In this article, You will read the Biomass Energy (Bio-energy) in India – for UPSC.
Biomass Energy
- Biomass is renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. Biomass energy is energy generated or produced by living or once-living organisms.
- Biomass continues to be an important fuel in many countries, especially for cooking and heating in developing countries. The use of biomass fuels for transportation and for electricity generation is increasing in many developed countries as a means of avoiding carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel use.
- Biomass contains stored chemical energy from the sun. Plants produce biomass through photosynthesis. Biomass can be burned directly for heat or converted to renewable liquid and gaseous fuels through various processes.
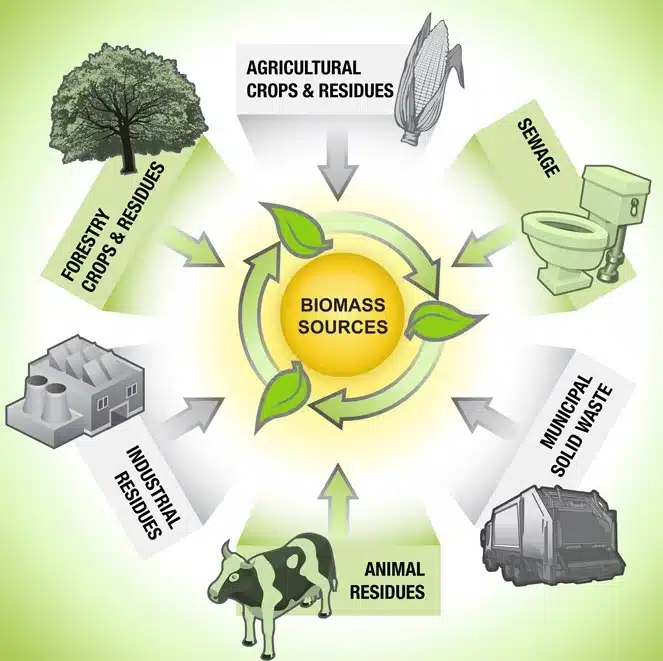
- Biomass sources for energy include:
- Wood and wood processing wastes—firewood, wood pellets, and wood chips, lumber and furniture mill sawdust and waste, and black liquor from pulp and paper mills
- Agricultural crops and waste materials—corn, soybeans, sugar cane, switchgrass, woody plants, and algae, and crop and food processing residues
- Biogenic materials in municipal solid waste—paper, cotton, and wool products, and food, yard, and wood wastes
- Animal manure and human sewage
Converting biomass to energy
Biomass is converted to energy through various processes, including:
- Direct combustion (burning) to produce heat
- Direct combustion is the most common method for converting biomass to useful energy. All biomass can be burned directly for heating buildings and water, for industrial process heat, and for generating electricity in steam turbines.
- Thermochemical conversion to produce solid, gaseous, and liquid fuels
- Thermochemical conversion of biomass includes pyrolysis and gasification. Both are thermal decomposition processes in which biomass feedstock materials are heated in closed, pressurized vessels called gassifiers at high temperatures.
- Chemical conversion to produce liquid fuels
- A chemical conversion process known as transesterification is used for converting vegetable oils, animal fats, and greases into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), which are used to produce biodiesel.
- Biological conversion to produce liquid and gaseous fuels
- Biological conversion includes fermentation to convert biomass into ethanol and anaerobic digestion to produce renewable natural gas. Ethanol is used as a vehicle fuel.
- Renewable natural gas – also called biogas or biomethane – is produced in anaerobic digesters at sewage treatment plants and at dairy and livestock operations. It also forms in and may be captured from solid waste landfills.
- Anaerobic digestion or Biomethanation: Biomethanation or methanogenesis, is a scientific process whereby anaerobic microorganisms in an anaerobic environment decompose biodegradable matter producing methane-rich biogas and effluent. The three functions that take place sequentially are hydrolysis, acidogenesis, and methanogenesis.
- Cogeneration
- Co-generation is producing two forms of energy from one fuel. One of the forms of energy must always be heat and the other may be electricity or mechanical energy. In a conventional power plant, fuel is burnt in a boiler to generate a high-pressure system. The steam is used to drive a turbine to produce electric power. The exhaust steam is generally condensed to water which goes back to the boiler.
- As the low-pressure steam has a large quantum of heat that is lost in the process of condensing, the efficiency of conventional power plants is only around 35%. In a cogeneration plant, the low-pressure exhaust steam coming out of the turbine is not condensed, but used for heating purposes in factories or houses, and thus very high-efficiency levels, in the range of 75%-90%, can be reached.
- Since co-generation can meet both power and heat needs, it has other advantages as well in the form of significant cost savings for the plant and reduction in emissions of pollutants due to reduced fuel consumption.
Advantages of Biomass Energy
- Versatile: Biomass energy can have different uses ranging from cooking gas to generation of power with minimum effect on the environment.
- Renewable: It is a renewable source of energy and can be provided by nature in abundance.
- No net CO2 emissions (ideally): The emission of CO2 far too less in Biomass energy than other conventional sources of energies.
- Emits less SO2 and NOx than fossil fuels: The sulphur and nitrogen pollutants are minimal in biomass consumption.
Disadvantages of Biomass Energy
- Low energy density/yield: Some biofuels, like Ethanol, is relatively inefficient as compared to gasoline. In fact, it has to be fortified with fossil fuels to increase its efficiency. In some cases (e.g. corn-derive bioethanol) may yield no net energy.
- Land conversion: Land needed to produce biomass may be in demand for other purposes such as conservation or housing or agriculture use which may lead to a possible decrease in agricultural food production. It may also lead to biodiversity loss.
- Apart from the above there are usually problems associated with intensive agriculture like:
- Nutrient pollution
- Soil depletion
- Soil erosion
- Other water pollution problems.
Bio-energy role meeting India’s energy demands:
- Energy demand: Bioenergy can help to meet the growing demand for energy within the country, especially in rural areas. Nearly 25% of its primary energy comes from biomass resources and close to 70% of rural population depend on biomass to meet their daily energy needs. Biomass can further help in meeting rural energy demands.
- Climate change mitigation: Bioenergy provides important benefits compared to fossil fuels, in particular regarding GHG emissions. Biomass recycles carbon from the air and spares the use of fossil fuels, reducing the additional fossil carbon from the ground into the atmosphere.
- Market growth: The market for renewable energy systems in rural and urban markets in India is set to grow exponentially. Despite this, bioenergy does not figure in most energy studies and is classified as ‘non-commercial’ energy. Plants like Jatropha, Neem and other wild plants are identified as the potential sources for biodiesel production in India.
- Waste to energy: Biofuels can augment waste to wealth creation. Being a derivative of renewable biomass resources such as plastic, municipal solid waste, forestry residues, agricultural wastes, surplus food grains etc. it has huge potential to help the country achieve the renewable energy goal of 175 GW.
- Income generation: Adopting biofuels as an alternative source of energy can significantly improve farmers’ income, generate employment opportunities etc.
- Reduce imports: India’s energy demands met by imports are about 46.13% of total primary energy consumption. Bioenergy can help in reducing these imports and boost India’s energy security and self-reliance.
Various Government efforts in reaping Bioenergy:
- 10 GW national target: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has set the national target is to achieve 10 GW of installed biomass power by 2022.
- National Policy on Biofuels: The policy is aimed at taking forward the indicative target of achieving 20% blending of biofuels with fossil-based fuels by 2025.
- Policy for biomass and bagasse cogeneration: MNRE has further developed a policy for biomass and bagasse cogeneration that will help in meeting India’s energy demands. It includes financial incentives and subsidies, both for biomass projects and sugar mills that use this technology.
- Fiscal Incentives: Government gives 10 years Income tax holidays. Concessional customs and excise duty exemption for machinery and components for initial setting up of Biomass power projects. General sales tax exemption is available in certain States.
- Waste to energy projects: Waste to energy projects are also being set up for generation of energy from urban, industrial and agricultural waste such as vegetable and other market wastes, slaughterhouse waste, agricultural residues and industrial wastes & effluents.
- National Biomass Repository: MNRE also plans on creating a ‘National Biomass Repository’ through a nation-wide appraisal program which will help ensure availability of biofuels produced from domestic feedstock.
National Mission on use of Biomass in coal-based thermal power plants
- To address the issue of air pollution due to farm stubble-burning and to reduce carbon footprints of thermal power generation, the Ministry of Power has decided to set up a National Mission on the use of Biomass in coal-based thermal power plants.
- The proposed National Mission on biomass will also contribute to the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
- It would further support the energy transition in the country and our targets to move towards cleaner energy sources.
- Objectives of the mission:
- To increase the level of co-firing from the present 5% to higher levels to have a larger share of carbon-neutral power generation from the thermal power plants.
- Biomass co-firing stands for adding biomass as a partial substitute fuel in high efficiency coal boilers.
- To take up R&D activity in boiler design to handle the higher amount of silica, alkalis in the biomass pellets.
- To facilitate overcoming the constraints in the supply chain of biomass pellets and agro- residue and its transport up to the power plants.
- To consider regulatory issues in biomass co-firing.
- To increase the level of co-firing from the present 5% to higher levels to have a larger share of carbon-neutral power generation from the thermal power plants.

SOOO Tesss 🤤😈
Biomass have been in news since a long time and now bio fuels are taking away the news these days. Bio fuels are now being the replacement of crude oil which is simply made out of leftover oils from various sources including household waste oil. It decreases the waste and helps build a system of efficient fuel energy. Even various companies like Aris Bio energy buys oil from your door step makes it more dependable source of sustainable energy for everyone. We should not forget the importance of such small efforts in the direction of our planet safety.