In this article, You will read the Geothermal Energy in India – for UPSC.
Geothermal Energy
- Geothermal energy is natural heat from the interior of the earth that can be used to generate electricity as well as to heat up buildings.
- Below the earth’s crust, there is a layer of hot and molten rock, called magma. Heat is continually produced in this layer, mostly from the decay of naturally radioactive materials such as uranium and potassium. The amount of heat within 10,000 meters (about 33,000 feet) of the earth’s surface contains 50,000 times more energy than all the oil and natural gas resources in the world.
- Geothermal resource falls into three major categories:
- i) Geopressurized zones,
- ii) Hot-rock zones and
- iii) Hydrothermal convection zones.
- Of these three, only the first is currently being exploited on a commercial basis.
- The natural examples of geothermal energy are given below.
- Geysers
- Lava Fountain
- Hot Springs
Advantages
- Renewable: It is believed that enough heat is radiated from the center of the earth to fulfill human energy demand for all the times to come.
- Easy to exploit in some cases: Since ancient times, people having been using this source of energy for taking baths, heating homes, preparing food and today this is also used for direct heating of homes and offices. This makes geothermal energy cheaper and affordable.
- CO2 production less than with fossil fuel: This is one of the main advantages of using geothermal energy since it does not create any pollution and helps in creating a clean environment. Being the renewable source of energy, geothermal energy has helped in reducing global warming and pollution.
- High net energy yield: With the growing demand for energy, additional units with modular designs can be installed easily. The cost of electricity production is almost competitive with conventional energy sources.
Disadvantages
- Not available everywhere: Geothermal hot spots are scattered and are at far away regions than the areas that need energy
- H2S pollution: Large quantities of H2S “The rotten eggs” gas can be released and inhaling it in too many quantities is fatal.
- Geothermal energy harnessing produces some water pollution (some what similar to mining).
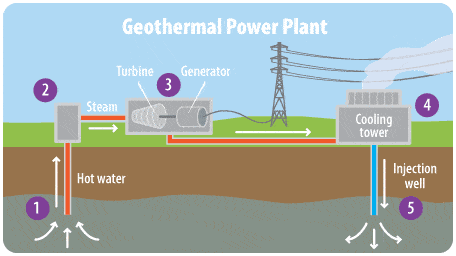
How is it captured?
- Geothermal systems can be found in regions with a normal or slightly above normal geothermal gradient (gradual change in temperature is known as the geothermal gradient, which expresses the increase in temperature with depth in the earth’s crust. The average geothermal gradient is about 2.5-3 °C/100 m) and especially in regions around plate margins where the geothermal gradients may be significantly higher than the average value.
- The most common current way of capturing the energy from geothermal sources is to tap into naturally occurring “hydrothermal convection” systems where cooler water seeps into the earth’s crust, is heated up, and then rises to the surface. When heated water is forced to the surface, it is relatively easy to capture that steam and use it to drive electric generators.
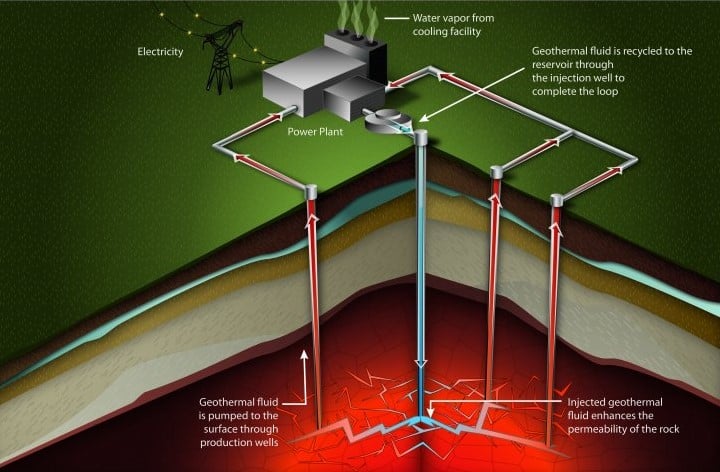
Challenges
- The Resource and Location
- There is geothermal energy beneath the entirety of the earth’s surface, but not all of that energy can be harnessed. There is only a small percentage of land that lies above suitable pockets of water and steam that can heat homes or power electrical plants, limiting the possibility of installation of geothermal power plants. Many of the places that are ideal for providing substantial amounts of geothermal energy that can be converted into electricity are also located in areas that are extremely tectonically active. When there is a constant risk of earthquakes or volcanic activity, corporations are hesitant to install large-scale electricity generating facilities.
- Infrastructure
- Aside from the lack of adequate resources, one of the reasons that geothermal electricity is not widely used in the United States is due to a lack of infrastructure for it. By nature, a geothermal energy source could only be used to produce the baseline power for an electrical grid which causes problems in and of itself. Equipment for drilling wells and setting up power plants is extraordinarily expensive and training people to staff a geothermal power plant is time consuming and costly. There is also the restriction of where the geothermal energy can be used. Once the energy is extracted form the underground wells, it cannot be transported to a different facility whose grid is more in need, it has to be used as it is extracted.
- High Cost
- Geothermal energy is an expensive resource to tap into, with price tags ranging from around $2-$7 million for a plant with a 1 megawatt capacity. However, where the upfront costs are high, the outlay can be recouped as part of a long-term investment.
- Renewable Does Not Mean Unlimited
- Contrary to popular belief, the water and steam that is extracted from the earth is not boundless. Every well only has so much water that can be extracted and without proper reinjection of used water back into the wells, there is not enough pressure to propel the steam and water upwards. If the pressure gradient is not adequately reestablished, not only is there the potential for the energy source to dwindle, but there is also the possibility of greater geological impacts like the creation of sink holes.
- Location Restricted
- The largest single disadvantage of geothermal energy is that it is location specific. Geothermal plants need to be built in places where the energy is accessible, which means that some areas are not able to exploit this resource. Of course, this is not a problem if you live in a place where geothermal energy is readily accessible, such as Iceland.
- Transmission barrier
- Geothermal power plants must be located near specific areas near a reservoir because it is not practical to transport steam or hot water over distances over distances greater than two miles. Since many of the best geothermal resources are located in rural areas, developers may be limited by their ability to supply electricity to the grid. New power lines are expensive to construct and difficult to site.
- Environmental Side Effects
- Although geothermal energy does not typically release greenhouse gases, there are many of these gases stored under the Earth’s surface which are released into the atmosphere during digging. While these gases are also released into the atmosphere naturally, the rate increases near geothermal plants. However, these gas emissions are still far lower than those associated with fossil fuels.
- Earthquakes
- Geothermal energy also runs the risk of triggering earthquakes. This is due to alterations in the Earth’s structure as a result of digging. This problem is more prevalent with enhanced geothermal power plants, which force water into the Earth’s crust to open up fissures to greater exploitation of the resource. However, since most geothermal plants are away from population centres, the implications of these earthquakes are relatively minor.
- Sustainability
- In order to maintain the sustainability of geothermal energy fluid needs to be pumped back into the underground reservoirs faster than it is depleted. This means that geothermal energy needs to be properly managed to maintain its sustainability.
- It is important for industry to assess the geothermal energy pros and cons in order to take account of the advantages while mitigating against any potential problems.
- Execution challenges:
- Harmful radioactive gases can escape from within the earth through the holes drilled by the constructors. The plant must be able to contained any leaked gases and ensure safe disposal of the same.
Geothermal Energy in India
- In India, exploration and study of geothermal fields started in 1970.
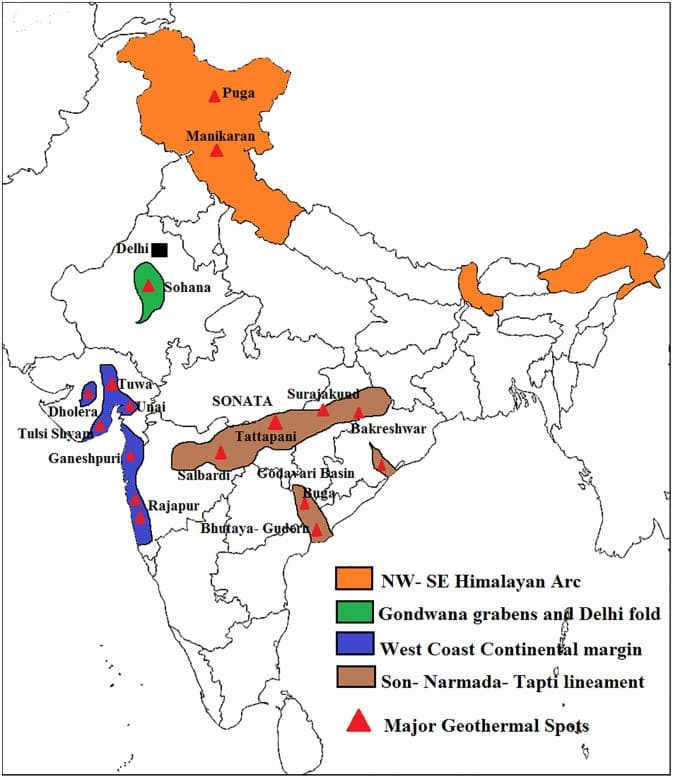
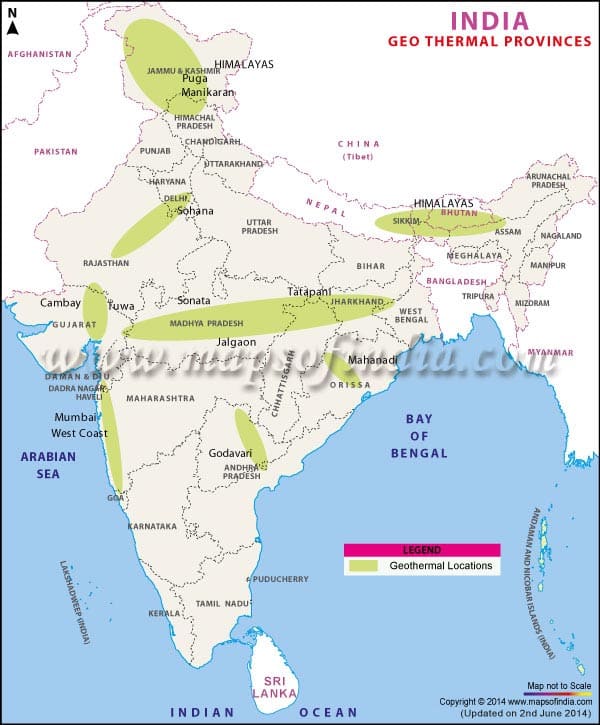
- Geological Survey of India has found around 350 geothermal energy locations in the country. The most promising of these is in the Puga valley of Ladakh.
- India has 7 geothermal provinces [viz. Himalayas, Sohana, West Coast, Cambay (Gujarat), Godavari, Mahanadi and Son-Narmada-Tapi (SONATA)] and a number of geothermal springs.
- Geothermal resources in India have been mapped by GSI and a broad estimate suggests that there could be 10 gigawatts (GW) geothermal power potential, as per the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- In 2013, the Chhattisgarh government has decided to establish the Geothermal Power Plant in the country at Tattapani in the Balrampur district.
- In 2021, an agreement was signed to establishing the first geothermal Power Project in Ladakh.
- Satellites like the IRS-1 have played an important role, through infrared photographs, in locating geothermal areas.
- Government Initiatives
- For Industrial Projects, the government has planned to provide a capital subsidy of up to 30%.
- First Geothermal power plant to come in Chhattisgarh by joint cooperation of NTPC and Chhattisgarh Renewable Energy Development Agency (CREDA). Tattapani geothermal field in SONATA geothermal province.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) provides large incentives and subsidies for Research, Design, Development and Demonstration (RDD&D) for harnessing geothermal energy in India.
- Ministry of renewable energy has planned to generate geothermal energy up to 1000 MW by 2022.
Major sites for geothermal energy in India
- Puga geothermal field
- Chhumathang geothermal field
- Manikaran geothermal field
- Beas valley
- Satluj and spiti valley
- Tapoban geothermal field, Chamoli, Uttarakhand and Alaknanda Valley
- Tatapani geothermal field
- Salbardi region
- Anhoni- Samoni area
- Unkeshwar
- Godavari Graben
- Andaman-Nicobar region
- Damodar Valley basins
- Western thermal province
- Cambay geothermal region
- Konkan geothermal provinces
- Sohna thermal region
- Tuwa and Chhabsar geothermal fields, Gujarat
- Lasundra geothermal province

👍👍
Geothermal Energy is one of the best resource for INdia, as lowest pollution and highest power generation. your artcle is informative and priomary guides on the Geothermal energy.
Good.👍👍👍👍