In this article, You will read Petroleum Reserves in India – for UPSC IAS.
Petroleum
- Crude petroleum consists of a mixture of hydrocarbons—solid, liquid, and gaseous. These include compounds belonging to the paraffin series and also some unsaturated hydrocarbons and a small proportion belonging to the benzene group.
- Petroleum and petroleum products are mainly used as motive power. It is a compact and convenient liquid fuel that has revolutionized transportation on land, in the air, and on water. It can be easily transported from the producing areas to the consuming areas with the help of tankers and more conveniently, efficiently, and economically by pipelines.
- It emits very little smoke and leaves no ash, (as is the case in coal utilization), and can be used up to the last drop. It provides the most important lubricating agents and is used as an important raw material for various petrochemical products.
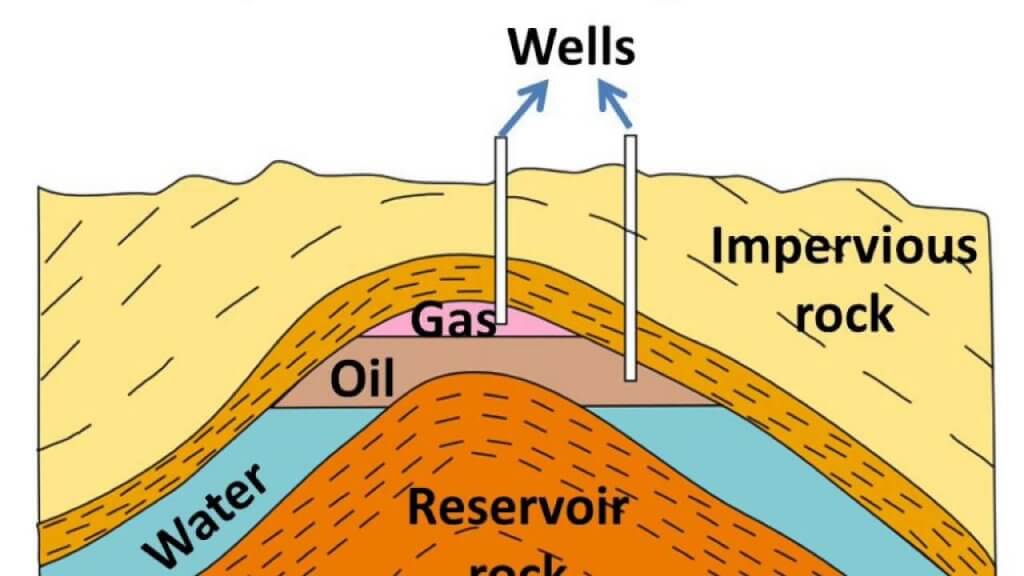
Origin and Occurrence
- Petroleum has an organic origin and is found in sedimentary basins, shallow depressions, and in the seas (past and present).
- Most of the oil reserves in India are associated with anticlines and fault traps in the sedimentary rock formations of tertiary times, about 3 million years ago.
- Some recent sediment, less than one million years also show evidence of incipient oil.
- An oil reservoir must have three pre-requisite conditions
- Porosity so as to accommodate sufficiently large amounts of oil
- Permeability to discharge oil and/or gas when the well has been drilled
- The porous sand beds sandstone, conglomerates of fissured limestone containing oil should be capped by impervious beds so that oil does not dissipate by percolation in the surrounding rocks.
- Most important petroleum reserve of the world are found in:
- Miocene rocks (e.g. Mumbai High)
- Mid folding rocks
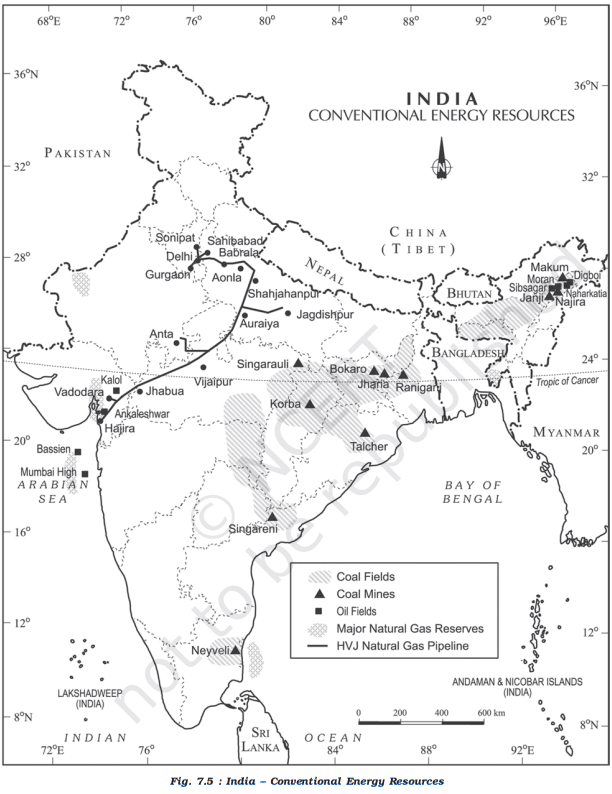
Oilfields in India
North-eastern India
- The major oilfields in north-eastern India are those of Brahmaputra valley of north-east India and its neighboring areas including Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Tripura, Manipur, Mizoram, and Meghalaya.
- Assam: It is the oldest oil-producing state in India
- The Digboi field: It is the oldest oil field in India. Most oil is sent to the refinery at Digboi.
- The Naharkatiya field: Oil from this area is sent to oil refineries at Noonamati in Assam and Barauni in Bihar through the pipeline. It was discovered in 1953.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Oil reserves are found in Manabhaum, Kharsang and Charai.
- Tripura: Oil reserves are found at Manmumbhanga, Manu, Ampi Bazar.
- Assam: It is the oldest oil-producing state in India
Western India Onshore field
- Gujarat: The oil fields are found around the Gulf of Khambat. The main oil belt extends from Surat to Amreli. Kachchh, Vadodara, Bharuch, Surat, Ahmedabad, Kheda, Mehsana, etc. are the main producing districts. Ankleshwar, Lunej, Kalol, Nawgam, Kosamba, Kathana, Barkol, Mehsana, and Sanand are the important oilfields of these regions.
- Ankleshwar: The first major oil find came in 1958 with the discovery of Ankleshwar field located about 80 km south of Vadodara and nearly 160 km south of Khambhat. Ankleshwar anticline is about 20 km long and 4 km wide. Oil is available at depths varying from 1,000 to 1,200 metres. It has a capacity of 2.8 million tonnes per annum. It is estimated that 25 lakh tonnes per year of oil can be obtained from this field. Oil from this field is sent to refineries at Trombay and Koyali.
- Khambhat or Lunej field: The oil and Natural Gas Commission drilled test wells in 1958 at Lunej near Ahmadabad and confirmed the occurrence of a commercially exploitable oil field. The annual production is 15 lakh tonnes of oil and 8-10 lakh cubic metres of gas. The total reserves are estimated at 3 crore tonnes
- Ahmedabad and Kalol field: It lies about 25 km northwest of Ahmedabad. This field and a part of the Khambhat basin contain ‘pools’ of heavy crude trapped in chunks of coal. Nawgam, Kosamba, Mehsana, Sanand, Kathana, etc. are important producers.
- Rajasthan: One of the largest on-land oil discoveries was made in the Banner district of Rajasthan in 2004. State-of-the-art technology with innovative geological modelling was used in discovering this oil field. Two important discoveries, viz., Sarswati and Rajeshwari, with a total 35 million tonnes of in-place oil reserves were made earlier in 2002.
Western Coast Off-Shore Oilfields
- Mumbai High:
- The greatest success achieved by the ONGC with respect to offshore surveys for oil was that of Mumbai High in 1974. It is located on the continental shelf off the coast of Maharashtra about 176 km northwest of Mumbai.
- Here the rock strata of Miocene age covers an area of 2,500 sq km with estimated reserves of about 330 million tonnes of oil and 37,000 million cubic metres of natural gas. Production on a commercial scale began in 1976. Oil is taken from a depth of over 1,400 metre with the help of a specially designed platform known as Sagar Samrat.
- Production from this field declined between 1989-90 and 1993-94 due to overexploitation.
- Bassein: Located to the south of Mumbai High, this is a recent discovery endowed with reserves which may prove to be higher than those of the Mumbai High. Huge reserves have been found at a depth of 1,900 metre. Production has started and is expected to pick up fast.
- Aliabet: It is located at Aliabet Island in the Gulf of Khambhat about 45 km off Bhavnagar. Huge reserves have been found in this field.
East Coast
- The basin and delta regions of the Godawari, the Krishna, and the Cauvery rivers hold great potential for oil and gas production, both onshore and offshore.
- Tamil Nadu: The Narimanam and Kovilappal oilfields in the Cauvery on-shore basin are expected to produce about 4 lakh tonnes of crude oil annually.
- Andhra Pradesh produces less than one percent of the total crude oil of India. Oilfields have recently been discovered in the Krishna-Godavari basin.
Probable Areas
- There are vast possibilities of finding oil from about one lakh sq km area of sedimentary rocks in different parts of the country. Some of the outstanding areas which hold possibilities of oil are:
- Jawalamukhi, Nurpur, Dharamsala, and Bilaspur in Himachal Pradesh.
- Ludhiana, Hoshiarpur and Dasua in Punjab,
- The Gulf of Mannar off the Tirunelveli Coast.
- The off-shore area between Point Calimere and Jaffna peninsula.
- Off-shore deep water area in the Bay of Bengal
- The marine delta region of the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Cauvery rivers.
- Stretch of sea between South Bengal and Baleshwar coast.
- Off-shore area of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Petroleum Refining
- India’s first oil refinery started working way back in 1901 at Digboi in Assam.
- 1954: another refinery at Tarapur (Mumbai).
- Refinery hub and refining capacity exceeds the demand. Excess refined oil and other petroleum products are exported.
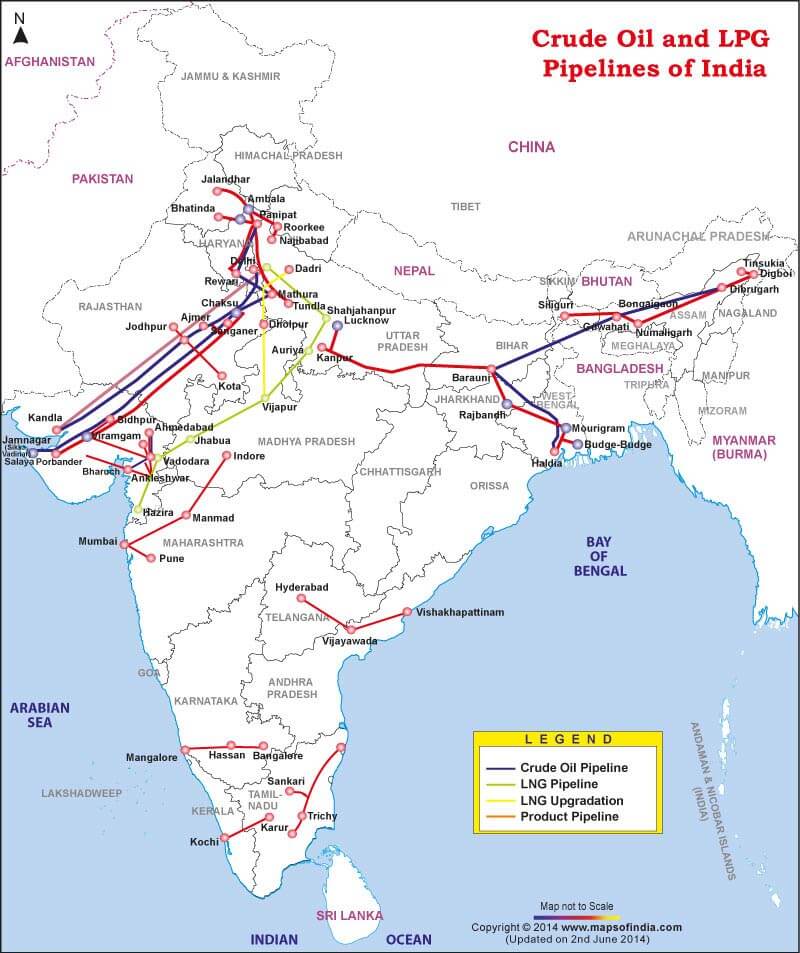
- Oil from wells is transported to nearest refineries through pipelines.
Advantages of Pipeline
- Ideal to transport liquids and gases.
- Pipelines can be laid through difficult terrains as well as under water.
- It needs very little maintenance.
- Pipelines are safe, accident-free and environmental friendly.
Disadvantages of Pipelines
- It is not flexible, i.e., it can be used only for a few fixed points.
- Its capacity cannot be increased once it is laid.
- It is difficult to make security arrangements for pipelines.
- Detection of leakage and repair is also difficult.
Crude Oil Pipelines
- Salaya-Mathura Pipeline (SMPL)
- Paradip-Haldia-Barauni Pipeline (PHBPL)
- Mundra-Panipat Pipeline (MPPL)
Petroleum Product Pipelines
- Guwahati-Siliguri Pipeline (GSPL)
- Koyali-Ahmedabad Pipeline (KAPL)
- Barauni-Kanpur Pipeline (BKPL)
- Panipat-Delhi Pipeline (PDPL)
- Panipat-Rewari Pipeline (PRPL)
- Chennai – Trichy – Madurai Product Pipeline (CTMPL)
- Chennai-Bangalore Pipeline
- Naharkatia-Nunmati-Barauni Pipeline (first pipeline constructed in India)
- Mumbai High-Mumbai-Ankleshwar-Koyali Pipeline.
- Hajira-Bijapur-Jagdishpur (HBJ) Gas Pipeline
- Jamnagar-Loni LPG Pipeline
- Kochi-Mangalore-Bangalore pipeline
- Vishakhapatnam Secunderabad pipeline
- Mangalore-Chennai pipeline
- Vijayawada-Vishakhapatnam pipeline
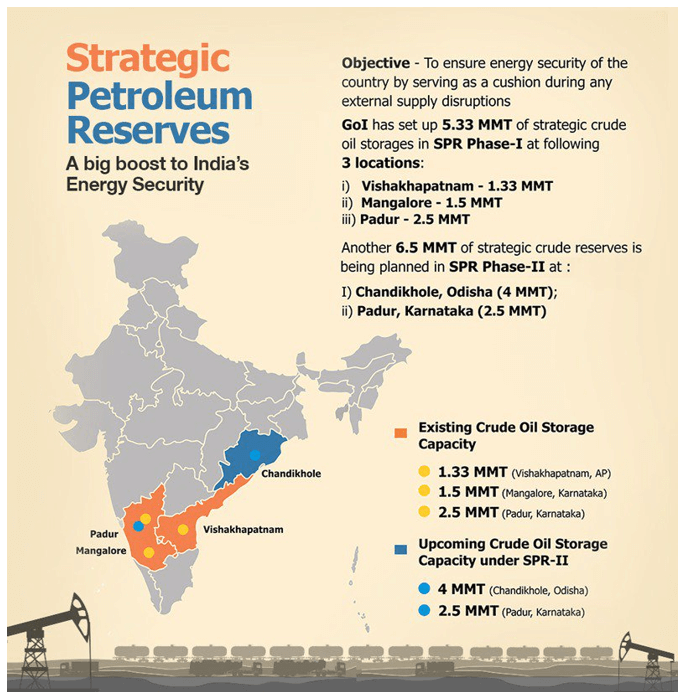
Strategic Petroleum Reserves
- Strategic petroleum reserves are huge stockpiles of crude oil to deal with any crude oil-related crisis like the risk of supply disruption from natural disasters, war, or other calamities.
- According to the agreement on an International Energy Programme (I.E.P.), each International Energy Agency (IEA) country has an obligation to hold emergency oil stocks equivalent to at least 90 days of net oil imports.
- In case of a severe oil supply disruption, IEA members may decide to release these stocks to the market as part of collective action.
- India became an associate member of the International Energy Agency in 2017.
- India’s strategic crude oil storage are currently located at Visakhapatnam (Andhra Pradesh), Mangaluru (Karnataka), and Padur (Karnataka).
- The government has also given approval for setting up of two additional facilities at Chandikhol (Odisha) and Padur (Karnataka).
- The concept of dedicated strategic reserves was first mooted in 1973 in the US, after the OPEC oil crisis.
- Underground storage is, by far the most economic method of storing petroleum products because the underground facility rules out the requirement of large swathes of land, ensures less evaporation and, since the caverns are built much below the sea level, it is easy to discharge crude into them from ships.
- The construction of the Strategic Crude Oil Storage facilities in India is being managed by Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserves Limited (ISPRL).
- ISPRL is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Oil Industry Development Board (OIDB) under the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas.
List of Major Oil Fields in India (with few details)
DIGBOI :
- Located in the Dibrugarh district of Assam, is the oldest oilfield of India
- Over 800 oil wells have been drilled so far
- Most of the oil is sent to an oil refinery at Digboi.
NAHARKATIA :
- Located at a distance of 32 km southwest of Digboi at the left bank of Burhi Dihing river
- Out of the 60 successful wells drilled so far 56 are producing natural gas
- Oil is sent to Noonmati (Assam) and Barauni (Bihar).
MORAN-HUGRIJAN :
- Located about 40 km southwest of Naharkatiya
- Discovered in 1953 and started production in 1956
- As many as 20 wells have been drilled which yield oil as well as gas.
RUDRASAGAR :
- Located in the Upper Assam Valley
- Discovered by ONGC and OIL in 1961
- Oil deposits are found in the Barail rocks
SIVSAGAR :
- Located in the Upper Assam Valley on the bank of the Brahmaputra
- Once the capital of the Ahom rulers
- In Sivsagar district oilfields are located at Lakwa, Lakhmani, Rudrasagar, Geleki and Moran.
ANKALESHWAR :
- Located 80 km south of Vadodara in Gujarat was discovered in 1958
- Ankleshwar anticline is about 20km long and 4 km wide
- Pandit Nehru called it ‘the Fountain of Prosperity’
- Oil is sent to Trombay and Kalol refineries.
KALOL :
- 25 km north of Ahmedabad
- Here ‘pools’ of heavy crude are trapped in chunks of coal at a depth of 1400 m
- Production of oil started in 1961.
NAWGAM :
- 24 km south of Ahmedabad in Gujarat
- Yields both oil and gas
MEHSANA :
- North of Ahmedabad
- Famous for milk production and petroleum
- Dudhsagar Dairy is well known
- Established in 1967, the Mehsana fields have grown into the highest onshore-producing asset of the ONGC.
SANAND :
- 16 km west of Ahmedabad
- Produces both oil and gas
- Tata Nano and Ford car plants are located here.
LUNEZ :
- First drilled in 1958 by the ONGC
- Located 60 km west of Vadodara
- Produces both oil and gas
- Drilling operation started in 1958
- Estimated reserves – 30 million tonnes of oil
- Oil – 15 lakh tonnes / year
- Gas- 8-10 lakh cubic m/year
KOSAMBA :
- Located between Narmada and Tapi rivers in the Surat district of Gujarat
- ONGC produces oil here.
KATHANA :
- North Kathana is a 7 sq. km oil field located near Khambhat town in Gujarat
- Oilfields are managed by the GSPC.
ALIABET :
- Located in the Gulf of Khambhat on the Aliabet Island about 45 km off Bhavnagar
- Huge reserves have been found
BASSEIN :
- Located to the south of the Mumbai High
- Recently discovered which may prove to be higher than those of the Mumbai High
- Production has already been started
MUMBAI HIGH :
- Located 176 km north-west of Mumbai on the continental shelf
- Reserves – 330 million tonnes of oil and 37,000 million cubic meters of natural gas
- Sagar Samrat- specially designed platform for oil extraction
- Produces about two-third crude oil of India
RAWA :
- Located in Krishna – Godawari off – shore basin is expeted to produce 1 to 3 million tonnes of crude oil annually
- Developed by Cairn India in partnership with ONGC, Videocon and Rawa Oil.
- It produces both oil and gas.
K-G BASIN :
- The basin and delta of Krishna and Godawari hold great potential of oil and gas
- Rawa field, Reliance’s gas field
- Extensive exploration work is going on in the region.
NARIMANAM AND KOVILAPPAL :
- Located in the Cauvery on–shore basin, expected to produce about 4 lakh tonnes of crude oil annually.
- Oil will be refined at the Panaigudi refinery near Chennai.
MANGLA :
- Major oilfields located in Rajasthan in the Barmer district
- It consists of over 16 separate oil and gas fields of which the major three are Mangla, Bhagyam and Aishwarya
- The current operator of the fields is Cairn India.

Very Very helpful notes , as in last mains my notes are not organized and not that of good quality, i didn’t qualify mains. But sir in this time , surely your quality notes will help me to get a very good marks. Also it saves my efforts and time to get quality content. Thanks you so much sir .
Thanks, Samrat for your kind words.
did you got good marks
thanks very helpful
Thanks Sir…for such Excellent crispy notes!
Crisp & handy at the same time.