In this article, You will read Difference between Antigens and Antibodies – for UPSC IAS.
Antigens and Antibodies
Antigens and antibodies play vital but distinct roles in illness and disease. One tries to wreak havoc on our health while the other fights to protect it.
Simply put, antigens can make you sick, and antibodies are how your body defends itself against antigens.
An antibody is a glycoprotein which is produced in response to and counteracts a particular antigen. On the other hand, an antigen is a foreign substance (usually harmful) that induces an immune response, thereby stimulating the production of antibodies.
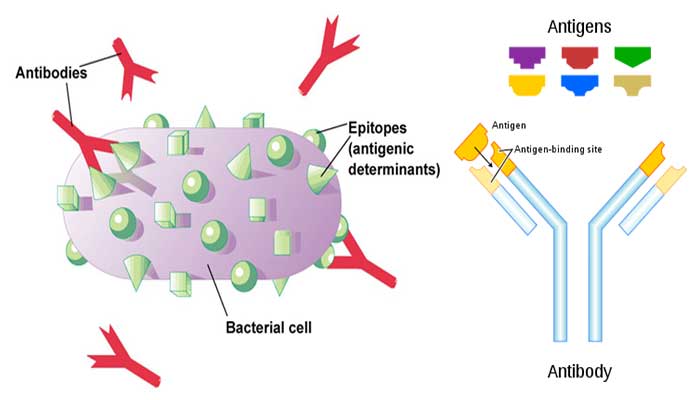
Antigen
Antigens, or immunogens, are substances or toxins in your blood that trigger your body to fight them.
Antigens are usually bacteria or viruses, but they can be other substances from outside your body that threaten your health. This battle is called an immune response.
The presence of antigens rouses your body’s illness-fighting white blood cells, called lymphocytes. This presence of antigens causes white blood cells to make cells called antibodies to fight against the antigens.
There are two main types of antigens, heteroantigens and autoantigens:
- Heteroantigens are substances that are foreign to your body and involve substances made by or found within:
- viruses
- bacteria
- protozoa
- blood and red blood cells from other people
- snake venom
- allergens such as pollen
- certain proteins in foods
- Autoantigens, or self-antigens, are made by your body to fight your cells and are usually a sign of an illness such as an autoimmune condition.
Antibody
Antibodies are also called immunoglobulins or Ig. They are Y-shaped proteins made by your immune system’s B lymphocytes or B cells.
B cells attack and eliminate viruses and other toxins outside the cell. They do this by making specific antibodies for a single type of antigen.
These tailored antibodies lock on to their specific antigens and tag them for attack. Antibodies also block these antigens, keeping them away from your healthy cells. Ultimately, antibodies kill these antigens, stopping infection.
The main types of antibodies (immunoglobulins) include:
- IgG. These are the most abundant types of antibodies in your plasma. They detoxify harmful substances and provide long-term protection.
- IgM. These are the first antibodies made by B cells in response to antigens.
- IgA. These antibodies collect antigens and remove them from your body in your mucus or other body fluids.
- IgE. These antibodies trigger allergies and protect against parasites. Small amounts are in your skin, lungs, and mucosal membranes.
- IgD. These antibodies bind to B cells and signal them to release IgM antibodies.
Each antibody guards against its target antigen and many types of antibodies are found throughout your body. They play a vital role in your body’s defense against illness and disease.
Difference between Antigens and Antibodies
| Antigen | Antibodies | |
| Also called | Also called Immunogens | Also called Immunoglobulins |
| Molecular Type | Antigens are usually lipids. However, they can also be proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids | All antibodies are proteins |
| Effect | Antigens cause allergic reactions or even illnesses | Protects against the effects of the antigen either by lysis or immobilization of the particle |
| Specific Binding Site | Epitopes are regions of the antigen where interacts with the antibodies | Paratopes are variable regions of an antibody that binds to an epitope. |
| Origins | Antigens have origins outside the body | Antibodies always originate within the body |
Difference between mRNA Vaccine and Traditional Vaccines
- Vaccines work by training the body to recognise and respond to the proteins produced by disease-causing organisms, such as a virus or bacteria.
- Traditional vaccines are made up of small or inactivated doses of the whole disease-causing organism, or the proteins that it produces, which are introduced into the body to provoke the immune system into mounting a response.
- mRNA vaccines tricks the body into producing some of the viral proteins itself.
- They work by using mRNA, or messenger RNA, which is the molecule that essentially puts DNA instructions into action. Inside a cell, mRNA is used as a template to build a protein.
Functioning of mRNA Vaccines:
- To produce a mRNA vaccine, scientists produce a synthetic version of the mRNA that a virus uses to build its infectious proteins.
- This mRNA is delivered into the human body, whose cells read it as instructions to build that viral protein, and therefore create some of the virus’s molecules themselves.
- These proteins are solitary, so they do not assemble to form a virus.
- The immune system then detects these viral proteins and starts to produce a defensive response to them.
Advantages of Using mRNA based Vaccines:
- mRNA vaccines are considered safe as mRNA is non-infectious, non-integrating in nature, and degraded by standard cellular mechanisms.
- They are highly efficacious because of their inherent capability of being translatable into the protein structure inside the cell cytoplasm.
- Additionally, mRNA vaccines are fully synthetic and do not require a host for growth, e.g., eggs or bacteria. Therefore, they can be quickly manufactured inexpensively to ensure their “availability” and “accessibility” for mass vaccination on a sustainable basis.
