Q. Consider the following pairs:
Notes:
Q. Consider the following statements:
- In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by ‘the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
- Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2
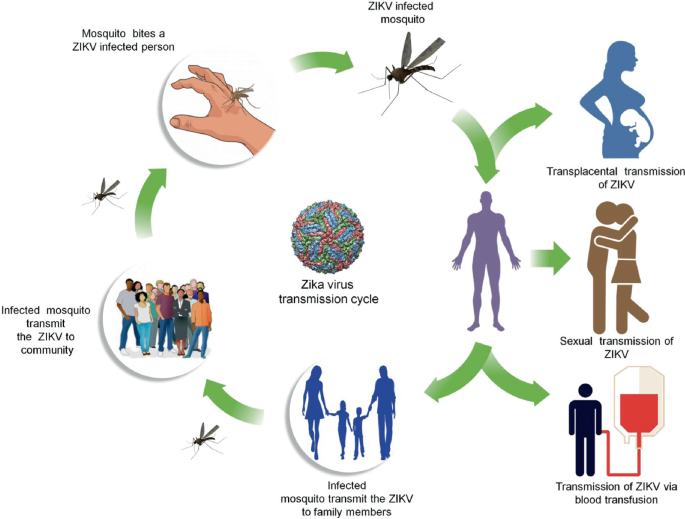
Zika Virus
- Zika virus is primarily transmitted by the bite of an infected mosquito from the Aedes genus, mainly Aedes aegypti, in tropical and subtropical regions. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where the virus was first isolated in 1947.
- Aedes mosquitoes usually bite during the day, peaking during early morning and late afternoon/ evening. This is the same mosquito that transmits dengue, chikungunya and yellow fever.
- Zika virus is also transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy, through sexual contact, transfusion of blood and blood products, and organ transplantation.
- The infection, known as Zika fever or Zika virus disease, often causes no or only mild symptoms, similar to a very mild form of dengue fever.
- No vaccine is yet available for the prevention or treatment of Zika virus infection. While there is no specific treatment, paracetamol (acetaminophen) and rest may help with the symptoms.
Q. What is the purpose of ‘evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna’ (eLISA) project?
(a) To detect neutrinos
(b) To detect gravitational waves
(c) To detect the effectiveness of missile defence system
(d) To study the effect of solar flares on our communication systems
Answer: (b) To detect gravitational waves
evolved Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (eLISA)
- The evolved Laser Interfermoter Space Antenna (eLISA) is a mission aiming at exploring the Gravitational Universe from space for the first time.
- It involves scientists from eight European countries ‒ Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, The Netherlands, Spain, Switzerland, and the UK ‒ as well as the support of several US-based ones.
- The eLISA mission consists of a “Mother” and two “Daughter” spacecrafts. These will orbit the Sun in a triangular configuration. The three satellites will form a precision interferometer, with the two Daughter spacecrafts connected to the Mother one by 1 million km long laser beams. This interferometer will be capable of detecting gravitational waves at frequencies in the range of 0.1 mHz to 1 Hz.
- Such a frequency interval is not accessible on Earth due to arm length limitations and to noise caused by the terrestrial gravity gradient noise: in this sense, eLISA will complement the efforts of ground-based gravitational-wave detectors.
Q. The terms ‘Event Horizon’, ‘Singularity’, `String Theory’ and ‘Standard Model’ are sometimes seen in the news in the context of
(a) Observation and understanding of the Universe
(b) Study of the solar and the lunar eclipses
(c) Placing satellites in the orbit of the Earth
(d) Origin and evolution of living organisms on the Earth
Answer: (a) Observation and understanding of the Universe
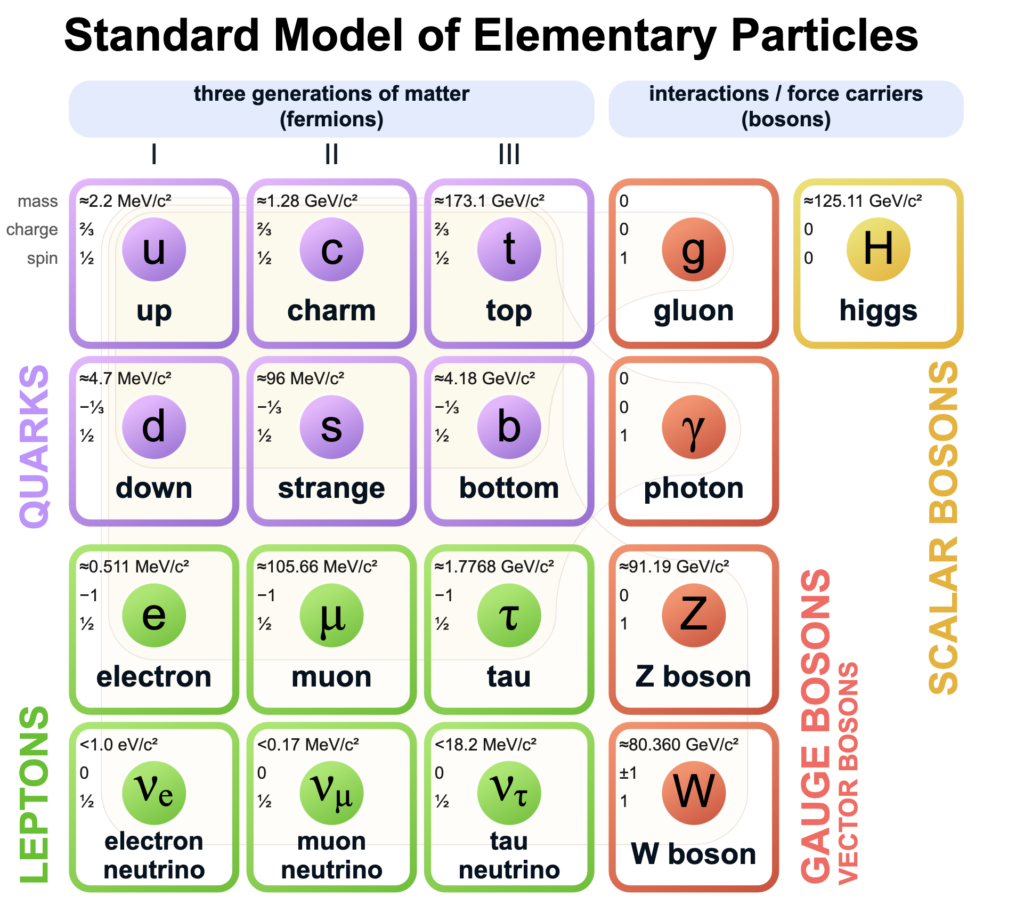
Standard Model
- The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetic, weak and strong interactions – excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles.
- It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists worldwide, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks.
- Since then, proof of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy.
Singularity
- A singularity refers to a place in the universe where our laws of physics simply break down.
- The term first came into popular use in Albert Einstein’s 1915 Theory of General Relativity. In the theory, a singularity describes the center of a black hole, a point of infinite density and gravity within which no object inside can ever escape, not even light.
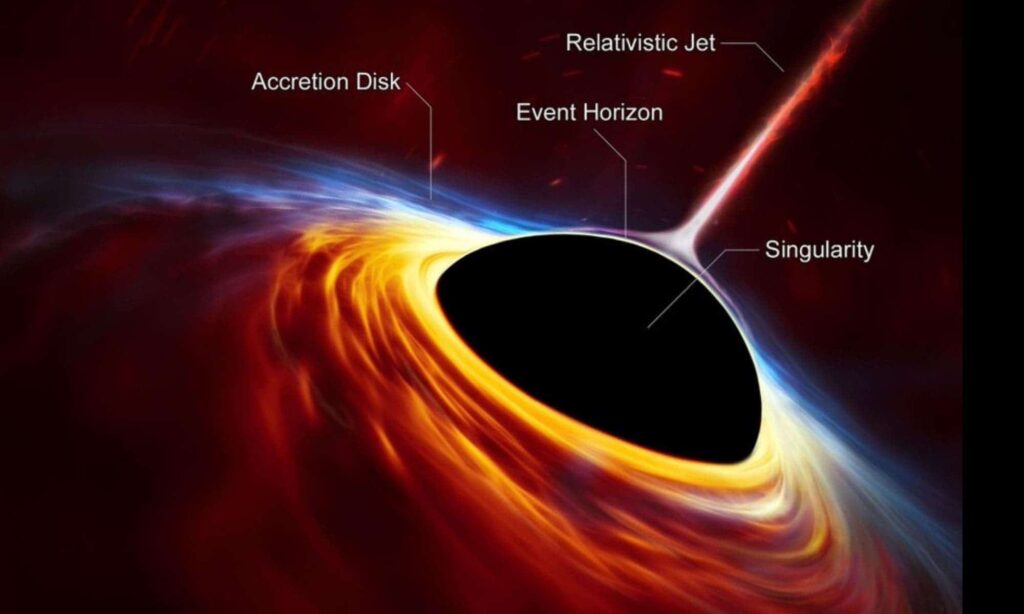
Event horizon
- The event horizon is a boundary that marks the outer edge of black holes. It is the point at which nothing, not even light, can escape.
- Because light can’t escape, black holes themselves neither emit nor reflect it, and nothing about what happens within them can reach an outside observer. But astronomers can observe black holes thanks to light emitted by surrounding matter that hasn’t yet dipped into the event horizon.
Accretion Disk
- The main light source from a black hole is a structure called an accretion disk.
Q. What is the application of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer Technology?
(a) Production of biolarvicides
(b) Manufacture of biodegradable plastics
(c) Reproductive cloning of animals
(d) Production of organisms free of diseases
Answer: (c) Reproductive cloning of animals
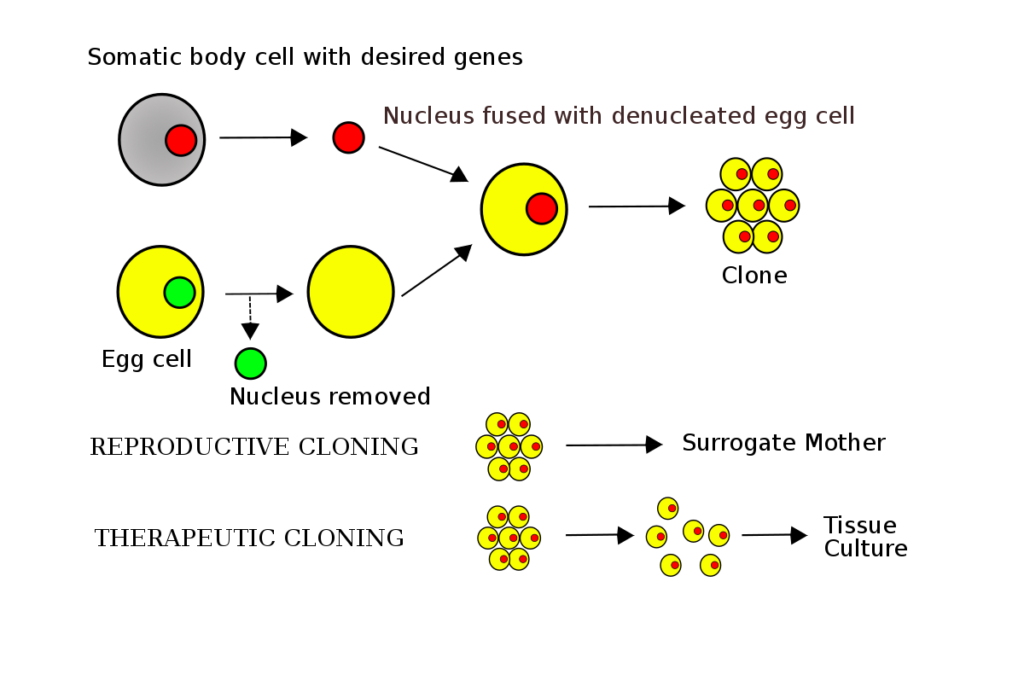
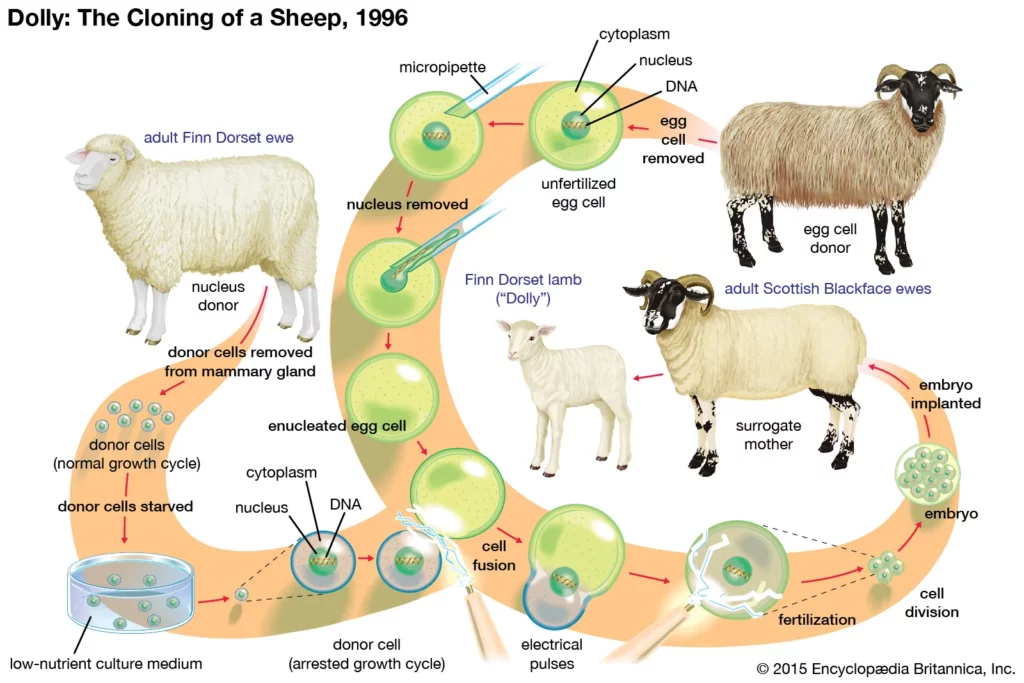
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
- Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is a laboratory technique for cloning for creating an ovum with a donor nucleus.
- Cloning is the production of an exact copy of a complete organism, any other living part, or a cell.
- Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer Technology was used for the first time by Ian Wilmut and his colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh for cloning the sheep “Dolly” on 5th July 1996 and was the first mammal to be cloned.
- Technology of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer:
- A somatic cell is isolated and extracted from an adult female.
- Then the nucleus and all of its DNA from an egg cell is removed.
- After that the nucleus from the somatic cell is transferred to the egg cell.
- After being inserted into the egg, the somatic cell nucleus is reprogrammed by the host cell and is stimulated with a shock.
- The egg cell, with its new nucleus, will behave just like a freshly fertilised egg.
- It developed into an embryo, which is implanted into a surrogate mother.
- Potential Applications of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer:
- Stem cell research- Somatic cell nuclear transplantation is being used in stem cell research. These cells are deemed to have a pluripotent potential because they have the ability to give rise to all of the tissues found in an adult organism. This could be used in therapies or disease research. This allows stem cells to create any cell type, which could then be transplanted to replace damaged or destroyed cells.
- Organ transplants- Another application of SCNT stem cell research to generate tissues or even organs for transplant into the specific patient. The resulting cells would be genetically identical to the somatic cell donor, thus avoiding any complications from immune system rejection.
- Therapeutic applications- SCNT have ample scope of success in therapy and curing diseases. It can be used to treat diseases like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease etc. In 2014, the New York Stem Cell Foundation was successful in creating SCNT stem cells derived from adult somatic cells. One of these lines of stem cells was derived from the donor cells of a type 1 diabetic. These insulin producing cells could be used for replacement therapy in diabetics, demonstrating real SCNT stem cell therapeutic potential.
- Reproductive cloning- Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer technique is currently the basis for cloning animals (such as the famous Dolly the sheep), and has been theoretically proposed as a possible way to clone humans. But there are moral and ethical objections against reproductive cloning. In 2018, the first successful cloning of primates using somatic cell nuclear transfer, (the same method as Dolly the sheep), was successfully done with the birth of two live female clones .
- Preservation of endangered species- Interspecies nuclear transfer (iSCNT) is a means of somatic cell nuclear transfer used to facilitate the rescue of endangered species, or even to restore species after their extinction.
- Somatic cell nuclear transfer can be both boon and bane. It might help in many ways but it also has its share of effects which might include reduction of gene diversity, Nature’s rule like survival of fittest, ethical and moral issues. If got into wrong hands (Terrorists, crime syndicate) it might prove to be a disaster in waiting. Thus caution is needed with proper regulation for its usage.
Q. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future?
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Genome Sequencing
- Genome sequencing is figuring out the order of DNA nucleotides, or bases, in a genome—the order of Adenine, Cytosine, Guanines, and Thymine that make up an organism’s DNA.
- A genome is a complete set of DNA that contains all of the genes of an organism. The human genome is made up of a tiny chromosome in the cell’s mitochondria and 23 pairs of chromosomes that are found in the nucleus of the cell. A genome contains all of the information required for a person to develop and function.
- Whole Genome Sequencing:
- All organisms (bacteria, plants, and mammals) have their own genetic code, or genome, which is made up of nucleotide bases. Whole genome sequencing is a laboratory procedure used to determine the order of bases in the genome of an organism in a single step.
- Significance of Genome Sequencing:
- Genome sequencing has become an important tool in pharmacogenomics, clinical diagnosis, and translational vaccine development.
- Whole genome sequencing provides detailed and precise data for identifying outbreaks sooner.
- Additionally, whole genome sequencing is used to characterize bacteria as well as track outbreaks.
- Dramatic advancements in DNA-sequencing technologies have massively reduced the time and cost required to sequence an entire human genome.
- Genomic information has been instrumental in identifying inherited disorders and characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression.
- Whole genome sequencing provides detailed and precise data for identifying outbreaks sooner.
- Genome sequencing has become an important tool in pharmacogenomics, clinical diagnosis, and translational vaccine development.
- Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Biological research: The ability to read genetic sequences is extremely useful in biological research because the base sequence contains information for making proteins as well as regulating gene functions.
- Forensics: Sequencing has proven to be a powerful tool in forensics. Because differences in DNA and RNA sequences can differentiate organisms down to species and individual levels, it can help to classify diseases, identify therapeutic targets, and customize treatments.
- Diagnostics:
- Pre-natal screening: It has also been used in prenatal screening to determine whether the foetus has any genetic disorders or anomalies.
- Evaluate disorders: Genome sequencing has been used to assess rare disorders, preconditions for disorders, and even cancer from a genetic viewpoint, rather than as diseases of specific organs.
- Drug Efficacy: Genome sequencing can provide information about drug efficacy or adverse drug effects.
- The relationship between drugs and the genome is called pharmacogenomics.
- Vaccine development: Sequencing of viruses (e.g. ebola, coronavirus) and bacteria has led to the development of vaccines against them, once knowing their variants or strains.
- Genomic data of pathogens could reveal hidden pathways of transmission.
- Population Studies:Advanced analytics and AI could be applied to critical datasets generated by collecting genomic profiles across the population, allowing for a better understanding of disease causation and potential treatments.
- This is especially relevant for rare genetic diseases, where large datasets are required to find statistically significant correlations.
- Agriculture and food security: Genome sequencing has the power to revolutionize food security and sustainable agriculture by reducing the risks from disease outbreaks, and improving agriculture through effective plant and animal breeding, detecting multiple pathogens, etc.
Genome India
- Genome India is a national project launched in 2020. It is funded by the Department of Biotechnology, and spearheaded bythe Centre for Brain Research (CBR).
- In the first phase of the study, the project aims to identify genetic variations in 10,000 representative individuals from across India using whole genome sequencing.
- Project aimed to:
- Create an exhaustive catalogue of genetic variations in Indians.
- Create a reference haplotype structure for Indians.
- Create low-cost genome-wide arrays for research and diagnostics.
- Create a biobank for DNA and plasma samples for future research.
- Significance: Creating an Indian genome database allows researchers to learn about genetic variants unique to India’s population groups and use this information to tailor drugs and therapies.
- Objective: To “unravel the genetic underpinnings of chronic diseases currently on the rise in India.
IndiGen Programme
- The IndiGen programme launched in 2019 aims to undertake whole genome sequencing of thousands of individuals representing diverse ethnic groups from India.
- The goal is to enable genetic epidemiology and develop public health technology applications using population genome data.
- IndiGen is endorsed by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
- The outcomes of the IndiGen will be utilized towards understanding the genetic diversity on a population scale, making available genetic variant frequencies for clinical applications, and enabling genetic epidemiology of diseases.
Indian Initiative on Earth Bio-Genome Sequencing
- The project was launched in 2020 and is part of the Earth Biogenome Project. The project will allow for the collection and preservation of endangered and economically significant species.
- The genetic information that has been decoded will also be useful in preventing biopiracy.
- The initial phase of IIEBS will include the whole genome sequencing of 1,000 plant and animal species, which will take five years to complete.
- The Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute (JNTBGRI) plays a key role in a nationwide project to decode the genetic information of all known species of plants and animals in the country.
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents?
- Service providers
- Data centers
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Cybersecurity incidents
- Cybersecurity incidents mean any real and suspected adverse event in relation to cybersecurity that violates an explicitly or implicitly applicable security policy resulting in unauthorized access, denial of services, unauthorised used of computer resources for processing or storage of data or changes in data without authorization.
- In India, section 70-B of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (the “IT Act”) gives the Central Government the power to appoint an agency of the government to be called the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) to report such incidents.
- Rule 12 of the CERT Rules gives every person, company or organisation have the option to report cybersecurity incidents to the CERT-In.
- It also places an obligation on them to mandatorily report the following kinds of incidents as early as possible:
- Targeted scanning/probing of critical networks/systems;
- Compromise of critical system/information;
- Unauthorized access to IT system/data;
- Defacement of website or intrusion into a website and unauthorized changes such as inserting malicious code, links to external websites, etc.;
- Malicious code attacks such as spreading of virus/worm/Trojan/botnets/spyware;
- Attacks on servers such as database, mail, and DNS and network devices such as routers;
- Identity theft, spoofing and phishing attacks;
- Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks;
- Attacks on critical infrastructure, SCADA systems and wireless networks;
- Attacks on applications such as e-governance, e-commerce, etc’s.
Challenges Posed by Cyber Attacks on India
- Critical Infrastructure Vulnerability: India’s critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and communication networks, is vulnerable to cyber attacks that can disrupt essential services and endanger public safety and national security.
- For example, in October 2019, there was an attempted cyber-attack on the Kudankulam Nuclear power plant.
- Financial Sector Threats: The financial sector in India faces a high risk of cyberattacks from cybercriminals who seek to profit from stealing or extorting money. Attacks on banks, financial institutions, and online payment systems can cause financial losses, identity theft, and a loss of trust in the financial system.
- For instance, in March 2020, a malware attack on the City Union Bank’s SWIFT system led to unauthorised transactions worth USD 2 million.
- Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns: As India moves towards a digital economy, the amount of personal and government data stored online increases. This also increases the risk of data breaches, where hackers access and leak sensitive information. Data breaches can have serious consequences for the privacy and security of individuals and organisations.
- For example, in May 2021, the personally identifiable information (PII) and test results of 190,000 candidates for the 2020 Common Admission Test (CAT), used to select applicants to the IIMs, were leaked and put up for sale on a cybercrime forum.
- Cyber Espionage: Cyber espionage is the use of cyber attacks to spy on or sabotage the interests of other countries or entities. India, like other countries, is a target for cyber espionage activities that aim to steal confidential information and gain a strategic edge. Cyber espionage can affect India’s national security, foreign policy, and economic development.
- For example, in 2020, a cyber espionage campaign called Operation SideCopy (a Pakistani threat actor) was uncovered, which targeted Indian military and diplomatic personnel with malware and phishing emails.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are complex and prolonged cyber attacks, usually carried out by well-resourced and skilled groups. These attacks are designed to infiltrate and remain hidden in the target’s network for a long time, allowing them to steal or manipulate data, or cause damage.
- APTs are difficult to detect and counter, as they use advanced techniques and tools to evade security measures.
- For example, in February 2021, a cyber security firm called RedEcho revealed that a China-linked APT group had targeted 10 entities in India’s power sector, with malware that could potentially cause power outages.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Supply chain vulnerabilities refer to the weaknesses in the software or hardware components that are used by government and businesses for their operations. Cyber attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to compromise the systems and services that depend on these components, and cause widespread damage.
- For example, in December 2020, a global cyberattack on SolarWinds, a US-based software company that provides network management tools, affected several Indian organisations, including the National Informatics Centre (NIC), the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), and Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL).
Initiatives Regarding Cyber Security
- Indian Initiatives:
- National Cyber Security Policy: This policy aims to build a secure and resilient cyberspace for citizens, businesses, and the government. It outlines various objectives and strategies to protect cyberspace information and infrastructure, build capabilities to prevent and respond to cyber attacks, and minimise damages through coordinated efforts of institutional structures, people, processes, and technology.
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative: This initiative was launched to raise awareness about cyber crimes and create safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): This centre was established to provide a framework and eco-system for law enforcement agencies to deal with cyber crimes in a comprehensive and coordinated manner. It has seven components, namely:
- National Cyber Crime Threat Analytics Unit
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal
- National Cyber Crime Training Centre
- Cyber Crime Ecosystem Management Unit
- National Cyber Crime Research and Innovation Centre
National Cyber Crime Forensic Laboratory Ecosystem - Platform for Joint Cyber Crime Investigation Team.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre): This centre was launched in 2017 to create a secure cyberspace by detecting botnet infections in India and notifying, enabling cleaning and securing systems of end users to prevent further infections.
- Computer Emergency Response Team – India (CERT-In): It is an organisation of the MeitY which collects, analyses and disseminates information on cyber incidents, and also issues alerts on cybersecurity incidents.
- Critical information infrastructure (CII): It is defined as a computer resource, the destruction of which, shall have debilitating impact on national security, economy, public health or safety.
- The government has established the National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) to protect the CII of various sectors, such as power, banking, telecom, transport, government, and strategic enterprises.
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA): The DCyA is a tri-service command of the Indian Armed Forces that is responsible for handling cyber security threats. It has the capability to conduct cyber operations, such as hacking, surveillance, data recovery, encryption, and countermeasures, against various cyber threat actors.
- Global Initiatives:
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is an international treaty that seeks to address Internet and computer crime by harmonizing national laws, improving investigative techniques, and increasing cooperation among nations. It came into force on 1st July 2004. India is not a signatory to this convention.
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF): It brings together all stakeholders i.e., government, private sector and civil society on the Internet governance debate.
- UNGA Resolutions: The United Nations General Assembly established two processes on the issues of security in the information and communication technologies (ICT) environment.
- The Open-ended Working Group (OEWG) through resolution by Russia
- The Group of Governmental Experts (GGE) through resolution by USA
Q. Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) are used to create digital display in many devices. What are the advantages of OLED displays over Liquid Crystal displays?
- OLED displays can be fabricated on flexible plastic substrates.
- Roll-up displays embedded in clothing can be made using OLEDs.
- Transparent displays are possible using OLEDs.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None of the above statement is correct
Answer: (c) 1, 2 and 3
Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs)
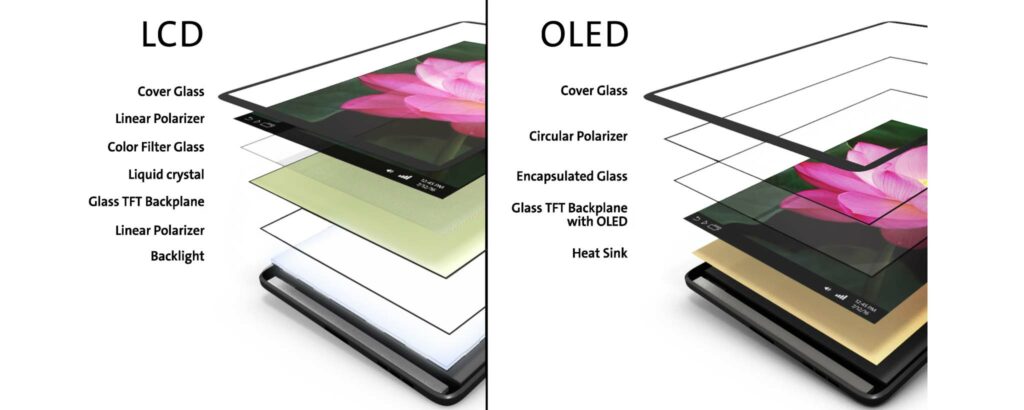
- Organic light emitting diodes (devices) or OLEDs are monolithic, solid-state devices that typically consist of a series of organic thin films sandwiched between two thin-film conductive electrodes.
- OLEDs are used to create digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, and portable systems such as smartphones and handheld game consoles. A major area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications.
- OLEDs use organic materials to emit light, rather than traditional backlighting used in LCD displays. This allows for less power consumption, better contrast, deeper blacks, and more vibrant colors.
- Attractive features of Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) displays using plastic substrate are:
- They are ultrathin and light.
- Besides, it can be fabricated on flexible plastic to utilize the flexibility of the substrate.
- Also can be fabricated on Roll-up displays embedded in clothing and
- Transparent displays are also possible.
- The key issue in achieving such displays is how to protect OLEDs from oxygen and moisture.
Liquid-crystal display (LCD)
- A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers.
- Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.
- LCD uses fluorescent tubes to lighten the picture, but can’t provide a clearer picture as LED delivers.
- In LCD display, it consists of millions of pixels made of crystal and arranged in a rectangular grid. In LCD it has backlights that provide light to each pixel. Each pixel has a red, green, and blue (RGB) sub-pixel that can be turned on or off. When all of the sub-pixels are turned off, then it’s black and when all the sub-pixels are turned on 100%, then it’s white.
- LCD is a combination of two states of matter, the solid and the liquid. The solid part is crystal and this liquid and crystal together make the visible image. LCD consists of two layers which are two polarized panels- filters and electrodes. LCD screen works by blocking the light rather than emitting the light. There are two types of pixel grids in LCD:
- Active Matrix Grid– It is a newer technology. In smartphone with LCD display uses this technology.
- Passive Matrix Grid– It is an older technology. Some older devices used this technology.
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding Smart India Hackathon 2017?
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme for developing every city of our country into Smart Cities in a decade.
- It is an initiative to identify new digital technology innovations for solving the many problems faced by our country.
- It is a programme aimed at making all the financial transactions in our country completely digital in a decade.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 2 only
Smart India Hackathon:
- Smart India Hackathon (SIH) was started in the year 2017. It was launched as a competition to develop innovative digital technologies to solve the issues of central government and ministries.
- It aims to inculcate the culture of product innovation, problem-solving and out-of-the-box thinking among students.
- It is an initiative by the Ministry of Education, All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), Persistent Systems and Inter Institutional Inclusive Innovation Centre (i4C).
- It engages the youth of the country directly in the nation-building process.
- Smart India Hackathon theme is “No problem is too big, No idea is too small”.
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT):
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in 2015.
- The main objective of AMRUT is to provide basic amenities to urban areas and improve the standard of living and quality of life of the poor and downtrodden people of urban areas.
- As of the first phase, about 500 cities have been covered.
- Purpose:
- To ensure that every household has access to a tap with the assured supply of water and a sewerage connection.
- The Priority zone of the Mission is water supply followed by sewerage.
- To increase the amenity value of cities by developing greenery and well maintained open spaces (e.g. parks).
- To reduce pollution by switching to public transport or constructing facilities for non-motorized transport (e.g. walking and cycling).
- To ensure that every household has access to a tap with the assured supply of water and a sewerage connection.
- Components:
- Capacity building, reform implementation, water supply, sewerage and septage management, storm water drainage, urban transport and development of green spaces and parks.
- The reforms aim at improving delivery of citizen services, bringing down the cost of delivery, improving financial health, augmenting resources and enhancing transparency. It also includes replacement of street lights with LED lights.
- Capacity building, reform implementation, water supply, sewerage and septage management, storm water drainage, urban transport and development of green spaces and parks.
Digital India:
- The program aimed at making all financial transactions in our country completely digital is part of the Digital India initiative and making towards a cashless transaction.
- The money transfer is done through Debit/ Credit cards, mobile wallets, Electronic Clearing Services (ECS), National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT), and Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), and so on.
- The Ministry responsible for promotions of digital transactions including digital payments is the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
