In this article, You will read Crop Classification & Types of Crops in India – for UPSC IAS.
Agriculture Season in India
- The agricultural crop year in India is from July to June. The Indian cropping season is classified into three main seasons of cultivation:
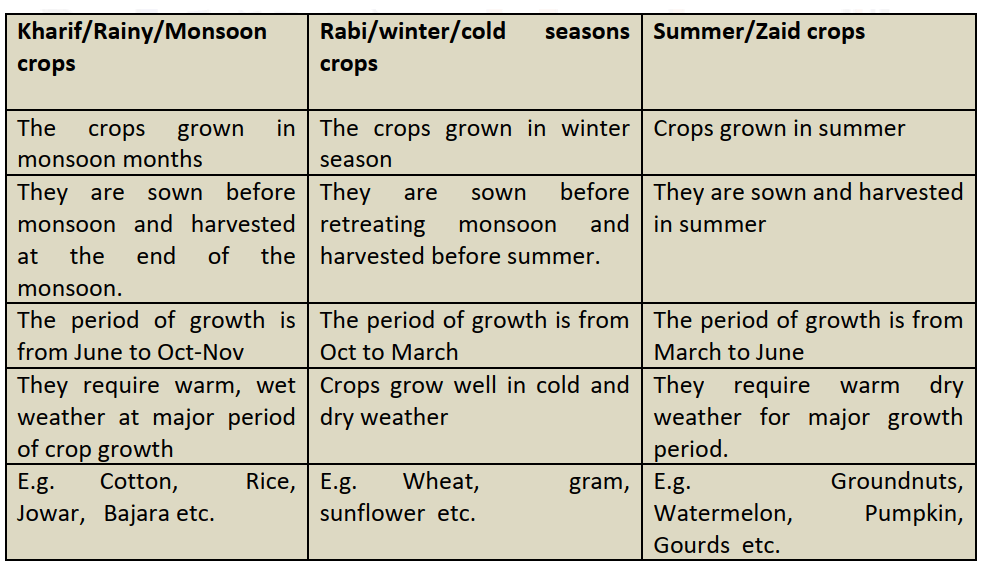
- Kharif – Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September-October. Important crops grown during this season are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean. Some of the most important rice-growing regions are Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra, particularly the (Konkan coast) along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Recently, paddy has also become an important crop of Punjab and Haryana. In states like Assam, West Bengal and Odisha, three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are Aus, Aman and Boro.
- Rabi – Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June. Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard. Though, these crops are grown in large parts of India, states from the north and north western parts such as Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are important for the production of wheat and other rabi crops. Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western temperate cyclones helps in the success of these crops. However, the success of the green revolution in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the abovementioned rabi crops.
- Zaid – In between the rabi and the kharif seasons, there is a short season during the summer months known as the Zaid season. Some of the crops produced during ‘zaid’ are watermelon, muskmelon, and cucumber. It is the summer cropping season where in short duration crops are grown mainly under artificial irrigation. Crops are sown at the beginning of summer season (Feb – March) and harvested in April – June.
Crop Classification
A variety of food and non-food crops are grown in different parts of the country depending upon the variations in soil, climate, and cultivation practices. These crops can be classified on the basis of different criteria enumerated below:
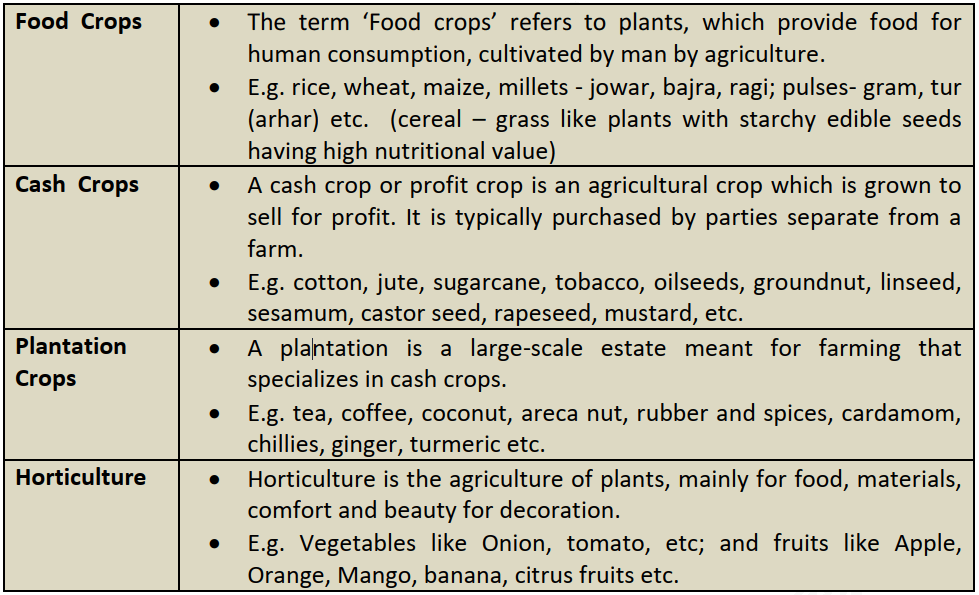
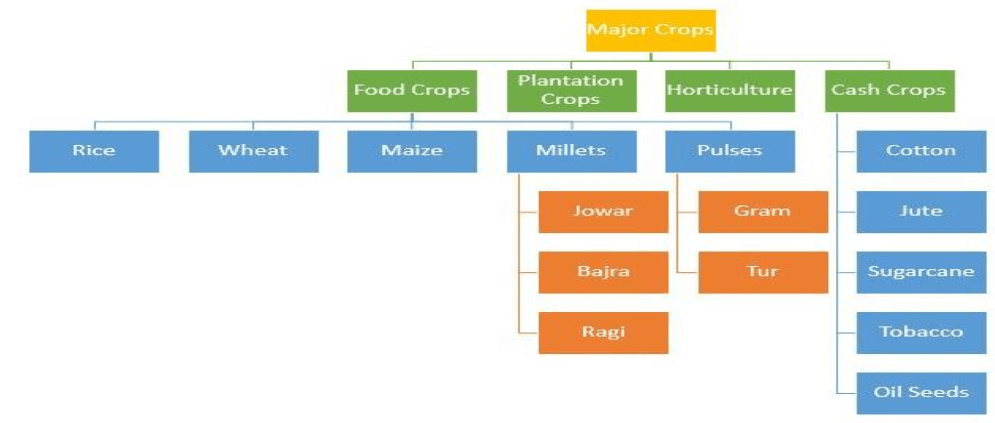
I. Crop Classification Based on the Type of Produce
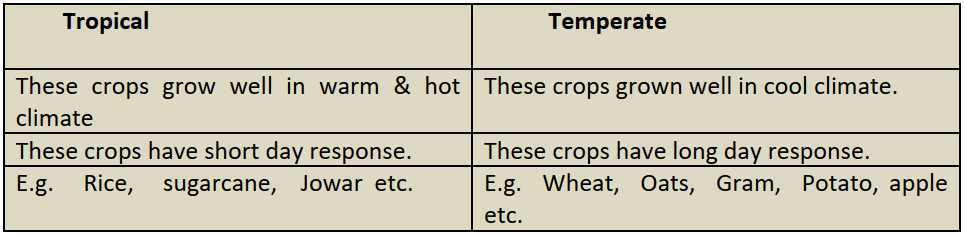
II. Crop Classification Based on Climate
III. Classification Based on Growing Season
IV. Classification Based on Life of Crops/Duration of Crops

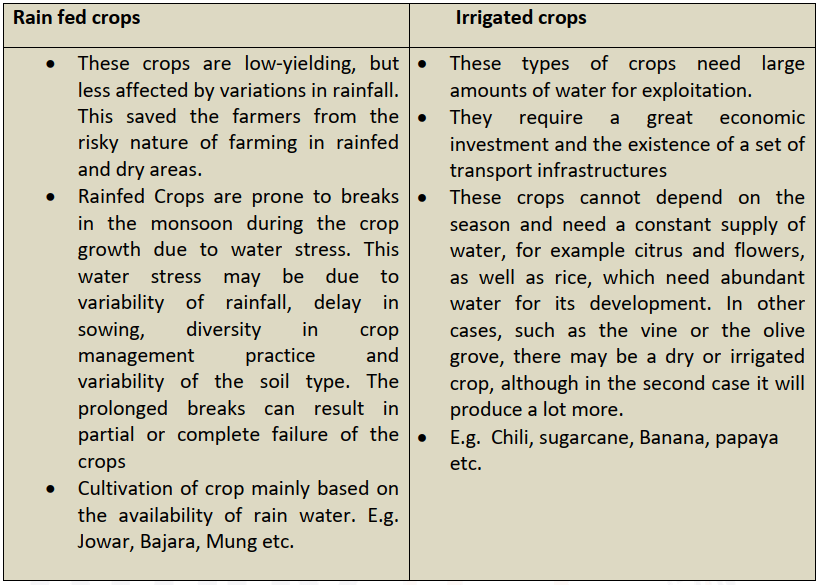
V. Classification Based on Water Availability

Types of Crops In India
- Millets
- These are staple food of poor people.
- These are also known as coarse grains, which have high nutritional value.
- Top Millets Producing States: Rajasthan > Karnataka > Maharashtra > Madhya Pradesh > Uttar Pradesh
- Major millets are Sorghum or Jowar, Pearl Millet or Bajra and Finger millet or ragi

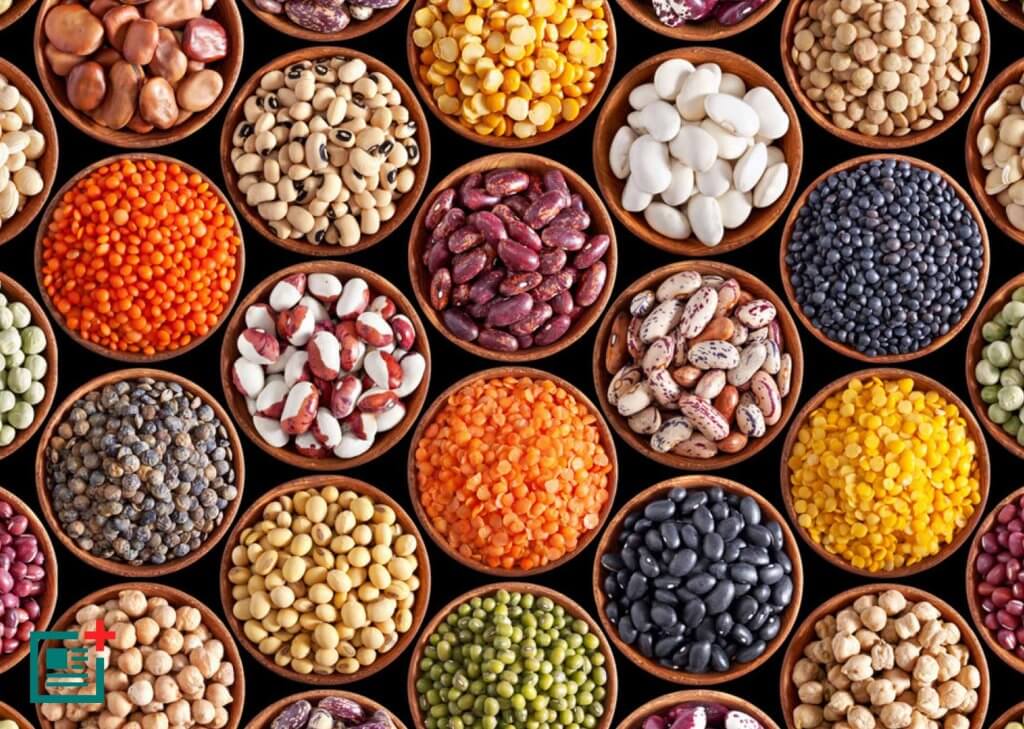
- Pulses or Legumes
- Pulses are major source of protein.
- Temperature: Between 20- 27°C.
- Rainfall: Around 25-60 cm.
- Soil Type: Sandy-loamy soil.
- Major pulses grown in India are tur (arhar), urad, moong, masur, peas and gram.
- Being leguminous crops, all these crops except arhar help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air. Therefore, these are mostly grown in rotation with other crops.

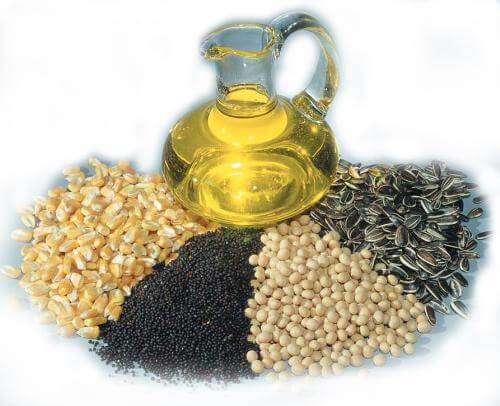
- Oil Seed Crops
- Different oil seeds are grown covering approximately 12 per cent of the total cropped area of the country.
- Main Oil-seeds produced in India are groundnut, mustard coconut, sesamum (til), soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and sunflower.
- Most of these are edible and used cooking mediums.
- However, some of these are also used as raw material in the production of soap, cosmetics and ointments.
- E.g. Groundnut or peanut, sunflower, castor, linseed, rapeseed & mustard etc.

- Sugar cane
- It is a tropical as well as a subtropical crop. It grows well in hot and humid climate with a temperature of 21°C to 27°C and an annual rainfall between 75cm and 100cm.
- Irrigation is required in the regions of low rainfall. It can be grown on a variety of Sugarcane and sugar Beet.

- Starch Crops or Tuber Crops
- Tuber crops consist of root crops, such as beets and carrots, and tuber crops, such as potatoes and sweet potatoes, and the leaves of root crops, such as beet tops
- E.g. Potato, cassava, sweet potato, radish etc.

- Fiber crops
- Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope.
- Fiber crops are characterized by having a large concentration of cellulose, which is what gives them their strength. The fibers may be chemically modified, like in viscose (used to make rayon and cellophane).
- E.g. Cotton, Jute, mesta, sun hemp, sisal hemp etc.

- Plantation Crops
- A plantation is a large farm or estate, usually in a tropical or subtropical country, where crops that are not consumed for food and are grown for sale in distant markets, rather than for local consumption.
- E.g. Tea – leaf, Coffee – seed, rubber, cocoa – seed, palm – oil, sugarcane, coconut etc.
- Spices
- A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring, coloring or preserving food.
- E.g. Ginger, garlic, chilli, cumin onion, coriander, cardamom, pepper, turmeric etc.


Wonderful article