondrial diseases.
- Pronuclear transfer reduces the effects of mutations that occur in the DNA of cellular organelles known as mitochondria. Hence, this technology is used for the prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring.
Assisted Reproductive Technology
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) refers to medical procedures used to help individuals or couples conceive a child.
- It involves various techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Gamete Donation, Intrauterine Insemination, Pre-implantation Genetic Testing, Surrogacy, Altruistic Surrogacy.
- ART is often used by individuals or couples facing fertility challenges, including infertility, genetic disorders, or reproductive system abnormalities.
- ART procedures typically involve the manipulation of sperm, eggs, or embryos in a laboratory setting before transferring them to the woman’s uterus.
- Legal Provisions:
- The ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology Act) Regulation 2021 provides a system for the implementation of the law on surrogacy by setting up of the National Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Board.
- The Act aims at the regulation and supervision of ART clinics and assisted reproductive technology banks, prevention of misuse, and safe and ethical practice of ART services.
Surrogacy
- Surrogacy is an arrangement in which a woman (the surrogate) agrees to carry and give birth to a child on behalf of another person or couple (the intended parent/s).
- A surrogate, sometimes also called a gestational carrier, is a woman who conceives, carries and gives birth to a child for another person or couple (intended parent/s).
- Altruistic surrogacy:
- It involves no monetary compensation to the surrogate mother other than the medical expenses and insurance coverage during the pregnancy.
- Commercial surrogacy:
- It includes surrogacy or its related procedures undertaken for a monetary benefit or reward (in cash or kind) exceeding the basic medical expenses and insurance coverage.
- Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021:
- Under the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, a woman who is a widow or a divorcee between the age of 35 to 45 years or a couple, defined as a legally married woman and man, can avail of surrogacy if they have a medical condition necessitating this option.
- It also bans commercial surrogacy, which is punishable with a jail term of 10 years and a fine of up to Rs 10 lakhs.
- The law allows only altruistic surrogacy where no money exchanges hands and where a surrogate mother is genetically related to those seeking a child.
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Answer: (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions.
- AI is the intelligence of machines or software, as opposed to the intelligence of humans or animals.
- Artificial Intelligence has various applications in today’s society in multiple industries, such as Healthcare, entertainment, finance, education, etc.
- Some high-profile applications are: advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search), recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon, and Netflix), understanding human speech (such as Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa), self-driving cars (e.g., Waymo), generative and creative tools (ChatGPT and AI art), and superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (such as chess and Go).
- AI has been used in disease diagnosis, creating songs like ‘I am AI’ and ‘Daddy’s Car’ and creating short stories and fictions. AI has been used in Text-to-speech conversion, e.g. Cerewave AI.
- Artificial Intelligence has also found use in power industry, e.g. Machine-learning assisted power transfer (based on AI) using magnetic resonance and AI used for energy efficiency.
- The various sub-fields of AI research are centered around particular goals and the use of particular tools. The traditional goals of AI research include reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, learning, natural language processing, perception, and support for robotics. General intelligence (the ability to complete any task performable by a human) is among the field’s long-term goals.
Natural language processing
- Natural language processing (NLP) refers to the branch of artificial intelligence or AI – concerned with giving computers the ability to understand text and spoken words in much the same way human beings can.
- Natural language processing (NLP) allows programs to read, write and communicate in human languages such as English. Specific problems include speech recognition, speech synthesis, machine translation, information extraction, information retrieval and question answering.
- NLP combines computational linguistics – rule-based modeling of human language – with statistical, machine learning, and deep learning models. Together, these technologies enable computers to process human language in the form of text or voice data and to ‘understand’ its full meaning, complete with the speaker or writer’s intent and sentiment.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)
- An artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a hypothetical type of intelligent agent. If realized, an AGI could learn to accomplish any intellectual task that human beings or animals can perform. Alternatively, AGI has been defined as an autonomous system that surpasses human capabilities in the majority of economically valuable tasks.
- Creating AGI is a primary goal of some artificial intelligence research and of companies such as OpenAI, DeepMind, and Anthropic.
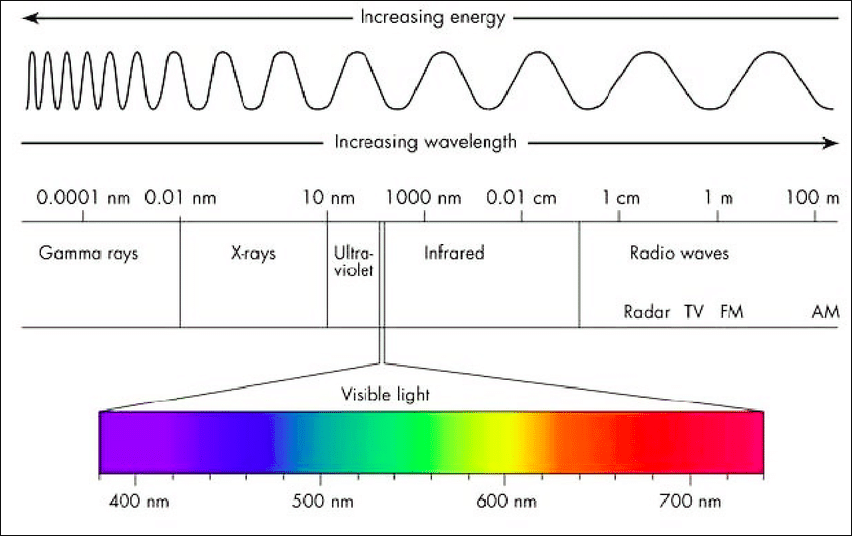
Q. With reference to Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology, which of the following statements are correct?
- VLC uses electromagnetic spectrum wavelengths 375 to 780 nm.
- VLC is known as long-range optical wireless communication.
- VLC can transmit large amounts of data faster than Bluetooth.
- VLC has no electromagnetic interference.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer: (c) 1, 3 and 4 only
Visible Light Communication Technology
- Visible light communication (VLC) is a wireless method that enables high-speed transmission of data with visible light.
- This data is transmitted by modulating the intensity of light given off by a light source. The signal is received by a photodiode device that transforms the data into forms that are readable and readily-consumed by end users.
- It makes use of Visible Light spectrum. It occupies the spectrum from 375 nm to 780 nm.
- Its biggest advantage is the size of the entire visible light spectrum, which is 10,000 times larger than the entire radio spectrum, which is also too congested due to its overuse.
- Aside from the size of the visible light spectrum, light travels 186,000 miles per second, which is way faster than the 344 meters per second traveled by radio waves in air. This means that communication using light is virtually instantaneous, which also makes VLC the fastest means of communication among those commercially available in the market.
- VLC systems operate at optical frequencies and emit no electromagnetic interference. Therefore, it can be used in Healthcare services.
- The nature of light is that it is unable to pass through opaque walls. Hence, VLCT is used in indoor environment/short range.
LiFi (Light Fidelity)
- LiFi (Light Fidelity) is a wireless communication technology that uses visible light, particularly LED bulbs, to transmit data.
- It was first demonstrated in 2011 by Professor Harald Haas from the University of Edinburgh, Scotland, who also coined the term LiFi.
- It provides high-speed, bidirectional, networked mobile communication in a similar manner as WiFi but with higher speeds, lower latency, and a larger bandwidth (thousands of terahertz).
- LiFi has the advantage of being useful in electromagnetic-sensitive areas like aircraft cabins, hospitals, and nuclear power plants without causing electromagnetic interference. Its utilisation of unused visible lights in human life has opened up new opportunities in wireless communications technology.
- LiFi works by modulating LED light to encode binary data, which is then received and decoded by photodiodes to transmit data wirelessly using visible light communication.
- Significance of LiFi:
- Light (electromagnetic waves) has been used in various applications by humans since time immemorial, but it remains unutilized in our daily lives, other than being used for lighting purposes. Tapping the potential of this unused light for wireless data transfer and the internet is the major hallmark of LiFi.
- The other significance of the LiFi is as follows:
- High speeds: LiFi can provide internet speeds over 100 Gbps, which is much faster than WiFi. This can enable high-speed applications.
- Security: Light cannot penetrate through walls that contain data within a closed area making it more secure.
- Decentralised means of communication: LiFi is a decentralised means of providing communication due to its working and components.
- Combined with blockchain technology, it can revolutionise the data transfer and communication technology with a quick and secure distributed system of transactions.
- No electromagnetic interference: LiFi uses visible light which does not cause electromagnetic interference. This allows its use in sensitive areas like aircraft and hospitals.
- High density: The visible light spectrum has 10,000 times more bandwidth than radio waves, thus it does not have the problem of ‘spectrum crunch’, as with the radio waves.
- This allows more devices to be connected.
- AR/VR: LiFi helps overcome technology challenges due to non-interference from other EM Waves and being faster, which allows Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality products to become wireless and reliable.
- Industry 4.0: LiFi can also enhance the capabilities industry and fulfill the dream of Industry 4.0 by:
- Increased Automation
- Better Decision-making
- Enhanced Security
- Greater Data Density
- Providing Connectivity in Radio Waves Hostile Industries, etc.
- Environmentally friendly: LiFi uses energy-efficient LED bulbs to transmit data. Being highly energy efficient, it results in lower carbon emissions.
- Cheaper deployment: LiFi can be implemented simply by installing LED bulbs. No new wiring or infrastructure is required making it easy to deploy.
- Prevention of “dead zones”: LED bulbs ensure that there are no dead zones as is the case with WiFi routers. Light can easily reach areas inside buildings where radio waves cannot penetrate.
LiFi vs WiFi
| Parameter | LiFi | WiFi |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Visible Light Communication | Radio waves |
| Frequency Band | 430 – 770 THz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz |
| Max Speed | Up to 224 Gbps | Up to 54 Mbps (802.11ax) |
| Latency | Low, <1 ms | Medium, >10 ms |
| Security | High, confined to the area illuminated | Medium, can penetrate walls |
| Energy Efficiency | High, uses LEDs | Medium |
| Reliability | High, less interference | Prone to interference |
| Mobility Support | Limited, needs line of sight | Good |
| Outdoor use | Challenging due to sunlight | Excellent |
| Health hazard | None | Concerns about radiofrequency radiation |
| Deployment costs | Low, leverages lighting infrastructure | High for WiFi routers |
Q. With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements:
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: (d) 1 and 3 only
Blockchain Technology
- Blockchain is a method of recording information that makes it impossible or difficult for the system to be changed, hacked, or manipulated. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that duplicates and distributes transactions across the network of computers participating in the blockchain.
- Blockchain technology is a structure that stores transactional records, also known as the block, of the public in several databases, known as the “chain,” in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes. Typically, this storage is referred to as a ‘digital ledger.’
- Every transaction in this ledger is authorized by the digital signature of the owner, which authenticates the transaction and safeguards it from tampering. Hence, the information the digital ledger contains is highly secure.
- An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.
- The blocks form a chain of data as the ownership changes hands. Hence, it has no single user control. The blocks confirm the exact time and sequence of transactions, and the blocks link securely together to prevent any block from being altered.
- Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and hence the entire blockchain is formed. The verification of each block make the blockchain tamper-evident and builds a ledger of transactions that network members can trust.
- The applications that depend on the basic features of the blockchain can be developed without asking anybody for permission or paying anyone. Since blockchain operates through a decentralized platform requiring no central supervision, it is used in voting, banking, messaging app, internet advertising, etc. Hence, it is not restricted to cryptocurrency.
Public Digital Infrastructure
- Digital public infrastructure (DPI) refers to blocks or platforms such as digital identification, payment infrastructure and data exchange solutions that help countries deliver essential services to their people, empowering citizens and improving lives by enabling digital inclusion.
- DPIs mediate the flow of people, money and information. First, the flow of people through a digital ID System. Second, the flow of money through a real-time fast payment system. And third, the flow of personal information through a consent-based data sharing system to actualize the benefits of DPIs and to empower the citizen with a real ability to control data.
- These three sets become the foundation for developing an effective DPI ecosystem.
- Each DPI layer fills a clear need and generates considerable value across sectors.
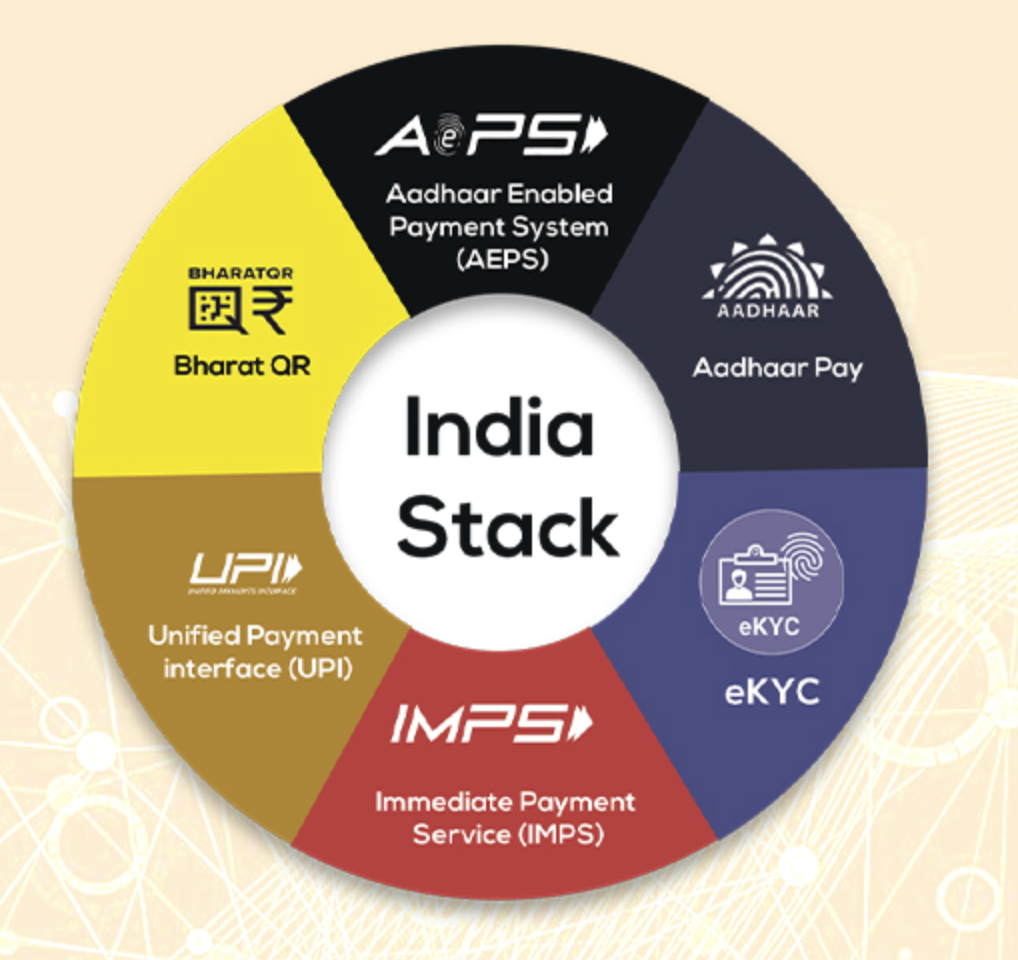
- India, through India Stack, became the first country to develop all three foundational DPIs,Digital identity (Aadhar),Real-time fast payment (UPI) and Account Aggregator built on the Data Empowerment Protection Architecture (DEPA).
- DEPA creates a digital framework that allows users to share their data on their own terms through a third-party entity, who are known as Consent Mangers.
India Stack
- IndiaStack is a set of APIs (Application programming interface) that allows governments, businesses, startups and developers to utilize a unique digital Infrastructure to solve India’s hard problems towards presence-less, paperless, and cashless service delivery.
- It aims to unlock the economic primitives of identity, data, and payments at population scale.
- The vision of India Stack is not limited to one country; it can be applied to any nation, be it a developed one or an emerging one.
- This project was conceptualized and first implemented in India, where its rapid adoption by billions of individuals and businesses has helped promote financial and social inclusion and positioned the country for the Internet Age.
Q. With reference to solar water pumps, consider the following statements:
- Solar power can be used for running surface pumps and not for submersible pumps.
- Solar power can be used for running centrifugal pumps and not the ones with piston.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (d) Neither 1 nor 2
Solar water pumps
- Solar water pumps are specially designed to utilize DC electric power from photovoltaic modules. The pumps must work during low light conditions, when power is reduced, without stalling or overheating. Low volume pumps use positive displacement (volumetric) mechanisms which seal water in cavities and force it upward. Lift capacity is maintained even while pumping slowly. These mechanisms include diaphragm, vane and piston pumps. These differ from a conventional centrifugal pump that needs to spin fast to work efficiently. Centrifugal pumps are used where higher volumes are required.
- A surface pump is one that is mounted at ground level. Surface pumps work well when they draw water through suction less than 10 or 20 feet. A submersible pump is one that is lowered into the water. Most deep wells use submersible pumps. And both are compatible with the photovoltaic array (For Solar power).
- The most common pump mechanics in Solar power pumps used are centrifugal pumps, multistage pumps, borehole pumps, and helical pumps.
- A solar water pump system is commonly seen in residential and commercial uses, as well as for irrigation of agricultural land.
- Through solar panels, the pump can eliminate the cost of energy and provide a more feasible option that uses energy from the sun.
- When it comes to stand-alone solar pumping systems, the main types include rotating and positive displacement pumps.
- Centrifugal pumps are the common choice for rotation and are designed for fixed head applications.
- Their output increases in proportion to their speed of rotation.
Q. In India, why are some nuclear reactors kept under “IAEA safeguards” while others are not?
(a) Some use uranium and others use thorium
(b) Some use imported uranium and others use domestic supplies
(c) Some are operated by foreign enterprises and others are operated by domestic enterprises
(d) Some are State-owned and others are privately-owned
Answer: (b) Some use imported uranium and others use domestic supplies
IAEA
- The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an international organisation dedicated to promoting the peaceful use of nuclear energy and prohibiting its use for military purposes, including the development of nuclear weapons.
- International Atomic Energy Agency was established in 1957 and its headquarters are located in Vienna, Austria.
- IAEA safeguards are a set of technical safeguards applied by IAEA to independently verify any nuclear facilities to check if it is not misused or deviated from peaceful uses.
- Under Article 3 of the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons Treaty, all the nonnuclear weapon states are required to conclude a safeguard agreement with IAEA.
