In this article, You will read the Ocean Energy (i.e. Ocean Thermal Energy, Wave Energy, and Tidal Energy) in India – for UPSC.
Ocean Energy
Ocean energy refers to all forms of renewable energy derived from the sea. There are three main types of ocean technology: wave, tidal, and ocean thermal. Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has declared Ocean Energy as renewable energy.
Types of Ocean Energy
- Wave energy is generated by converting the energy within ocean waves (swells) into electricity. There are many different wave energy technologies being developed and trialled to convert wave energy into electricity.
- The first wave energy, project with a capacity of 150 MW, has been set up at Vizhinjam near Trivandrum.
- Wave energy development has not been carried out in any country and the power in ocean waves has not been exploited to its full potential for human purposes except as power supplies for buoys and navigational aid
- Wave power is produced by the up and down motion of floating devices placed on the surface of the ocean.
- As the waves travel across the ocean, high-tech devices capture the natural movements of ocean currents and the flow of swells to generate power.
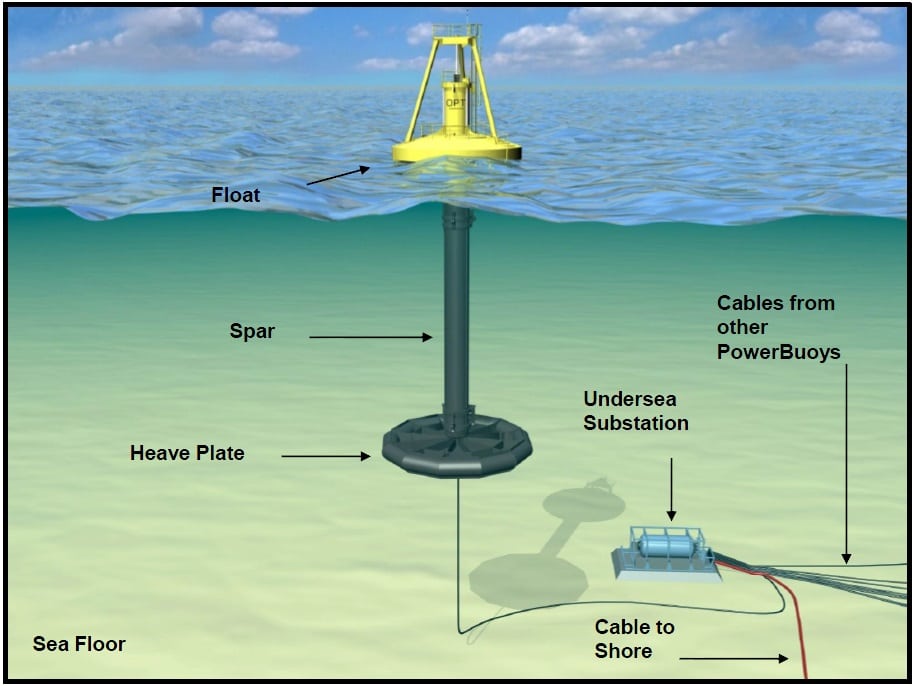
- Current Energy – It is very similar to the wind above the oceans. Underwater turbines, large propellers tethered to the seabed, are moved with the marine currents to generate electricity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), given the scale of open ocean currents, there is a promise of significant project scale growth when technologies harness lower-velocity currents.
- Tidal Energy- Like conventional hydroelectric dams, power plants are built on river estuaries and hold back huge amounts of tidal water twice a day which generates electricity when released. India is expected to have 9,000 MW of tidal energy potential.
- Tides are formed due to the gravitational effect of the sun and moon on the earth. The gravitational force causes a periodic rise and fall of the water level of sea in rhythm with the daily rhythm of the rising and setting of the sun and the moon.
- This periodic rise and fall, called a tide, can be used to produce electric power which in this case is known as tidal power. Tidal power has great potential in areas like the Gulf of Kutch in Gujarat, Gulf of Cambay and Sunder ban area of West Bengal where the height of the tide is sufficient for construction and economical functioning of tidal power plants.
- Energy can be extracted from tides by creating a reservoir or basin behind a barrage and then passing tidal waters through turbines in the barrage to generate electricity.
- A major tidal wave power project costing of Rs.5000 crores, is proposed to be set up in the Gulf of Kutch in Gujarat.

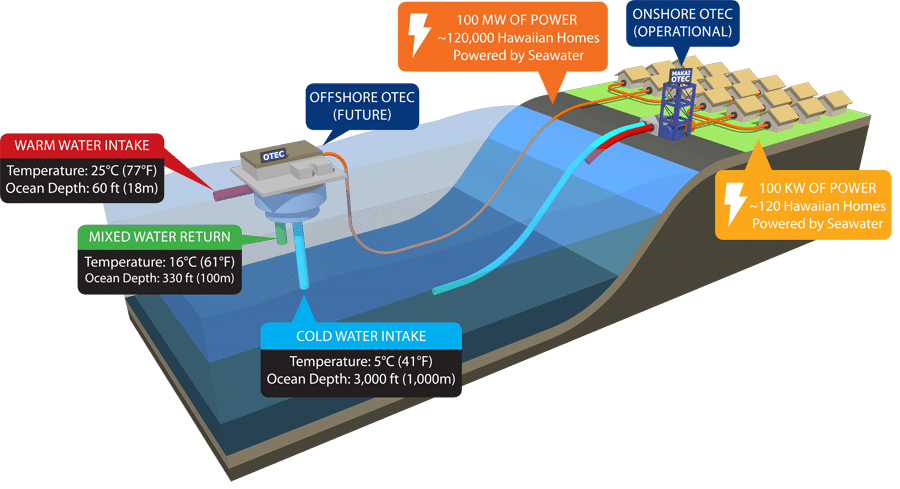
- Ocean Thermal Energy- Oceans are huge heat reservoirs as they cover almost 70% of Earth’s surface. The temperature difference between warm surface waters and the cold deeper layers can be used to generate steam and then power.
- Large amounts of solar energy are stored in the oceans and seas. On an average, the 60 million square kilometres of the tropical seas absorb solar radiation equivalent to the heat content of 245 billion barrels of oil.
- The process of harnessing this energy is called OTEC (Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion). It uses the temperature differences between the surface of the ocean and the depths of about loom to operate a heat engine, which produces electric power.
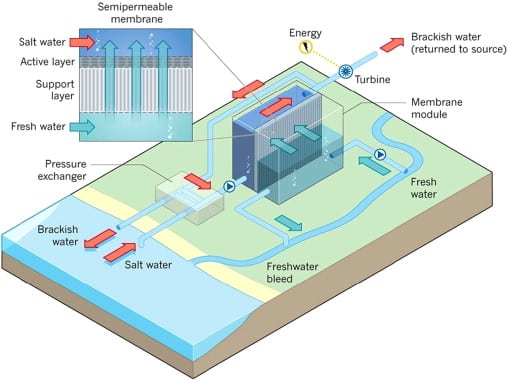
- Osmotic Energy- This technique produces energy from the movement of water across a membrane between a saltwater reservoir and fresh water reservoir. It is also called Salinity Gradient Energy.
Salient Features
- Predictable and Reliable: Unlike wind, ocean energy sources are more predictable. The endless flows create a reliable supply source for future availability.
- Global presence: Tidal streams and ocean currents are available almost everywhere across the globe.
- Energy-rich: Moving water is more than 800 times denser than moving air, which multiplies the kinetic energy by the same factor and opens up the scope of huge amounts of energy.
- Unlimited usage area: Land is a scarce resource for many regions so on-shore solutions have to compete and can extend to a limit but ocean energies are provided by the vast and deep oceans ending the competition.
Limitations
- Deployment is currently limited in our country and already deployed technologies are under utilised.
- Either there is not much research done on the technologies or most are currently at the initial stage of R&D, demonstration and commercialization.
- Uncertainty of the marine environment and commercial scale risks like- corrosion of materials due to the salinity of seawater, offshore maintenance difficulties, the environmental impact on landscapes and the marine ecosystem and competition from other marine activities such as fishing.
Potential
- Total identified potential of Tidal Energy is about 12455 MW, with potential locations identified at Khambat & Kutch regions, and large backwaters, where barrage technology could be used.
- The total theoretical potential of wave energy is estimated to be about 40,000 MW. This energy is however less intensive than what is available in more northern and southern latitudes.
- OTEC has a theoretical potential of 180,000 MW in India subject to suitable technological evolution.
- Ocean energy has the potential to grow fully, fuelling economic growth, reducing carbon footprint and creating jobs not only along the coasts but also inland along its supply chains.
Suggestions
- India has a long coastline with the estuaries and gulfs which can be fully used to harness this energy.
- Tidal streams and ocean currents are huge and almost endless resources which can be used with relatively small environmental interactions for large scale electricity generation.
- Basic R&D is being looked after by National Institute of Ocean Technology, Chennai under the Ministry of Earth Sciences but more inputs by other prominent institutions will help us understand and develop the technologies faster.
